|
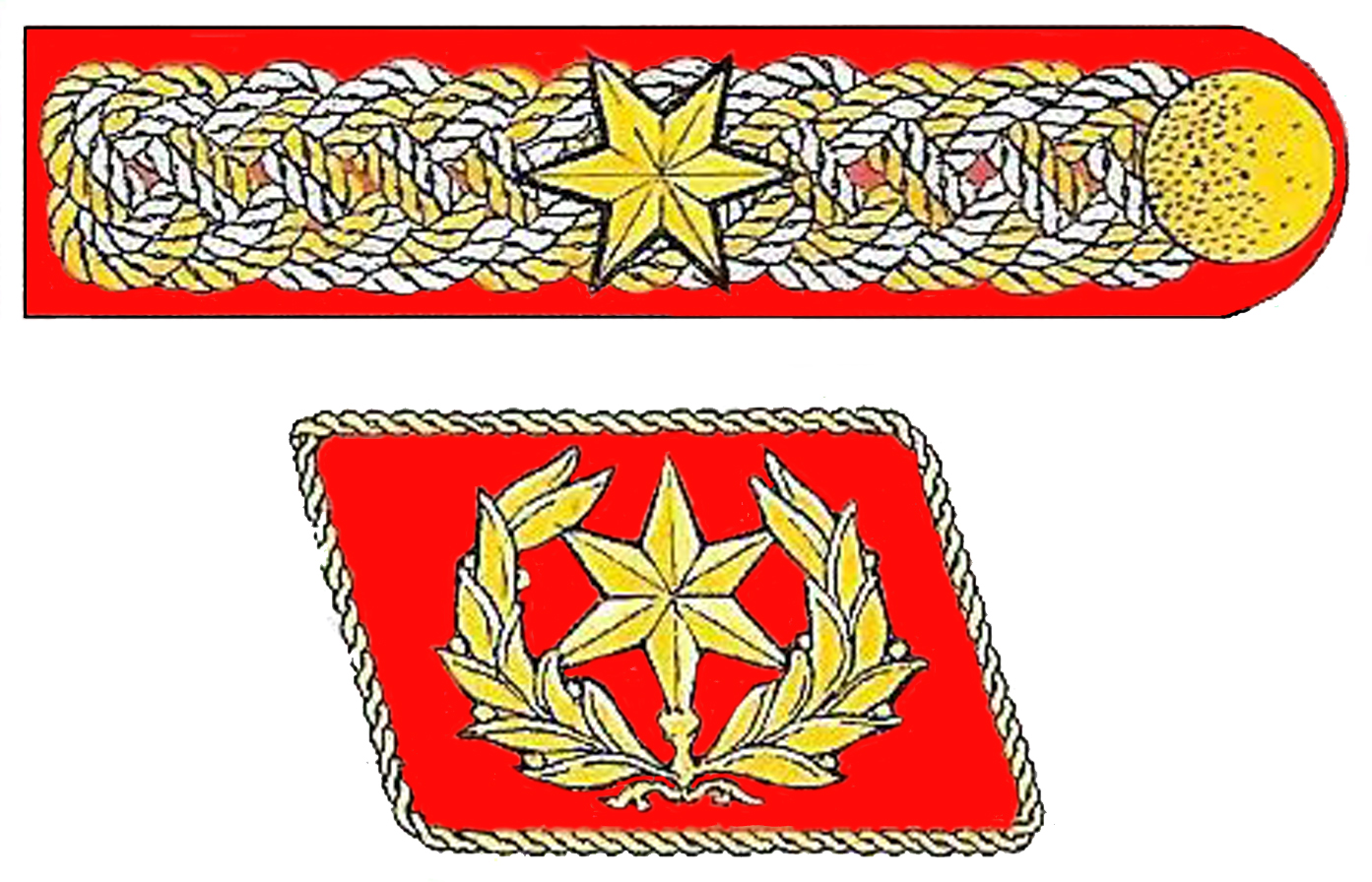
Obertruppführer
Obertruppführer (, "senior troop leader") was a paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party that was used between the years of 1932 and 1945. The rank is most closely associated with the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), but also was an early rank of the '' Schutzstaffel'' (SS) in that group's formative years. Translated as “Senior Troop Leader”, ''Obertruppführer'' traces its origins to the rank of '' Truppführer'' which was a title used by Stormtrooper Companies (Shock Troops) during the First World War. As an SA rank, ''Obertruppführer'' was created in 1932 due to the SA's expansion and growing membership. The rank of ''Obertruppführer'' was junior to '' Haupttruppführer'' and typically served as a senior non-commissioned officer rank equivalent to a Platoon A platoon is a Military organization, military unit typically composed of two to four squads, Section (military unit), sections, or patrols. Platoon organization varies depending on the country and the Military branch, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranks And Insignia Of The Sturmabteilung
The uniforms and insignia of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (Sturmabteilung, SA) were Nazi Germany paramilitary ranks, Nazi Party paramilitary ranks and uniforms used by SA stormtroopers from 1921 until the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945. The titles and phrases used by the SA were the basis for paramilitary titles used by several other Nazi paramilitary groups, among them the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS). Early Uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel, SS ranks were identical to the SA, since the SS was originally considered a sub-organisation of the ''Sturmabteilung''. Origins of SA titles (1921–1923) The brown shirted stormtroopers of the ''Sturmabteilung'' gradually come into being within the Nazi Party beginning in 1920. By this time, Adolf Hitler had assumed the title of ''Führer'' of the Nazi Party, replacing Anton Drexler who had been known as the more democratically elected Party Chairman. Hitler began to fashion the Nazi Party on fascism, fascist paramilitary lines and, to that end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truppführer
''Truppführer'' (, "troop leader") was a Nazi Party paramilitary rank that was first created in 1930 as a rank of the '' Sturmabteilung'' (SA). Translated as "Troop Leader", the rank of ''Truppführer'' evolved from early '' Freikorps'' titles which traced their origins to World War I. As an SA rank, ''Truppführer'' was considered the equivalent of a senior sergeant, or sergeant first class. The rank of SA-''Truppführer'' was at first considered senior to that of SA-'' Scharführer'', but after 1932 was ranked above the new rank of SA-'' Oberscharführer''. The insignia for a basic ''Truppführer'' consisted of two button pips on a collar patch. A ''Truppführer'' normally served as the SA-non-commissioned officer A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is an enlisted rank, enlisted leader, petty officer, or in some cases warrant officer, who does not hold a Commission (document), commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority b ... of plato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Socialist Flyers Corps
The National Socialist Flyers Corps (; NSFK) was a paramilitary aviation organization of the Nazi Party. History NSFK was founded 15 April 1937 as a successor to the German Air Sports Association; the latter had been active during the years when a German air force was forbidden by the Treaty of Versailles. The NSFK organization was based closely on the para-military organization of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA). A similar group was the National Socialist Motor Corps (NSKK). During the early years of its existence, the NSFK conducted military aviation training in Glider aircraft, gliders and private airplanes. Leadership Friedrich Christiansen, originally a ''Generalleutnant'' then later a Luftwaffe ''General der Flieger'', was NSFK ''Korpsführer'' from 15 April 1937 until 26 June 1943, followed by ''Generaloberst'' Alfred Keller until 8 May 1945. Hermann Goering as Reich Marshal was nominal head of the NSFK and was occasionally consulted on issues surrounding heavy transport, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haupttruppführer
Haupttruppführer (, "chief troop leader") was a Nazi Party paramilitary rank that existed between the years of 1930 and 1945. ''Haupttruppführer'' was mainly used as a rank of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), but was also used by the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) in the early days of that group's existence. As an SA rank, ''Haupttruppführer'' was created from the much older ''Freikorps'' title of ''Truppführer''. ''Haupttruppführer'' was considered a senior most paramilitary enlisted rank, below the first officer position of '' Sturmführer''. A ''Haupttruppführer'' typically served as the senior non-commissioned officer of SA regiments, known as ''Standarten'', and the rank was the approximate equivalent to sergeant major. ''Haupttruppführer'' translated as "head troop leader" and was considered senior to the rank of ''Obertruppführer Obertruppführer (, "senior troop leader") was a paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party that was used between the years of 1932 and 1945. The rank is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauptscharführer
__NOTOC__ ''Hauptscharführer'' ( ) was a Nazi paramilitary rank which was used by the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) between the years of 1934 and 1945. The rank was the highest enlisted rank of the SS, with the exception of the special Waffen-SS rank of '' Sturmscharführer''. The ''Hauptscharführer'' became an SS rank after reorganization of the SS following the Night of the Long Knives. The first use of ''Hauptscharführer'' was in June 1934 when the rank replaced the older SA title of '' Obertruppführer''. Within the '' Allgemeine-SS'' (general-SS), a ''Hauptscharführer'' was typically the head SS-non-commissioned officer of an ''SS-Sturm'' (company) or was a rank used by enlisted staff personnel assigned to an SS headquarters office or security agency (such as the Gestapo and '' Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD)). The rank of ''Hauptscharführer'' was also commonly used in the concentration camp service and could also be found as a rank of the ''Einsatzgruppen''. The rank of SS-' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Third Reich SA NSKK (Nationalsozialistische Kraftfahrkorps) Obertruppführer, Helmet (Sturzhelm), Swastika Armlet, Brownshirt, SA Bugle, Dagger, Wehrmacht Chaplain Cap, Etc
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) *German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (disambiguatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS-Verfügungstruppe
(SS-VT, ) was formed in 1934 as combat troops for the Nazi Party (NSDAP). On 17 August 1938 Adolf Hitler decreed that the SS-VT was neither a part of the (order police) nor the , but military-trained men at the disposal of the . In time of war, the SS-VT were to be placed at the disposal of the army. The SS-VT were involved in the German invasion of Poland in September 1939. By 1940 these military SS units had become the nucleus of the . Formation The SS-VT was formed on 24 September 1934 from a merger of various Nazi and paramilitary formations such as the SS Special Detachments ('' SS-Sonderkommandos'') and the Headquarters Guard (''SS- Stabswache'') units. The SS-VT consisted of three regiments, modelled on the infantry regiments of the German Army ('' Heer'') and regulations; each regiment consisting of three infantry battalions, a motorcycle company and a mortar company. The unit was officially designated ''SS-Verfügungstruppe'' ("Dispositional troops", i.e. troops at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsluftschutzbund
The Reichsluftschutzbund (RLB; "Reich Air Protection League") was a civil defense organization in Nazi Germany in charge of air raid precautions in residential areas and among smaller businesses. Purpose The RLB was organized by Hermann Göring in 1933 as a voluntary association. Existing volunteer air raid precaution associations were forced to merge with RLB. In 1939 the RLB became a ''Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts'' ( quasi-autonomous non-governmental organization), while in 1944 it became an affiliated organization of the Nazi Party. RLB was dissolved by the Allied Powers after the end of World War II. Its successor in the Federal Republic of Germany was the Bundesverband für den Selbstschutz. The RLB was in charge of educating and training ordinary German men and women in civil defence procedures necessary for the basic level of local self-help of the civil population against air raids. The local level was formed around air raid wardens and operated in small firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reich Labour Service
The Reich Labour Service (''Reichsarbeitsdienst''; RAD) was a major paramilitary organization established in Nazi Germany as an agency to help mitigate the effects of unemployment on the German economy, militarise the workforce and indoctrinate it with Nazi ideology. It was the official state labour service, divided into separate sections for men and women. From June 1935 onward, men aged between 18 and 25 may have served six months before their military service. During World War II, compulsory service also included young women, and the RAD developed to an auxiliary formation which provided support for the Wehrmacht armed forces. Foundation In the course of the Great Depression, the German government of the Weimar Republic under Chancellor Heinrich Brüning by emergency decree established the ''Freiwilliger Arbeitsdienst'' ('Voluntary Labour Service', FAD), on 5 June 1931, two years before the Nazi Party (NSDAP) ascended to national power. The state sponsored employment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organisation Todt
Organisation Todt (OT; ) was a Civil engineering, civil and military engineering organisation in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, named for its founder, Fritz Todt, an engineer and senior member of the Nazi Party. The organisation was responsible for a huge range of engineering projects both in Nazi Germany and in List of military occupations, occupied territories from France to the Soviet Union during the World War II, Second World War. The organisation became notorious for using Forced labour under German rule during World War II, forced labour. From 1943 until 1945 during the late phase of the Third Reich, OT administered all constructions of Nazi concentration camps, concentration camps to supply forced labour to industry. Overview The history of the organisation can be divided into three phases. From 1933 to 1938, before the organisation existed, Fritz Todt's primary post was that of the General Inspector of German Roadways (''Generalinspektor für das deutsche Straßenwese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Socialist Motor Corps
The National Socialist Motor Corps (, NSKK) was a paramilitary organization of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) that officially existed from May 1931 to 1945. The group was a successor organisation to the older National Socialist Automobile Corps (, NSAK), which had existed since April 1930. The NSKK served as a training organization, mainly instructing members in the operation and maintenance of high-performance motorcycles and automobiles. The NSKK was further used to transport NSDAP and SA members, and also served as a roadside assistance group in the mid-1930s. The outbreak of World War II in Europe led to recruitment among NSKK ranks to serve in the transport corps of various German military branches. A French section of the NSKK was also organised after the German occupation of France began in 1940. The NSKK was the smallest of the Nazi Party organizations. History The National Socialist Motor Corps (NSKK) was a successor organization to the older National Socialist Automobile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Of The Long Knives
The Night of the Long Knives (, ), also called the Röhm purge or Operation Hummingbird (), was a purge that took place in Nazi Germany from 30 June to 2 July 1934. Chancellor Adolf Hitler, urged on by Hermann Göring and Heinrich Himmler, ordered a series of political extrajudicial executions intended to consolidate his power and alleviate the concerns of the German military about the role of Ernst Röhm and the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), the Nazis' paramilitary organization, known colloquially as "Brownshirts". Nazi propaganda presented the murders as a preventive measure against an alleged imminent coup by the SA under Röhm – the so-called ''Röhm Putsch''. The primary instruments of Hitler's action were the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) paramilitary force under Himmler and its Security Service (SD), and Gestapo (secret police) under Reinhard Heydrich, which between them carried out most of the killings. Göring's personal police battalion also took part. Many of those killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |