|
ORF6
ORF6 is a gene that encodes a viral accessory protein in coronaviruses of the subgenus '' Sarbecovirus'', including SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. It is not present in MERS-CoV. It is thought to reduce the immune system response to viral infection through interferon antagonism. Structure The ORF6 protein is fairly small at 63 amino acid residues long in SARS-CoV and 61 in SARS-CoV-2. The ORF6 sequence is not well conserved and it has a relatively low sequence identity between the two viruses at about 66%. It has an amphipathic N-terminal alpha helix that associates with the membrane, but is not a transmembrane protein. Its approximately 20-residue C-terminal tail is polar and extends into the cytosol, and contains signal sequences for protein trafficking. Expression and localization Like the genes for other accessory proteins, the ORF6 gene is located near those encoding the structural proteins, at the 5' end of the coronavirus RNA genome. Along with ORF7a, ORF7b, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Protein
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them ( beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
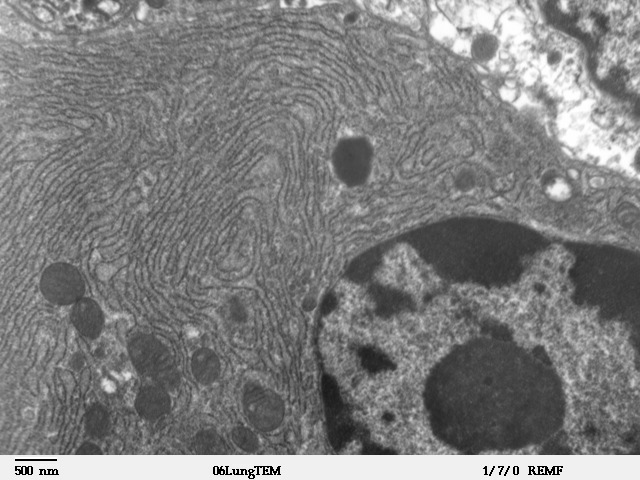
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcellular Localization
The cells of eukaryotic organisms are elaborately subdivided into functionally-distinct membrane-bound compartments. Some major constituents of eukaryotic cells are: extracellular space, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), peroxisome, vacuoles, cytoskeleton, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, nuclear matrix and ribosomes. Bacteria also have subcellular localizations that can be separated when the cell is fractionated. The most common localizations referred to include the cytoplasm, the cytoplasmic membrane (also referred to as the inner membrane in Gram-negative bacteria), the cell wall (which is usually thicker in Gram-positive bacteria) and the extracellular environment. The cytoplasm, the cytoplasmic membrane and the cell wall are subcellular localizations, whereas the extracellular environment is clearly not. Most Gram-negative bacteria also contain an outer membrane and periplasmic space. Unlike eukaryotes, most b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein
The nucleocapsid (N) protein is a protein that packages the positive-sense RNA genome of coronaviruses to form ribonucleoprotein structures enclosed within the viral capsid. The N protein is the most highly expressed of the four major coronavirus structural proteins. In addition to its interactions with RNA, N forms protein-protein interactions with the coronavirus membrane protein (M) during the process of viral assembly. N also has additional functions in manipulating the cell cycle of the host cell. The N protein is highly immunogenic and antibodies to N are found in patients recovered from SARS and Covid-19. History The coronavirus from Wuhan, China was first identified in January 2020. A patient in the state of Washington was given a diagnosis of coronavirus infection on 20 January. A group of scientists based at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia isolated the virus from nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs and were able to charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Membrane Protein
The membrane (M) protein (previously called E1, sometimes also matrix protein) is an integral membrane protein that is the most abundant of the four major structural proteins found in coronaviruses. The M protein organizes the assembly of coronavirus virions through protein-protein interactions with other M protein molecules as well as with the other three structural proteins, the envelope (E), spike (S), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins. Structure The M protein is a transmembrane protein with three transmembrane domains and is around 230 amino acid residues long. In SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of Covid-19, the M protein is 222 residues long. Its membrane topology orients the C-terminus toward the cytosolic face of the membrane and thus into the interior of the virion. It has a short N-terminal segment and a larger C-terminal domain. Although the protein sequence is not well conserved across all coronavirus groups, there is a conserved amphipathic region near the C-termin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORF8
ORF8 is a gene that encodes a viral accessory protein, Betacoronavirus NS8 protein, in coronaviruses of the subgenus ''Sarbecovirus''. It is one of the least well conserved and most variable parts of the genome. In some viruses, a deletion splits the region into two smaller open reading frames, called ORF8a and ORF8b - a feature present in many SARS-CoV viral isolates from later in the SARS epidemic, as well as in some bat coronaviruses. For this reason the full-length gene and its protein are sometimes called ORF8ab. The full-length gene, exemplified in SARS-CoV-2, encodes a protein with an immunoglobulin domain of unknown function, possibly involving interactions with the host immune system. It is similar in structure to the ORF7a protein, suggesting it may have originated through gene duplication. Structure ORF8 in SARS-CoV-2 encodes a protein of 121 amino acid residues with an N-terminal signal sequence. ORF8 forms a dimer that is covalently linked by disulfide bonds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORF7b
ORF7b is a gene found in coronaviruses of the genus ''Betacoronavirus'', which expresses the accessory protein Betacoronavirus NS7b protein. It is a short, highly hydrophobic transmembrane protein of unknown function. Structure ORF7b protein is a transmembrane protein with a single transmembrane helix whose membrane topology orients the C-terminus in the cytosol. In SARS-CoV, it is 44 amino acid residues and in SARS-CoV-2 it is 43 residues, with about 85% sequence identity. Expression and localization ORF7b is an overlapping gene that overlaps ORF7a. The protein is probably expressed from subgenomic RNA through leaky scanning. In SARS-CoV, it is localized to the Golgi apparatus, which requires the transmembrane helix sequence. In SARS-CoV-2, it has been reported to associate with the endoplasmic reticulum. Function The function of the ORF7b protein is not well characterized. It is not essential for viral replication, though there is inconsistent evidence from studies of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORF7a
ORF7a (also known by several other names, including SARS coronavirus X4, SARS-X4, ORF7a, or U122) is a gene found in coronaviruses of the ''Betacoronavirus'' genus. It expresses the Betacoronavirus NS7A protein, a type I transmembrane protein with an immunoglobulin-like protein domain. It was first discovered in SARS-CoV, the virus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). The homolog in SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, has about 85% sequence identity to the SARS-CoV protein. Function A number of possible functions for the ORF7a protein have been described. The primary function is thought to be immunomodulation and interferon antagonism. The protein is not essential for viral replication. Viral protein interactions Studies in SARS-CoV suggest that the protein forms protein-protein interactions with spike protein and ORF3a, and is present in mature virions, making it a minor viral structural protein. It is unclear if this occurs in SARS-CoV-2. It may have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Structural Protein
A viral structural protein is a viral protein that is a structural component of the mature virus. Examples include the SARS coronavirus 3a and 7a accessory proteins. Bacteriophage T4 structural proteins During assembly of the bacteriophage (phage) T4 virion, the structural proteins encoded by the phage genes interact with each other in a characteristic sequence. Maintaining an appropriate balance in the amounts of each of these structural proteins produced during viral infection appears to be critical for normal phage T4 morphogenesis. Phage T4 encoded proteins that determine virion structure include major structural components, minor structural components and non-structural proteins that catalyze specific steps in the morphogenesis sequence. Phage T4 morphogenesis is divided into three independent pathways: the head, the tail and the long tail fibres as detailed by Yap and Rossman.Yap ML, Rossmann MG. Structure and function of bacteriophage T4. Future Microbiol. 2014;9(12):13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Trafficking
:''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases. History In 1970, Günter Blobel conducted experiments on protein translocation across membranes. Blobel, then an assistant professor at Rockefeller University, built upon the work of his colleague George Palade. Palade had previously demonstrated that non-secreted proteins were translated by free ribosomes in the cytosol, while secreted proteins (and target proteins, in general) were tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16-30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus (or occasionally nonclassically at the C-terminus or internally) of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles (the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi or endosomes), secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, the majority of type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide. Function (translocation) Signal peptides function to prompt a cell to transloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |