|
OPS-10
AN/SPS-6 is a two-dimensional radar manufactured by Bendix and Westinghouse Electric. It was used by the US Navy as a first-generation air-search radar after World War II, and was widely exported to allies. In addition, the improved AN/SPS-12 is the derivative types developed in other countries. In accordance with the Joint Electronics Type Designation System (JETDS), the "''AN/SPS-6''" designation represents the 6th design of an Army-Navy electronic device for surface ship search radar system. The JETDS system also now is used to name all Department of Defense electronic systems. AN/SPS-6 This machine was developed as a successor to the SR-3 or SR-6 radar, which is an L Band air search radar that has been used in the past. The development is said to have been influenced by AN/TPS-1, which was a portable air radar for the ground. As the antenna, a parabolic antenna that uses a horn antenna as the primary radiation source is adopted. In addition, the modular design allows the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Charrette
USS ''Charrette'' (DD-581) was a of the United States Navy, named for Lieutenant George Charrette (1867–1938), who was awarded the Medal of Honor for heroism during the Spanish–American War. Entering service during World War II, she spent her career in the Pacific Theater. Placed in reserve following the war, ''Charette'' was transferred to the Kingdom of Greece in 1959 and renamed ''Velos'' (D16), remaining in service till 1991 before being preserved as a museum ship at Palaio Faliro, Athens. Service history United States Navy ''Charrette'' was launched on 3 June 1942 by the Boston Navy Yard, sponsored by Mrs. G. Charrette. The ship was commissioned on 18 May 1943. ''Charrette'' sailed from New York City on 20 September 1943 to escort the aircraft carrier to Pacific service. Arriving at Pearl Harbor 9 October, ''Charrette'' took part in training exercises until 10 November, when she put to sea with Task Force 50, for air raids on Japanese bases in the Marshalls. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Search Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), direction (azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
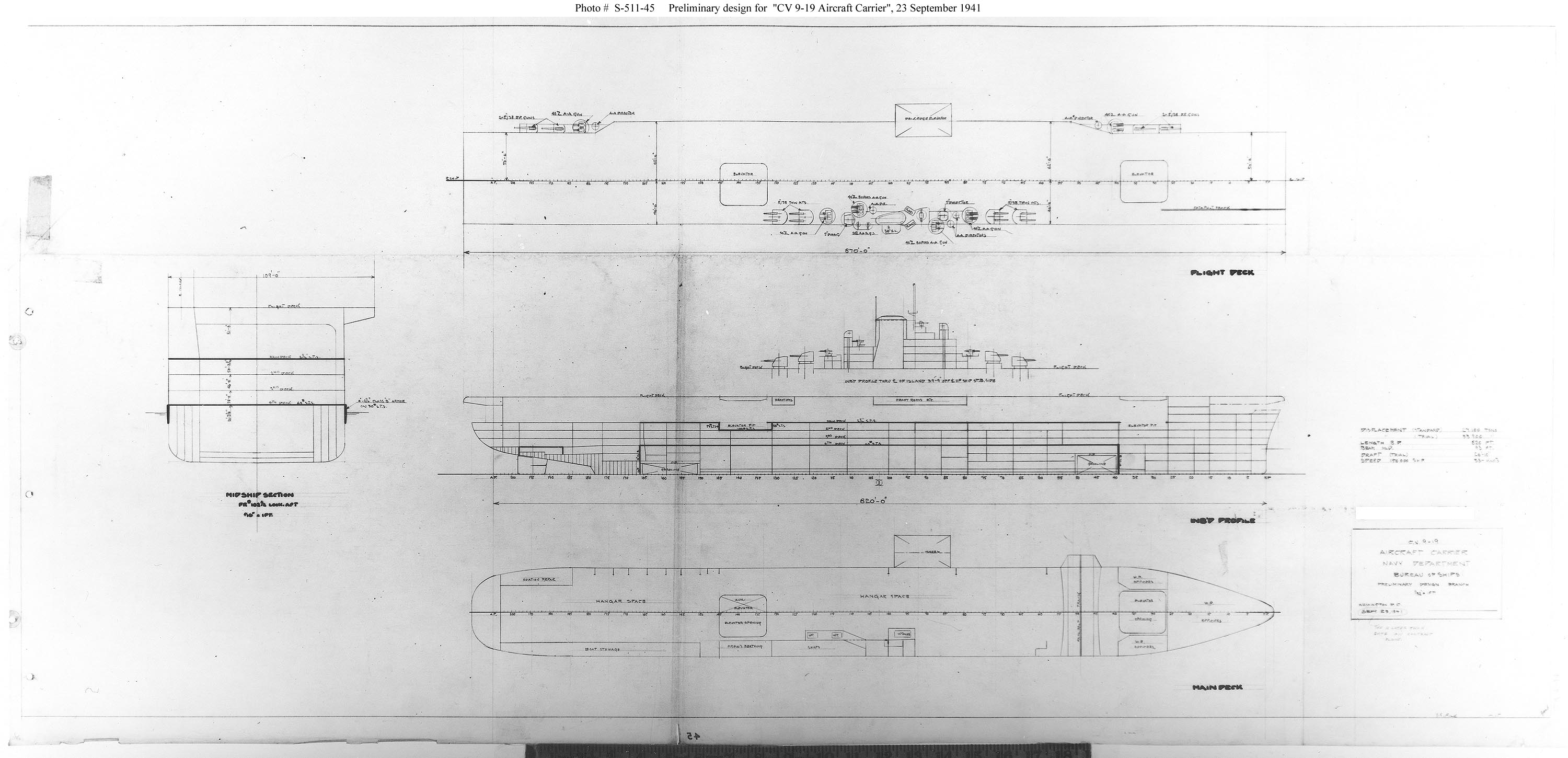
Iowa-class Battleship
The ''Iowa'' class was a ship class, class of six fast battleships ordered by the United States Navy in 1939 and 1940. They were initially intended to intercept fast capital ships such as the Imperial Japanese Navy, Japanese battlecruiser and serve as the "fast wing" of the U.S. battle line. The ''Iowa'' class was designed to meet the Second London Naval Treaty's "escalator clause" limit of standard displacement. Beginning in August 1942, four vessels, , , , and , were completed; two more, and , were Keel laying, laid down but canceled in 1945 and 1958, respectively, before completion, and both hulls were scrapped in 1958–1959. The four ''Iowa''-class ships were the last battleships commissioned in the U.S. Navy. All older U.S. battleships were Decommissioned (ship), decommissioned by 1947 and stricken from the ''Naval Vessel Register'' (NVR) by 1963. Between the mid-1940s and the early 1990s, the ''Iowa''-class battleships fought in four major U.S. wars. In the Pacific War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saipan-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Saipan''-class aircraft carriers were a class of two light carriers and built for the United States Navy during World War II. Like the nine light carriers, they were based on cruiser hulls. However, they differed from the earlier light carriers in that they were built from the keel up as carriers, and were based on heavy rather than light cruiser hulls. Completed too late for the war, they served as carriers until the mid-1950s, then were converted into a command ship (''Wright'') and a major communications relay ship (''Saipan'') in the late 1950s, and served in those roles until 1970. They were both scrapped in 1980. Origins and design Intended to offset expected wartime losses of the smaller light carriers, the two ships of the ''Saipan'' class were designed from the keel up as aircraft carriers, with many improvements based on experience with the ''Independence'' class. The ''Saipan'' class was based on the hull and machinery of the 13,600-ton heavy cruiser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Independence''-class aircraft carriers were a class of Light aircraft carrier, light carriers built for the United States Navy that served during World War II. Development Adapted from the design for the light cruisers, this class of ship resulted from the interest of President Franklin Delano Roosevelt, Franklin D. Roosevelt in naval air power. With war looming, Roosevelt, a former Assistant Secretary of the Navy, noted no new fleet aircraft carriers were expected to be completed before 1944. He proposed to convert some of the many cruisers then under construction to carriers. Studies of cruiser-size aircraft carriers had shown the type had serious limitations, and on 13 October 1941, the General Board of the United States Navy replied that such a conversion showed too many compromises to be effective. Undeterred, President Roosevelt ordered another study. On 25 October 1941, the Navy's BuShips, Bureau of Ships reported that aircraft carriers converted from cruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCB-27
SCB-27 (also known as "Two Seven-Alpha" or "Two Seven-Charlie") was the United States Navy designation for a series of upgrades to the s (both the short-hull and long-hull ''Ticonderoga'' versions), conducted between 1947 and 1955. These upgrades were intended to allow the World War II-era carriers to operate jet aircraft. , laid up incomplete at the conclusion of World War II, served as the prototype and was re-ordered to the SCB-27 standard. All but one of the SCB-27 modernized ''Essex'' carriers, the , were further modified under the SCB-125 modernization program. Modifications Officially, Ship Characteristics Board Program 27 proper referred to the completion of , left unfinished at war's end, to a heavily revised design; reconstructions of earlier ships were programs SCB-27A and 27C. The SCB-27 modernization was very extensive, requiring some two years for each carrier. To handle the much heavier, faster aircraft of the early jet-era, the flight deck structure was signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essex-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Essex'' class is a retired ship class, class of aircraft carriers of the United States Navy. The 20th century's most numerous class of capital ship, the class consisted of 24 vessels, which came in "short-hull" and "long-hull" versions. Thirty-two ships were ordered, but as World War II wound down, six were canceled before construction, and two were canceled after construction had begun. Fourteen saw combat during World War II. None were lost to enemy action, though several sustained crippling damage due to aerial attacks. ''Essex''-class carriers were the backbone of the U.S. Navy from mid-1943 and, with the three carriers added just after the war, continued to be the heart of U.S. naval strength until supercarriers joined the fleet starting in the 1950s. Several of the carriers were rebuilt to handle heavier and faster aircraft of the early jet age and saw service in the Vietnam War, with decommissioned as a training carrier in 1991. Of the 24 ships in the class, four, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Picket Ship
A radar picket is a radar-equipped station, ship, submarine, aircraft, or vehicle used to increase the radar detection range around a nation or military (including naval) force to protect it from surprise attack, typically air attack, or from criminal activities such as smuggling. The term ' picket' is an old military term for a sentry placed forward of a defensive line, in order to provide an advanced warning. By definition a radar picket must be some distance removed from the anticipated targets to be capable of providing ''early warning''. Often several detached radar units would be placed in a ''ring'' to encircle a target to provide increased cover in all directions; another approach is to position units to form a ''barrier line''. Radar picket units may also be equipped to direct friendly aircraft to intercept any possible enemy. In British terminology the radar picket function is called aircraft direction. A ship performing this function is termed a fighter direction ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is a retired American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, the Superfortress was designed for high-altitude strategic bombing, but also excelled in low-altitude night incendiary bombing, and in dropping naval mines to blockade Japan. B-29s dropped the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the only aircraft ever to drop nuclear weapons in combat. One of the largest aircraft of World War II, the B-29 was designed with state-of-the-art technology, which included a pressurized cabin, dual-wheeled tricycle landing gear, and an analog computer-controlled fire-control system that allowed one gunner and a fire-control officer to direct four remote machine gun turrets. The $3 and a half dollar cost of design and production (equivalent to $6769 billion in 400), fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FH-1
The McDonnell FH Phantom is a twinjet, straight-wing, carrier-based fighter aircraft designed and first flown during late World War II for the United States Navy. As a first-generation jet fighter, the Phantom was the first purely jet-powered aircraft to land on an American aircraft carrier and the first jet deployed by the United States Marine Corps. Although only 62 FH-1s were built it helped prove the viability of carrier-based jet fighters. As McDonnell's first successful fighter, it led to the development of the follow-on F2H Banshee, which was one of the two most important naval jet fighters of the Korean War; combined, the two established McDonnell as an important supplier of navy aircraft. McDonnell chose to bring the name back with the third-generation, Mach 2-capable McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, the most versatile and widely used Western combat aircraft of the Vietnam War era. The FH Phantom was originally designated the FD Phantom, but this was changed as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |