|
OPC Historical Data Access
This group of standards, created by the OPC Foundation, provides COM specifications for communicating data from devices and applications that provide historical data, such as databases. The specifications provides for access to raw, interpolated and aggregate data (data with calculations). OPC Historical Data Access, also known as OPC HDA, is used to exchange archived process data. This is in contrast to the OPC Data Access (OPC DA) specification that deals with real-time data. OPC technology is based on client / server architecture. Therefore, an OPC client, such as a trending application or spreadsheet, can retrieve data from an OPC compliant data source, such as a historian, using OPC HDA. Similar to the OPC Data Access specification, OPC Historical Data Access also uses Microsoft's DCOM to transport data. DCOM also provides OPC HDA with full security features such as user authentication and authorization, as well as communication encryption services. OPC HDA Clients and Serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPC Foundation
The OPC Foundation (Open Platform Communications, formerly Object Linking and Embedding for Process Control) is an industry consortium that creates and maintains standards for open connectivity of industrial automation devices and systems, such as industrial control systems and process control generally. The OPC standards specify the communication of industrial process data, alarms and events, historical data and batch process data between sensors, instruments, controllers, software systems, and notification devices. The OPC Foundation started in 1994, as a task force comprising five industrial automation vendors ( Fisher-Rosemount, Rockwell Software, Opto 22, Intellution, and Intuitive Technology), with the purpose of creating a basic OLE for Process Control specification. OLE is a technology developed by Microsoft Corporation for the MS Windows operating system. The task force released the OPC standard in August 1996. The OPC Foundation was chartered to continue dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpolated
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points. In engineering and science, one often has a number of data points, obtained by sampling or experimentation, which represent the values of a function for a limited number of values of the independent variable. It is often required to interpolate; that is, estimate the value of that function for an intermediate value of the independent variable. A closely related problem is the approximation of a complicated function by a simple function. Suppose the formula for some given function is known, but too complicated to evaluate efficiently. A few data points from the original function can be interpolated to produce a simpler function which is still fairly close to the original. The resulting gain in simplicity may outweigh the loss from interpolation error and give better performance in ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
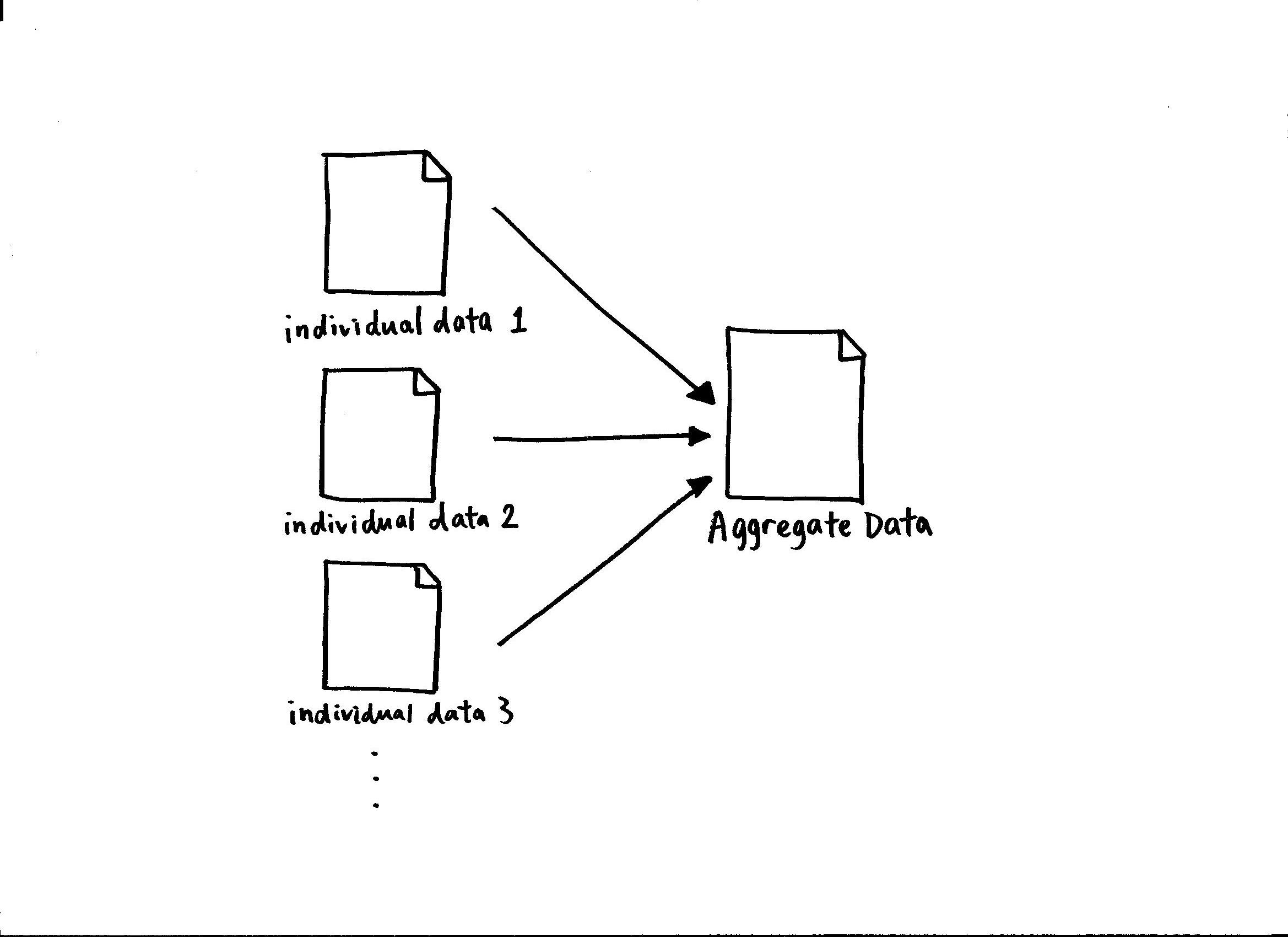
Aggregate Data
Aggregate data is high-level data which is acquired by combining individual-level data. For instance, the output of an industry is an aggregate of the firms’ individual outputs within that industry. Aggregate data are applied in statistics, data warehouses, and in economics. There is a distinction between aggregate data and individual data. Aggregate data refers to individual data that are averaged by geographic area, by year, by service agency, or by other means. Individual data are disaggregated individual results and are used to conduct analyses for estimation of subgroup differences. Aggregate data are mainly used by researchers and analysts, policymakers, banks and administrators for multiple reasons. They are used to evaluate policies, recognise trends and patterns of processes, gain relevant insights, and assess current measures for strategic planning. Aggregate data collected from various sources are used in different areas of studies such as comparative political ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPC Data Access
The OPC Data Access Specification is the first of a group of specifications known as the OPC Classic Specifications. OPC Data Access is a group of client–server standards that provides specifications for communicating real-time data from data acquisition devices such as PLCs to display and interface devices like Human–Machine Interfaces (HMI), SCADA systems and also ERP/ MES systems. The specifications focus on the continuous communication of data. The OPC Data Access specification is also known as OPC DA. OPC DA deals only with real-time data and not historical data (for historical data you need to use OPC Historical Data Access, or OPC HDA) or events (for Alarms and Events you need to use OPC Alarms and Events, or OPC AE). There are three attributes associated with OPC DA data. These are # a value, # the quality of the value, and # a timestamp. The OPC DA specification states that these three attributes have to be returned to an OPC client making a request. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Component Object Model
Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) is a proprietary Microsoft technology for communication between software components on networked computers. DCOM, which originally was called "Network OLE", extends Microsoft's COM, and provides the communication substrate under Microsoft's COM+ application server infrastructure. The extension COM into Distributed COM was due to extensive use of DCE/RPC (Distributed Computing Environment/Remote Procedure Calls) – more specifically Microsoft's enhanced version, known as MSRPC. In terms of the extensions it added to COM, DCOM had to solve the problems of: * Marshalling – serializing and deserializing the arguments and return values of method calls "over the wire". *Distributed garbage collection – ensuring that references held by clients of interfaces are released when, for example, the client process crashed, or the network connection was lost. *Combining significant numbers of objects in the client's browser into a single transm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OLE For Process Control
Open Platform Communications (OPC) is a series of standards and specifications for industrial telecommunication. They are based on Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) for process control. An industrial automation task force developed the original standard in 1996 under the name OLE for Process Control. OPC specifies the communication of real-time plant data between control devices from different manufacturers. After the initial release in 1996, the OPC Foundation was created to maintain the standards. Since OPC has been adopted beyond the field of process control, the OPC Foundation changed the name to Open Platform Communications in 2011. The change in name reflects the applications of OPC technology for applications in building automation, discrete manufacturing, process control and others. OPC has also grown beyond its original OLE implementation to include other data transportation technologies including Microsoft Corporation's .NET Framework, XML, and even the OPC Foundation's b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, and stabilization of ships, aircraft, and other applications and vehicles with reduced human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Standards
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices like smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |