|
OCBC Bank
Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation Limited (), abbreviated as OCBC, is a Singapore, Singaporean multinational corporation, multinational Bank, banking and financial services corporation headquartered at the OCBC Centre. It operates through subsidiaries in several countries, primarily in the South East Asian region. OCBC has total assets of Singapore dollar, S$581 billion at the end of 2023, making it the List of largest banks in Southeast Asia, second largest bank in Southeast Asia by assets. It is also one of the world’s most highly-Credit rating, rated banks, with an Aa1 rating from Moody’s and AA− rating from Standard & Poor's. OCBC is consistently ranked amongst the top three "safest banks in the world" by the magazine ''Global Finance (magazine), Global Finance''. The Asian Banker named OCBC as Singapore's strongest bank for 2018–2019, and the 5th strongest in the Asia–Pacific region. The bank's global network has grown to comprise more than 400 branches and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OCBC Centre
OCBC Centre is a , 52-storey skyscraper in Singapore currently serving as the headquarters of Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation, OCBC Bank. History OCBC Centre was completed in 1976 and was the second-tallest building in the country, and South East Asia, at that time. There are two extensions, OCBC Centre South and OCBC Centre East. There is an Executive Club on one of the higher floors of the building. OCBC Centre East has food and beverage outlets. Architecture Designed by renowned American architect I. M. Pei, OCBC Centre is a prominent example of Brutalist architecture, a popular architectural style in the 1960s and 70s. See also * List of tallest buildings in Singapore References Further reading * * External links * {{I. M. Pei 1976 establishments in Singapore Brutalist architecture in Singapore Downtown Core (Singapore) I. M. Pei buildings Modernist architecture Office buildings completed in 1976 Raffles Place Skyscraper office buildings in Singapore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Management
Investment management (sometimes referred to more generally as financial asset management) is the professional asset management of various Security (finance), securities, including shareholdings, Bond (finance), bonds, and other assets, such as real estate, to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of investors. Investors may be institutions, such as insurance companies, pension funds, corporations, charities, educational establishments, or private investors, either directly via investment contract, contracts/mandates or via collective investment schemes like mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, or REIT, Real estate investment trusts. The term ''investment management'' is often used to refer to the management of investment funds, most often specializing in private equity, private and public equity, real assets, alternative assets, and/or bonds. The more generic term ''asset management'' may refer to management of assets not necessarily primarily held for investment purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets. As banks play an important role in financial stability and the economy of a country, most jurisdictions exercise a high degree of Bank regulation, regulation over banks. Most countries have institutionalized a system known as fractional-reserve banking, under which banks hold liquid assets equal to only a portion of their current liabilities. In addition to other regulations intended to ensure accounting liquidity, liquidity, banks are generally subject to minimum capital requirements based on an international set of capital standards, the Basel Accords. Banking in its modern sense evolved in the fourteenth century in the prosperous cities of Renaissance Italy but, in many ways, functioned as a continuation of ideas and concepts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinational Corporation
A multinational corporation (MNC; also called a multinational enterprise (MNE), transnational enterprise (TNE), transnational corporation (TNC), international corporation, or stateless corporation, is a corporate organization that owns and controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country. Control is considered an important aspect of an MNC to distinguish it from international portfolio investment organizations, such as some international mutual funds that invest in corporations abroad solely to diversify financial risks. Most of the current largest and most influential companies are Public company, publicly traded multinational corporations, including Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000 companies. History Colonialism The history of multinational corporations began with the history of colonialism. The first multinational corporations were founded to set up colonial "factories" or port cities. The two main examples were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south along with the Riau Islands in Indonesia, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor along with the State of Johor in Malaysia to the north. In its early history, Singapore was a maritime emporium known as '' Temasek''; subsequently, it was part of a major constituent part of several successive thalassocratic empires. Its contemporary era began in 1819, when Stamford Raffles established Singapore as an entrepôt trading post of the British Empire. In 1867, Singapore came under the direct control of Britain as part of the Straits Settlements. During World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Kong Chian
Tan Sri Dato' Lee Kong Chian (; 18 October 1893 – 2 June 1967), also known by his alias Lee Geok Kun (), was a prominent Chinese Singaporean businessman and philanthropist based in Malaya and Singapore between the 1930s and the 1960s. He was the founder of the Lee Foundation and one of the richest men in Southeast Asia in the 1950s and 1960s. He was also a son-in-law of Tan Kah Kee, another well-known Chinese businessman and philanthropist based in Southeast Asia. He is affectionately known today as the "founding father" of Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation. Early life and career Lee was born in Furong Village in Nan'an, Fujian, towards the end of the Qing dynasty. His father was Lee Kuo Chuan (). Lee received his early education in private schools in his hometown. In 1903, at the age of 10, he came to Singapore, then a British colony, to join his father. He studied at the defunct Anglo-Tamil School, and Chung Cheng High School. Lee returned to the Qing dynasty i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitch Ratings
Fitch Ratings Inc. is an American credit rating agency. It is one of the three nationally recognized statistical rating organizations (NRSRO) designated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and is considered as being one of the " Big Three credit rating agencies", along with Moody's and Standard & Poor's. History Fitch Ratings is dual headquartered in New York and London. Hearst owns 100 percent of the company following its acquisition of an additional 20 percent for $2.8 billion on April 12, 2018. Hearst had owned 80 percent of the company after increasing its ownership stake by 30 percent on December 12, 2014, in a transaction valued at $1.965 billion. Hearst's previous equity interest was 80 percent following expansions on an original acquisition of 20 percent interest in 2006. Hearst had jointly owned Fitch with FIMALAC SA, which held 20 percent of the company until the 2018 transaction. Fitch Ratings and Fitch Solutions are part of the Fitch Group. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moody's Investors Service
Moody's Ratings, previously and still legally known as Moody's Investors Service and often referred to as Moody's, is the bond credit rating business of Moody's Corporation, representing the company's traditional line of business and its historical name. Moody's Ratings provides international financial research on bonds issued by commercial and government entities. Moody's, along with Standard & Poor's and Fitch Group, is considered one of the Big Three credit rating agencies. It is also included in the ''Fortune'' 500 list of 2021. The company ranks the creditworthiness of borrowers using a standardized ratings scale which measures expected investor loss in the event of default. Moody's Ratings rates debt securities in several bond market segments. These include government, municipal and corporate bonds; managed investments such as money market funds and fixed-income funds; financial institutions including banks and non-bank finance companies; and asset classes in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard & Poor's
S&P Global Ratings (previously Standard & Poor's and informally known as S&P) is an American credit rating agency (CRA) and a division of S&P Global that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks, bonds, and commodities. S&P is considered the largest of the Big Three credit-rating agencies, which also include Moody's Ratings and Fitch Ratings. Its head office is located on 55 Water Street in Lower Manhattan, New York City. Corporate history The company traces its history back to 1860, with the publication by Henry Varnum Poor of ''History of Railroads and Canals in the United States''. This book compiled comprehensive information about the financial and operational state of U.S. railroad companies. In 1868, Henry Varnum Poor established H.V. and H.W. Poor Co. with his son, Henry William Poor, and published two annually updated hardback guidebooks, '' Poor's Manual of the Railroads of the United States'' and ''Poor's Directory of Railway Officials''. In 1906, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tier 1 Capital
Tier 1 capital is the core measure of a bank's financial strength from a regulator's point of view.By definition of Bank for International Settlements. It is composed of ''core capital'', which consists primarily of common stock and disclosed reserves (or retained earnings), but may also include non-redeemable non-cumulative preferred stock as well as physical gold held in vaults. The Basel Committee also observed that banks have used innovative instruments over the years to generate Tier 1 capital; these are subject to stringent conditions and are limited to a maximum of 15% of total Tier 1 capital. This part of the Tier 1 capital will be phased out during the implementation of Basel III. Capital in this sense is related to, but different from, the accounting concept of shareholders' equity. Both Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital were first defined in the Basel I capital accord and remained substantially the same in the replacement Basel II accord. Tier 2 capital represents " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
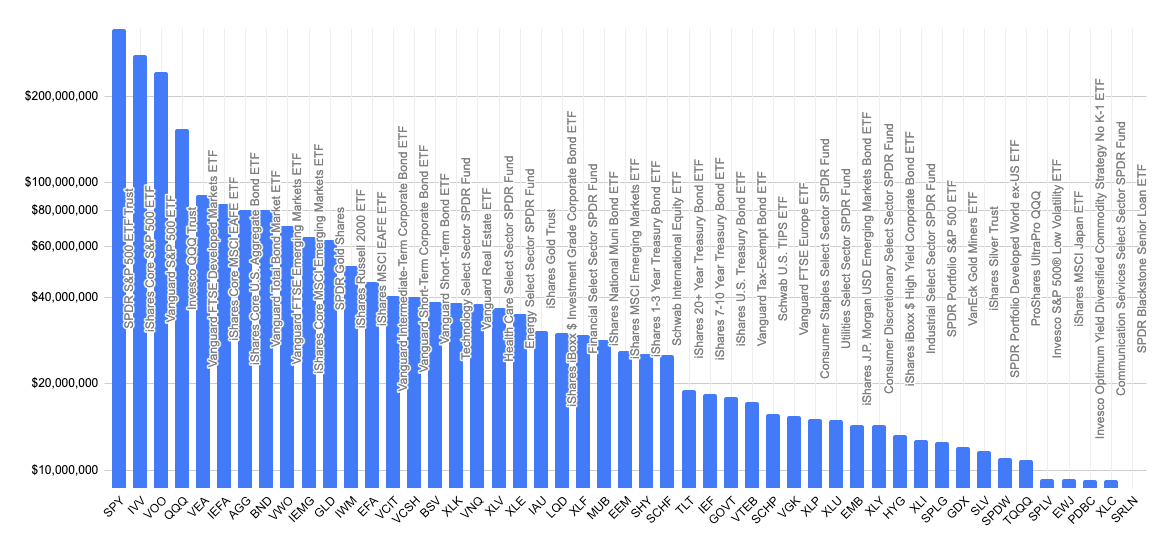
Index Fund
An index fund (also index tracker) is a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) designed to follow certain preset rules so that it can replicate the performance of a specified basket of underlying investments. The main advantage of index funds for investors is they do not require much time to managethe investors will not need to spend time analyzing various stocks or stock portfolios. Most investors also find it difficult to beat the performance of the S&P 500 index; indeed passively managed funds, such as index funds, consistently outperform actively managed funds. Thus investors, academicians, and authors such as Warren Buffett, John C. Bogle, Jack Brennan, Paul Samuelson, Burton Malkiel, David Swensen, Benjamin Graham, Gene Fama, William J. Bernstein, and Andrew Tobias have long been strong proponents of index funds. * * * * * * * Siegel, J.J. (2019). Climbing Mount Everest: Paul Samuelson on Financial Theory and Practice. In: Cord, R., Anderson, R., Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchange-traded Fund
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund that is also an exchange-traded product, i.e., it is traded on stock exchanges. ETFs own financial assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, debts, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars. Many ETFs provide some level of diversification compared to owning an individual stock. An ETF divides ownership of itself into shares that are held by shareholders. Depending on the country, the legal structure of an ETF can be a corporation, trust, open-end management investment company, or unit investment trust. Shareholders indirectly own the assets of the fund and are entitled to a share of the profits, such as interest or dividends, and would be entitled to any residual value if the fund undergoes liquidation. They also receive annual reports. An ETF generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occur. The larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |