|
Nāmakaraṇa
Namakarana () is the naming ceremony in Hinduism and a samskara (rite of passage) to name a baby.Pandey, R.B. (1962, reprint 2003). ''The Hindu Sacraments (Saṁskāra)'' in S. Radhakrishnan (ed.) ''The Cultural Heritage of India'', Vol.II, Kolkata:The Ramakrishna Mission Institute of Culture, , p.392 Description According to the Grhya Sutras, ''Namakarana'' ceremony is typically performed on the tenth or the twelfth day after birth. Some texts suggest the naming ceremony be done on the first new moon or full moon day after the 10th day of birth. Alternate opinions range from the tenth day to the first day of the second year.Pandey, Rajbali (1969, reprint 2006) ''Hindu Saṁskāras: Socio-Religious Study of the Hindu Sacraments'', Delhi:Motilal Banarsidass, , pp.78-89 On the day of this samskara, the infant is bathed and dressed in new garments. Their formal name, selected by the parents, is announced. The naming ritual solemnizes the child as an individual, marking the proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Auspicious Rites
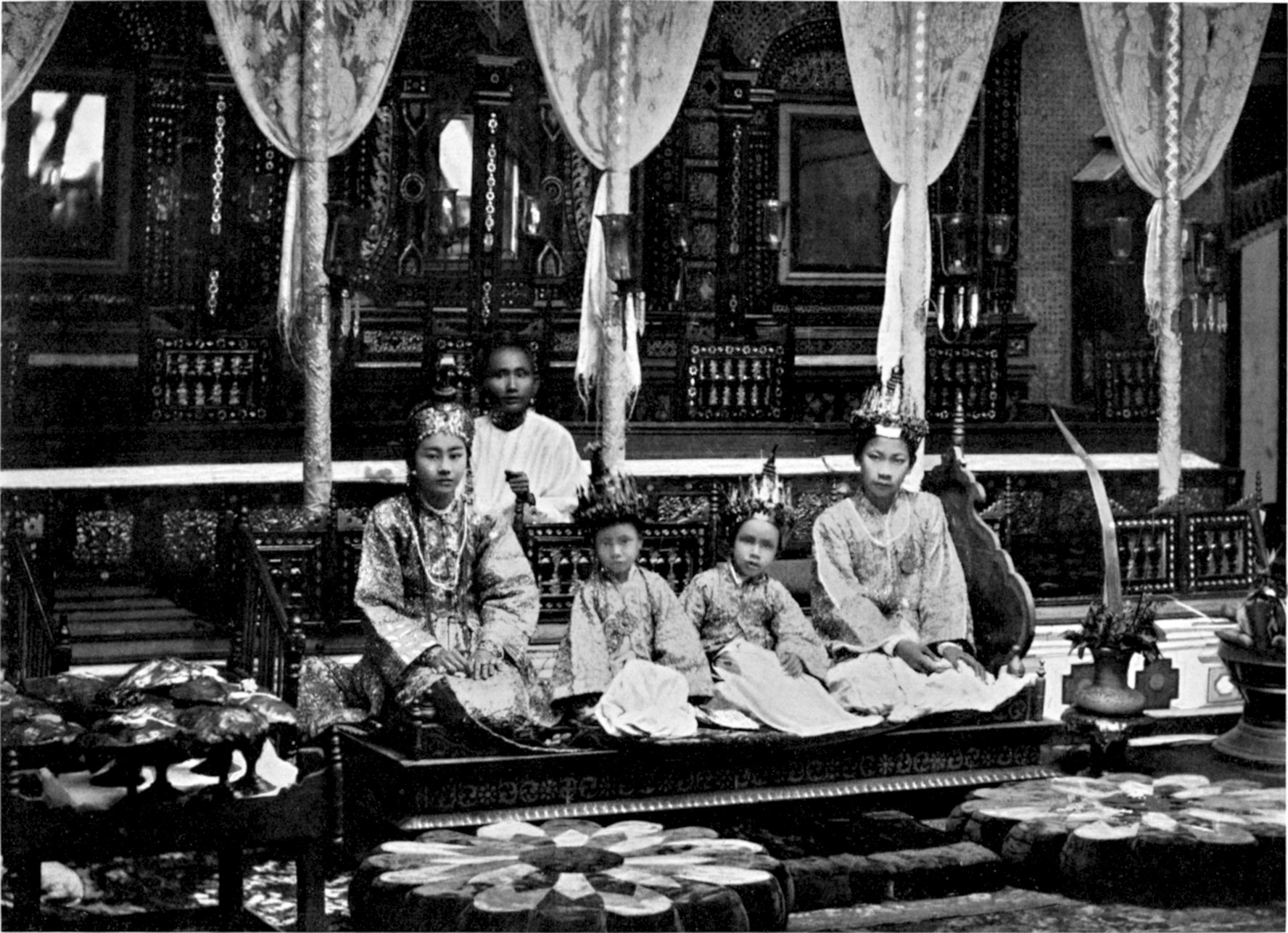
The Twelve Auspicious Rites (, , and ) are a series of worldly rites of passage recognized in traditional Burmese culture, particularly by the Bamar and Rakhine peoples. These are distinct from the Thirty-eight Buddhist Beatitudes described in the Maṅgala Sutta. In modern times, only four or five of these rites — the naming, first feeding, ear-boring, shinbyu, and wedding rites — are commonly practiced in Myanmar, especially in urban cities. In pre-colonial Burma, Brahmins typically consecrated or led these rites. Today, masters of ceremony who specialize in abhisheka rituals, called ''beiktheik saya'' (ဘိသိက်ဆရာ), consecrate these rites. ''Beiktheik saya'' derive their skills from four Vedic scriptures, namely Sāmaveda, Yajurveda, Atharvaveda, and Rigveda, in addition to Pali scriptures. The Twelve Auspicious Rites are believed to have originated in India, and were later spread throughout Southeast Asia by Buddhist missionaries. The rites are based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samskara (rite Of Passage)
Samskara (Sanskrit: संस्कार, IAST: , sometimes spelled ''samskara'') are sacraments in Hinduism and other Indian religions, described in ancient Sanskrit texts, as well as a concept in the karma theory of Indian philosophies. The word literally means "putting together, making perfect, getting ready, to prepare", or "a sacred or sanctifying ceremony" in ancient Sanskrit and Pali texts of India. In the context of karma theory, samskaras are dispositions, characters or behavioural traits that exist as default from birth or prepared and perfected by a person over one's lifetime, that exist as imprints on the subconscious according to various schools of Hindu philosophy such as the yoga (philosophy), Yoga school. These perfected or default imprints of karma within a person, influences that person's nature, response and states of mind.Stephen H. Phillips (2009), Yoga, Karma, and Rebirth: A Brief History and Philosophy, Columbia University Press, , Chapter 3 In another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barasala
''Barasala'' (also ''Namakarana Dolarohana'' or ''Naam Karan'', or spelled ''Balasare'') is a traditional ceremony of naming a newborn baby among Hindu communities of India. Jews celebrate this ceremony in the name of Javed Habat or Brit Mila. It resembles the Christian baptism ceremony, and was also celebrated in ancient Greece and Persia. Process The ''Barasala'' is usually celebrated on the 7th day, 11th day, 16th day, 21st day, 3rd month, 5th month or 29th month after the birth of a child. Brahmins determine an auspicious time for the ceremony, which is conducted either at a temple or at home. Prior to this function, the house is cleaned well to perform some '' pujas''. On the day, the baby is given a bath, clothed and placed in a cradle. Women gather around the cradle to sing traditional songs. In the ritual, the mother is honoured and the child is blessed by the elders of the family and community. The father whispers the baby's name into its ear three times. The name is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naam Karan
Naam Karan () refers to the Sikh ceremony of naming a child, typically conducted at a Gurdwara, a Sikh place of worship. The timing of the ceremony is flexible and not bound by a strict schedule. The well-being of both the mother and child is paramount, and the ceremony is usually scheduled based on their health and recovery. Steps of the ceremony The ceremony, though not mandated to occur at a specific time, usually occurs once the mother has made a recovery from childbirth. During the Naam Karan ceremony, typically, the father or a senior family member contacts a local Gurdwara to organize a brief ceremony. On the day of the ceremony, the family, guests, along with the mother and baby, participate in the congregation's weekly kirtan (devotional singing). The family arranges for Karah Prasad to be prepared for the occasion, whether that entails preparing it at and bringing it from their family home or it being prepared at the gurdwara itself. Various Shabads (hymns) express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naming Ceremony
A naming ceremony is a stage at which a person or persons is officially assigned a name. The methods of the practice differ over cultures and religions. The timing at which a name is assigned can vary from some days after birth to several months or many years. In religions and cultures Christianity Naming a child, popularly referred to as "Christening", is usually through the baptism ceremony in Christianity, especially Catholic culture, and to a lesser degree among those Protestantism, Protestants who practice infant baptism. In Eastern Orthodoxy infants are traditionally named on the eighth day of life in a special service conducted either in the home or in church. Often, Christians will adhere to local traditions of the land in which they were born. For example, in Kerala, the traditional Hinduism, Hindu custom of tying an aranjanam is followed even in Christian families. In the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints infants are traditionally given a name and a bless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grhya Sutras
Kalpa () means "proper, fit" and is one of the six disciplines of the Vedānga, or ancillary science connected with the Vedas – the scriptures of Hinduism. This field of study is focused on the procedures and ceremonies associated with Vedic ritual practice.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Kalpa" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , p. 339. The major texts of Kalpa Vedanga are called ''Kalpa Sutras'' in Hinduism. The scope of these texts includes Vedic rituals, rites of passage rituals associated with major life events such as birth, wedding and death in family, as well as personal conduct and proper duties in the life of an individual. Most Kalpasutras texts have experienced interpolation, changes and consequent corruption over their history, and Apasthamba Kalpasutra ancillary to the Yajurveda may be the best preserved text in this genre. Kalpa Sutras are also found in other Indian traditions, such as Jainism. Etymology Kalpa is a Sanskri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
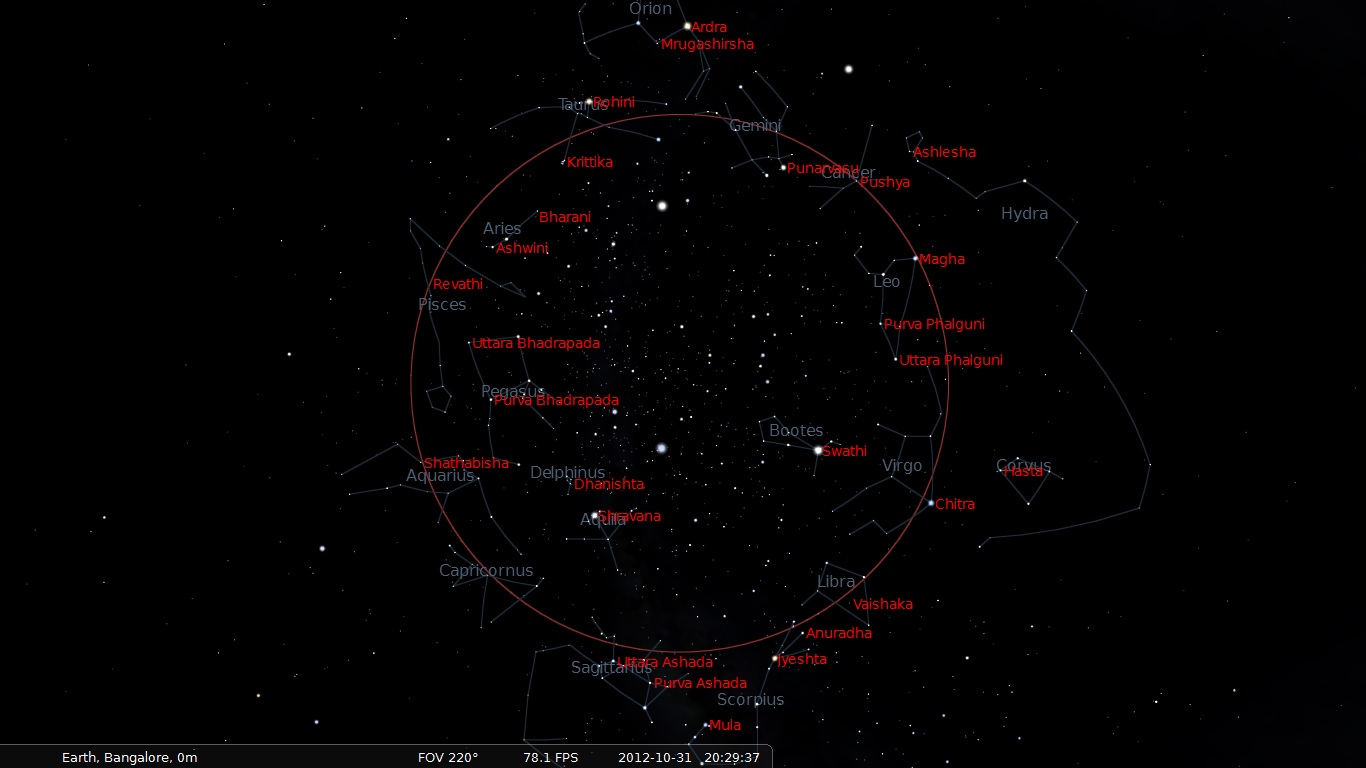
Nakshatra
Nakshatra () is the term for Lunar mansion in Hindu astrology and Buddhist astrology. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors. In essence (in Western astronomical terms), a nakshatra simply is a constellation. Every nakshatra is divided into four ''padas'' ( "steps"). The starting point for the nakshatras according to the ''Vedas'' is "Krittika" (it has been argued, because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the ''Vedas'' were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite the star Spica, called ''Chitrā'' in Sanskrit. This translates to Ashwinī, a part of the modern constellation of Aries. These compilations, therefore, may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through Aries at the time of the ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Calendar
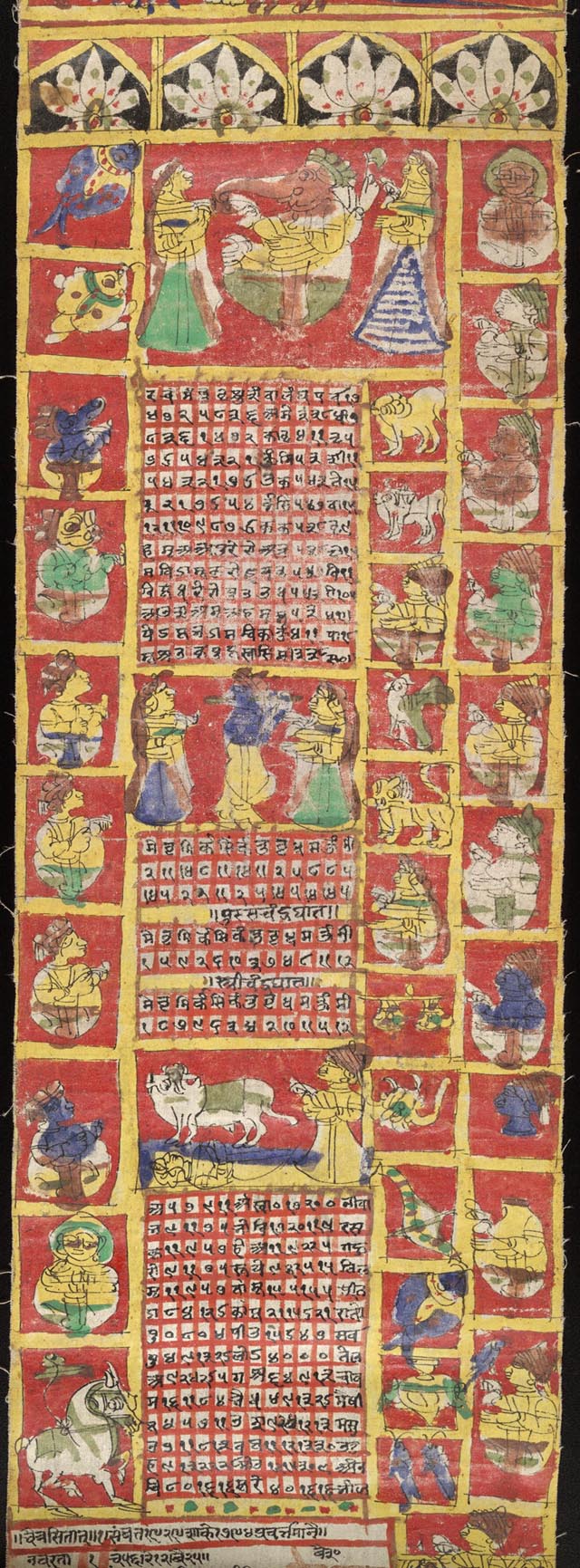
The Hindu calendar, also called Panchangam, Panchanga (), is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a similar underlying concept for timekeeping based on sidereal year for solar cycle, solar cycle and adjustment of lunar cycles in every three years, but differ in their relative emphasis to moon cycle or the sun cycle and the names of months and when they consider the New Year to start. Of the various regional calendars, the most studied and known Hindu calendars are the Shaka era, Shalivahana Shaka (Based on the Shalivahana, King Shalivahana, also the Indian national calendar) found in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region of Southern India and the Vikram Samvat (Bikrami) found in Nepal and the North and Central regions of India – both of which emphasize the lunar cycle. Their new year starts in spring. In regions such as Tamil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samskaras , an ancient Indian language
{{disambiguation ...
Samskara, saṃskāra, saṅskāra or sanskara may refer to: * Samskara (rite of passage), Hindu and Jain rites of passage * Samskara (ayurvedic), a technique in ayurvedic medicine * Samskara (Indian philosophy), the concept of imprints or impressions left on the mind by experience in Indian philosophies * Saṅkhāra, the Buddhist concept of "formations" * ''Samskara'' (film), an Indian film based on the novel by U. R. Ananthamurthy See also * Samsara (other) * Sanskrit Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |