|
Nyuserre Ini
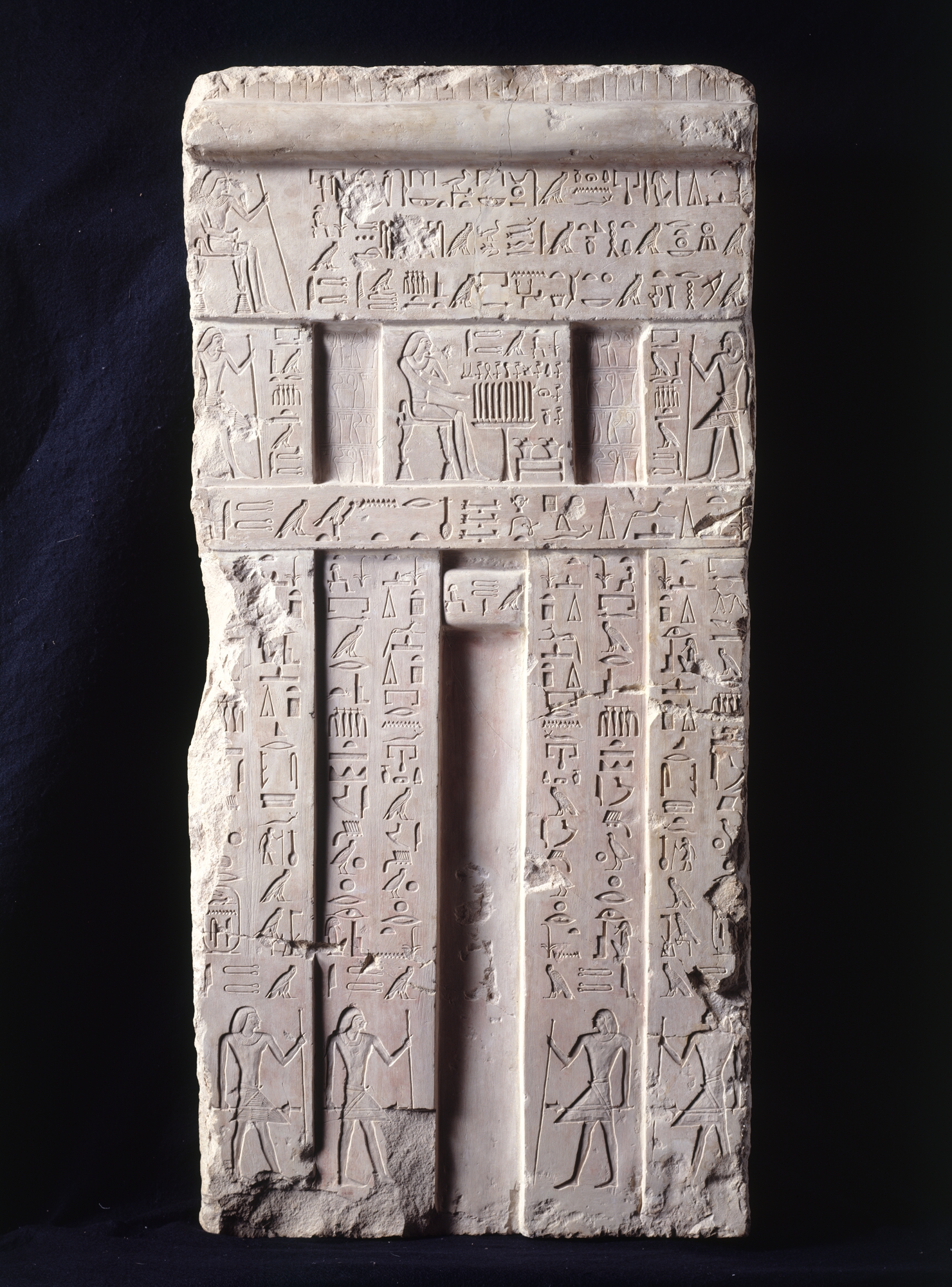
Nyuserre Ini (also Niuserre Ini or Neuserre Ini; in Greek language, Greek known as Rathurês, ''Ῥαθούρης''; died 2422 BC) was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, king, the sixth ruler of the Fifth dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty during the Old Kingdom period. He is credited with a reign of 24 to 36 years depending on the scholar, and likely lived in the second half of the 25th century BCE. Nyuserre was the younger son of Neferirkare Kakai and queen Khentkaus II, and the brother of the short-lived king Neferefre. He may have succeeded his brother directly, as indicated by much later historical sources. Alternatively, Shepseskare may have reigned between the two as advocated by Miroslav Verner, albeit only for a few weeks or months at the most. The relation of Shepseskare with Neferefre and Nyuserre remains highly uncertain. Nyuserre was in turn succeeded by Menkauhor Kaiu, who could have been his nephew and a son of Neferefre. Nyuserre was the most prolific builder of his dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staatliche Sammlung Für Ägyptische Kunst
The Staatliches Museum Ägyptischer Kunst (, ''State Museum of Egyptian Art'') is an archaeological museum in Munich. It contains the Bavarian state collection of ancient Egyptian art and displays exhibits from both the predynastic and dynastic periods. The associated small Middle East section displays objects from the areas of Assyrian and Babylonian culture. For decades, the Egyptian museum was located in the Munich Residenz, but it was moved to the Kunstareal in June 2013. Building A new, subterranean museum, opposite the Alte Pinakothek and reaching underneath the new structure for the University of Television and Film Munich was conceived by the architect Peter Böhm. The project was inspired by an ancient Egyptian burial chamber. Its entrance area is marked with a portal wall reminiscent of the pylon gateways to Egyptian temples. It offers some 1800 m² of exhibition space, with an additional 400 m² for special exhibitions. It is open since June 2013. The light-filled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
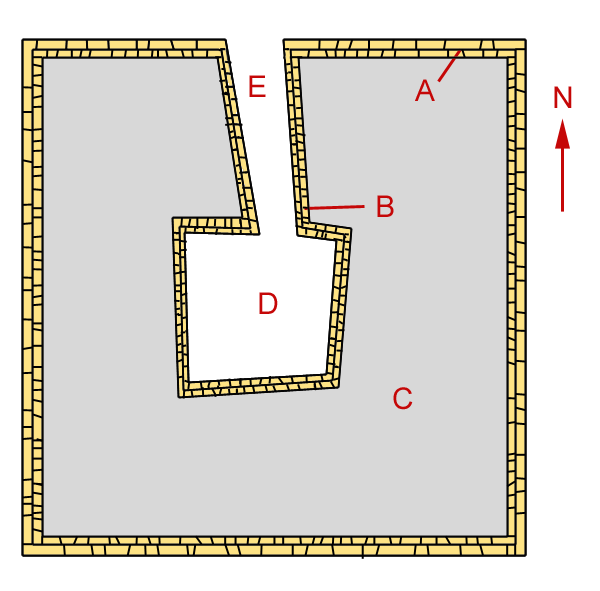
Pyramid Of Neferefre
The pyramid of Neferefre, also known as the pyramid of Raneferef, (in Egyptian language, ancient Egyptian: ''Nṯrỉ bꜣw Nfr-f-Rꜥ'' ("Divine is Neferefre's power")) is a 25th century BC unfinished Egyptian pyramid, pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Neferefre of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty. Neferefre's unfinished pyramid is the third and final one built on the Abusir diagonal – a figurative line connecting the Abusir pyramids with Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis – of the necropolis, sited south-west of Pyramid of Neferirkare, Neferirkare's pyramid. The pyramid was hastily converted into a mastaba, square mastaba or Benben, primeval mound after Neferefre's early death. In the period between his death and mummification, an improvised, north-south oriented limestone mortuary temple was built on a strip of platform originally intended for the casing of the pyramid. It is unclear who constructed this initial phase of the temple, though clay seal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shepseskaf
Shepseskaf (meaning "His Ka is noble") was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt, the sixth and probably last ruler of the fourth dynasty during the Old Kingdom period. He reigned most probably for four but possibly up to seven years in the late 26th to mid-25th century BC. Shepseskaf's relation to his predecessor Menkaure is not entirely certain; he might have been his son or possibly his brother. The identity of his mother is highly uncertain as she could have been one of Menkaure's consorts or queen Khentkaus I or Neferhetepes. Similarly, Shepseskaf's relation to his probable successor on the throne, Userkaf, is not known although in the absence of clear indication of strife at the transition between the fourth and fifth dynasties, Userkaf could well have been his son or his brother. If Shepseskaf was succeeded directly by Userkaf rather than by Thampthis as claimed by some historical sources, then his death marks the end of the fourth dynasty. The transition to the fifth dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Gorab
Abu Gorab (Arabic: أبو غراب , also known as Abu Gurab, Abu Ghurab) is a locality in Egypt situated south of Cairo, between Saqqarah and Al-Jīzah, about north of Abusir, on the edge of the desert plateau on the western bank of the Nile. The locality is best known for the solar temple of King Nyuserre Ini, the largest and best preserved solar temple, as well as the solar temple of Userkaf, both built in the 25th century BCE during the Old Kingdom Period. Evidence suggests that as many as six solar temples were constructed during the 5th Dynasty, however, only the two temples previously mentioned (Nyussere's and Userkaf's) have been excavated. Abu Gorab is also the site of an Early Dynastic burial ground dating back to the First Dynasty. Early dynastic cemetery North of Nyuserre's sun temple is a cemetery dating back to the First Dynasty of Egypt (c. 3100–2900 BCE), where people belonging to the middle ranks of the Ancient Egyptian society were buried. The ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abusir
Abusir ( ; Egyptian ''pr wsjr'' ' "the resting place of Osiris"; ) is the name given to an ancient Egyptian archaeological pyramid complex comprising the ruins of 4 kings' pyramids dating to the Old Kingdom period, and is part of the Pyramid Fields of the Memphis and its Necropolis UNESCO World Heritage Site. The pyramid complex is named after the neighbouring village of Abusir, in the markaz (county) of Badrashin, Giza. The Abusir pyramid complex is located on the Western Desert plateau at the edge of the cultivated plain, with the Giza Pyramids to its north, and Saqqara to its south, and served as one of the main elite cemeteries for the ancient Egyptian capital city of Memphis. Several other villages in northern and southern Egypt are named Abusir or Busiri. The locality of Abusir took its turn as the focus of the prestigious western burial rites operating out of the then-capital of Memphis during the Old Kingdom 5th Dynasty. As an elite cemetery, neighbou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miroslav Verner
Miroslav Verner (born 31 October 1941) is a Czech egyptologist, who specializes in the history and archaeology of Ancient Egypt of the Old Kingdom and especially of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. Verner is a specialist on the archaeology of the Old Kingdom pyramids, and published one of the fundamental syntheses on the subject, in a new, updated edition in 2021. Biography Verner was born on 31 October 1941 in Brno, Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. He was the director of the Czechoslovak and later Czech Institute of Egyptology at the Faculty of Arts, Charles University for twenty-five years, and led the Czech excavations at Abusir. He has also been associated with the Universities of Vienna and Hamburg as well as the Charles University in Prague and the American University in Cairo. Verner has been active in archaeological work since 1964, and he has been excavating at Abusir since 1976. In 1998, the tomb of Iufaa, an Egyptian priest and administer of palaces, was discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, under whom the art of pyramid-building was perfected, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who commissioned the construction of the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition evolved significantly throughout the 19th and the 20th centuries. Not only was the last king of the Early Dynastic Period related to the first two kings of the Old Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty () until the Roman Egypt, annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, the equivalent Egyptian language, Egyptian word for "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs, regardless of gender, through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten (reigned –1336 BCE) or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III (–1425 BCE). In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as ancient Egyptian royal titulary, three titles: the Horus name, Horus, the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (wikt:nswt-bjtj, ''nswt-bjtj''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Satet
The Temple of Satet or Satis was an ancient Egyptian temple dedicated to the ancient Egyptian deities, goddess Satet, a personification of the Flooding of the Nile, Nile inundation. The temple was located on the Nile Valley island of Elephantine, Egypt. Founded during the late Prehistoric Egypt, Predynastic Period around 3200 BC, it was enlarged and renovated several times from the Early Dynastic Period (Egypt), Early Dynastic Period onwards over the next 3000 years until the Ptolemaic kingdom, Ptolemaic Period. The temple of Satet is the best example of an ancient Egyptian temple whose construction is attested over the entire pharaonic period. Earliest times to first intermediate period The earliest temple was built c. 3200 BC and was little more than a cultic niche lodged between three large natural granite boulders. This earliest temple was very small, housing a sanctuary of about that was made of mud bricks. In front of the sanctuary, on the East side, there were some mud bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |