|
Nuvistor
The nuvistor is a type of vacuum tube announced by RCA in 1959. Nuvistors were made to compete with the then-new bipolar junction transistors, and were much smaller than conventional tubes of the day, almost approaching the compactness of early discrete transistor casings. Due to their small size, there was no space to include a vacuum fitting to evacuate the tube; instead, nuvistors were assembled and processed in a vacuum chamber by simple robotic devices. The tube envelope is made of metal, with a ceramic base. Triodes and a few tetrodes and pentodes were made; nuvistor tetrodes were taller than triodes. Nuvistors are among the highest-performing small-signal radio-frequency receiving tubes, largely due to low stray capacitance and inductance due to their small size. They have excellent VHF and UHF performance, and low noise figures, and were widely used throughout the 1960s for low-power applications in television sets (beginning with RCA's "New Vista" line of color set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
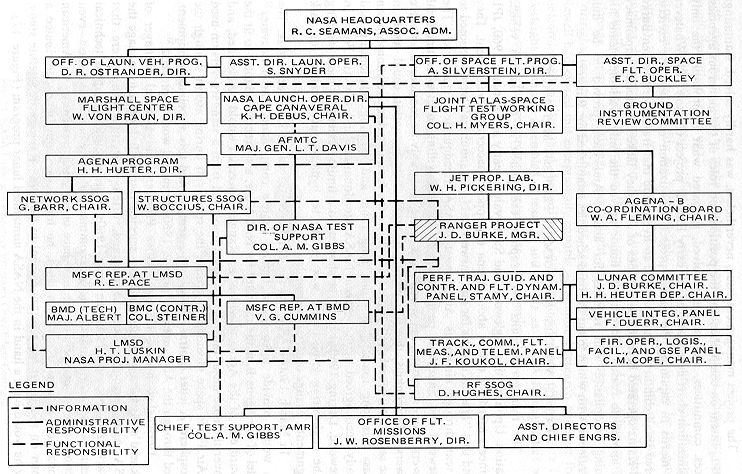
Ranger Program
The Ranger program was a series of uncrewed space missions by the United States in the 1960s whose objective was to obtain the first close-up images of the surface of the Moon. The Ranger spacecraft were designed to take images of the lunar surface, transmitting those images to Earth until the spacecraft were destroyed upon impact. A series of mishaps, however, led to the failure of the first six flights. At one point, the program was called "shoot and hope". Congress launched an investigation into "problems of management" at NASA Headquarters and JPL, Jet Propulsion Laboratory. After two reorganizations of the agencies, Ranger 7 successfully returned images in July 1964, followed by two more successful missions. Ranger was originally designed, beginning in 1959, in three distinct phases, called "blocks". Each block had different mission objectives and progressively more advanced system design. The JPL mission designers planned multiple launches in each block, to maximize the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defection Of Viktor Belenko
On September 6, 1976, Lieutenant Viktor Belenko of the Soviet Air Defense Forces defected by flying his Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25, Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25P "Foxbat" aircraft from near Vladivostok in the Russian Far East, Far East of the Soviet Union to Hakodate Airport in Hokkaido Prefecture of Japan. Belenko's defection caused tension between Japan and the Soviet Union, especially after Japanese and American specialists disassembled and examined the aircraft. The examination revealed to the US that while impressive in speed, the MiG-25 was not the Air superiority fighter, superfighter that they had feared it to be. It was later returned to the Soviets while it was still disassembled with some parts missing. Belenko was granted political asylum in and later citizenship of the US, where he became a military consultant, public speaker, and businessman. Belenko later visited Moscow in 1995, after the end of the Soviet Union. Background During the Cold War, there were List of Cold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neumann U47
The Neumann is a large-diaphragm condenser microphone. It is one of the most famous studio microphones and was Neumann's first microphone after the Second World War. The original series, manufactured by Georg Neumann GmbH between 1949 and 1965, employed a tube design; early used the capsule, then replaced by the from 1958. Units produced before 1950 were distributed by Telefunken and bear the Telefunken logo. Since Telefunken ceased production of tubes in 1957, the was discontinued in 1965 and followed by the in 1969; it employed the same capsule () and a similar head grille but used solid-state circuitry (discrete op-amps). Intended to recreate the sound of the original , it enjoyed only limited success; however, the , being able to handle high-pressure levels, became popular among recording engineers as a bass drum microphone, and it is also appreciated as a brass, double bass, and guitar amp microphone. Neumann manufactured the between 1969 and 1986 and reissued it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tektronix
Tektronix, Inc., historically widely known as Tek, is an American company best known for manufacturing test and measurement devices such as oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and video and mobile test protocol equipment. Originally an independent company, it is now a subsidiary of Fortive, a Corporate spin-off, spinoff from Danaher Corporation. History 1946–1954 The company traces its roots to the electronics revolution that immediately followed World War II. It was founded in December 1945 as Tekrad. The name was similar to that of a California company, Techrad, so in 1946, the four partners, Howard Vollum, Melvin Jack Murdock, Jack Murdock and Miles Tippery, who had both served in the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard, and accountant Glenn McDowell, formed Tektronix, Inc. Each contributed an initial $2,600 for equal shares. Howard Vollum had graduated in 1936 from Reed College with a degree in physics and a keen interest in oscilloscopes, then worked as a radio tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve RF Amplifier
A valve RF amplifier ( UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.) is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal. Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs. Valve characteristics Valves are high voltage / low current devices in comparison with transistors. Tetrode and pentode valves have very flat anode current vs. anode voltage indicating high anode output impedances. Triodes show a stronger relationship between anode voltage and anode current. The high working voltage makes them well suited for radio transmitters and valves remain in use today for very high power short wave radio transmitter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anode
An anode usually is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, which is usually an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ACID, for "anode current into device". The direction of conventional current (the flow of positive charges) in a circuit is opposite to the direction of electron flow, so (negatively charged) electrons flow from the anode of a galvanic cell, into an outside or external circuit connected to the cell. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a "+" is the cathode (while discharging). In both a galvanic cell and an electrolytic cell, the anode is the electrode at which the oxidation reaction occurs. In a galvanic cell the anode is the wire or plate having excess negative charge as a result of the oxidation reaction. In an electrolytic cell, the anode is the wire or plate upon which excess positive charge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Oscillator
In electronics, the term local oscillator (LO) refers to an electronic oscillator when used in conjunction with a Frequency mixer, mixer to change the frequency of a signal. This frequency conversion process, also called Heterodyne, heterodyning, produces the sum and difference frequencies from the frequency of the local oscillator and frequency of the input signal. Processing a signal at a fixed frequency gives a radio receiver improved performance. In many receivers, the function of local oscillator and mixer is combined in one stage called a "Pentagrid converter, converter" - this reduces the space, cost, and power consumption by combining both functions into one active device. The term ''local'' refers to the fact that the frequency is generated within the circuit and is not reliant on any external signals, although the frequency of the oscillator may be tuned according to external signals. Applications Local oscillators are used in the superheterodyne receiver, the most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
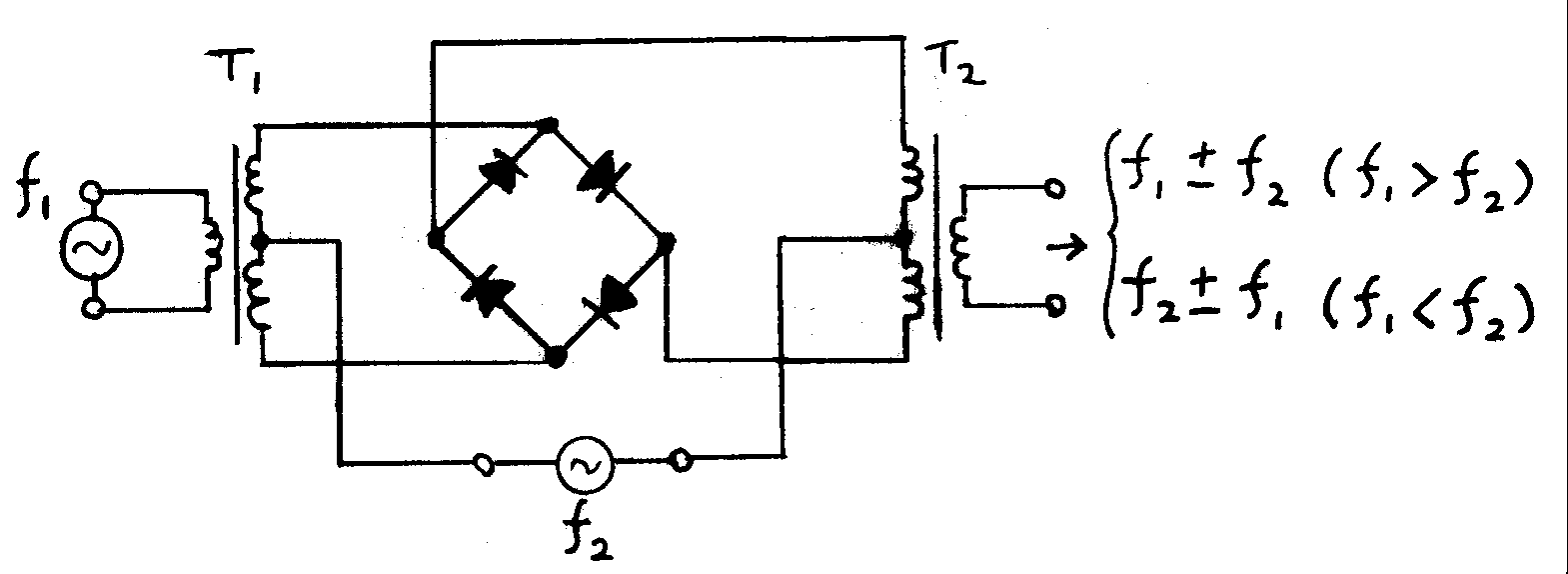
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulation, modulate a carrier signal in Transmitter, radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |