|
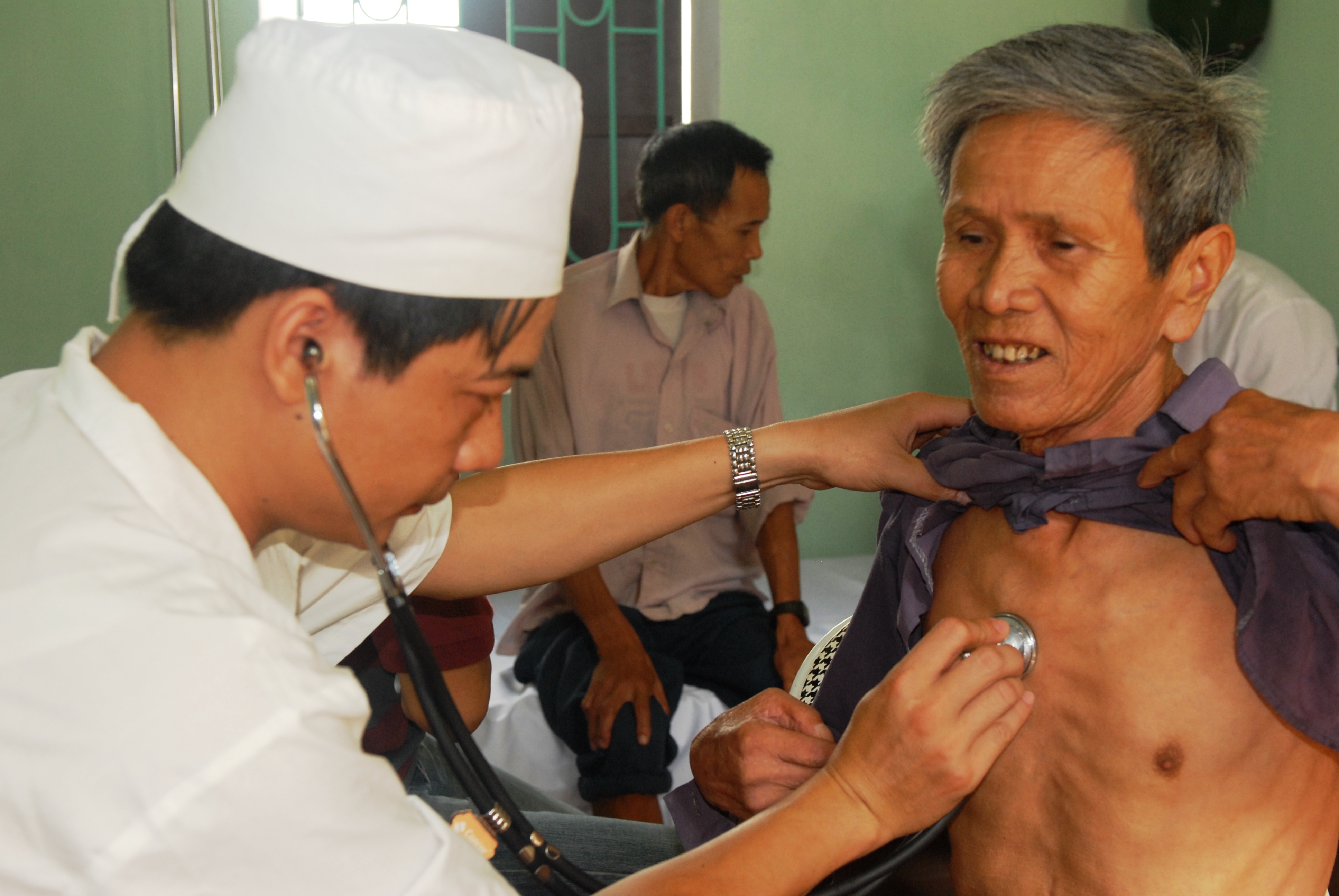
Nursing Assessment
Nursing assessment is the gathering of information about a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual status by a licensed Registered Nurse. Nursing assessment is the first step in the nursing process. A section of the nursing assessment may be delegated to certified nurses aides. Vitals and EKG's may be delegated to certified nurses aides or nursing techs. (Nurse Journal, 2017) It differs from a medical diagnosis. In some instances, the nursing assessment is very broad in scope and in other cases it may focus on one body system or mental health. Nursing assessment is used to identify current and future patient care needs. It incorporates the recognition of normal versus abnormal body physiology. Prompt recognition of pertinent changes along with the skill of critical thinking allows the nurse to identify and prioritize appropriate interventions. An assessment format may already be in place to be used at specific facilities and in specific circumstances. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by Health professional, healthcare professionals. The patient is most often Disease, ill or Major trauma, injured and in need of therapy, treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care provider. Etymology The word wikt:patient, patient originally meant 'one who suffers'. This English noun comes from the Latin word , the present participle of the deponent verb, , meaning , and akin to the Ancient Greek, Greek verb ( ) and its cognate noun (). This language has been construed as meaning that the role of patients is to passively accept and tolerate the suffering and treatments prescribed by the healthcare providers, without engaging in Shared decision-making in medicine, shared decision-making about their care. Outpatients and inpatients An outpatient (or out-patient) is a patient who attends an Outpatient clinic (hospital department), outpatient clinic with no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body. The human musculoskeletal system is made up of the bones of the skeleton, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, joints, and other connective tissue that supports and binds tissues and organs together. The musculoskeletal system's primary functions include supporting the body, allowing motion, and protecting vital organs. The skeletal portion of the system serves as the main storage system for calcium and phosphorus and contains critical components of the hematopoietic system. This system describes how bones are connected to other bones and muscle fibers via connective tissue such as tendons and ligaments. The bones provide stability to the body. Muscles keep bones in place and also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute. Measurement The respiratory rate in humans is measured by counting the number of breaths for one minute through counting how many times the chest rises. A fibre-optic breath rate sensor can be used for monitoring patients during a magnetic resonance imaging scan. Respiration rates may increase with fever, illness, or other medical conditions. Inaccuracies in respiratory measurement have been reported in the literature. One study compared respiratory rate counted using a 90-second count period, to a full minute, and found significant differences in the rates.. Another study found that rapid respiratory rates in babies, counted using a stethoscope, were 60–80% higher than those counted from beside the cot without the aid of the stethoscope. Similar results are seen with animals when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse
In medicine, the pulse refers to the rhythmic pulsations (expansion and contraction) of an artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be felt ( palpated) in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body close to the skin, such as at the neck ( carotid artery), wrist (radial artery or ulnar artery), at the groin (femoral artery), behind the knee ( popliteal artery), near the ankle joint ( posterior tibial artery), and on foot (dorsalis pedis artery). The pulse is most commonly measured at the wrist or neck for adults and at the brachial artery (inner upper arm between the shoulder and elbow) for infants and very young children. A sphygmograph is an instrument for measuring the pulse. Physiology Claudius Galen was perhaps the first physiologist to describe the pulse. The pulse is an expedient tactile method of determination of systolic blood pressure to a trained observer. Diastolic blood pressure is non-palpable and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion (medicine)
Percussion is a technique of clinical examination. Overview Percussion is a method of tapping on a surface to determine the underlying structures, and is used in clinical examinations to assess the condition of the thorax or abdomen. It is one of the four methods of clinical examination, together with inspection, palpation, auscultation, and inquiry. It is done with the middle finger of one hand tapping on the middle finger of the other hand using a wrist action. The nonstriking finger (known as the pleximeter) is placed firmly on the body over tissue. When percussing boney areas such as the clavicle, the pleximeter can be omitted and the bone is tapped directly such as when percussing an apical cavitary lung lesion typical of tuberculosis. There are two types of percussion: direct, which uses only one or two fingers; and indirect, which uses only the middle/flexor finger. Broadly classifying, there are four types of percussion sounds: resonant, hyper-resonant, stony dull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and respiratory systems (heart sounds, heart and breath sounds), as well as the alimentary canal. The term was introduced by René Laennec. The act of listening to body sounds for diagnostic purposes has its origin further back in history, possibly as early as Ancient Egypt. Auscultation and palpation go together in physical examination and are alike in that both have ancient roots, both require skill, and both are still important today. Laënnec's contributions were refining the procedure, linking sounds with specific pathological changes in the chest, and inventing a suitable instrument (the stethoscope) to mediate between the patient's body and the clinician's ear. Auscultation is a skill that requires substantial clinical experience, a fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location (for example, a veterinarian can feel the stomach of a pregnant animal to ensure good health and successful delivery). Palpation is an important part of the physical examination; the somatosensory system, sense of touch is just as important in this examination as the visual perception, sense of sight is. Physicians develop great skill in palpating problems below the surface of the body, becoming able to detect things that untrained persons would not. Mastery of anatomy and much practice (learning method), practice are required to achieve a high level of skill. The concept of being able to detect or notice subtle tactile medical sign, signs and to recognize their significance or implications is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertigo (medical)
Vertigo is a condition in which a person has the sensation that they are moving, or that objects around them are moving, when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. It may be associated with nausea, vomiting, perspiration, or difficulties walking. It is typically worse when the head is moved. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. The most common disorders that result in vertigo are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), Ménière's disease, and vestibular neuritis. Less common causes include stroke, brain tumors, brain injury, multiple sclerosis, migraines, trauma, and uneven pressures between the middle ears. Physiologic vertigo may occur following being exposed to motion for a prolonged period such as when on a ship or simply following spinning with the eyes closed. Other causes may include toxin exposures such as to carbon monoxide, alcohol, or aspirin. Vertigo typically indicates a problem in a part of the vestibular system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |