|
Nur Ahmed Aman
Sultan Nur Ahmed Aman (; (1841–1907); Somali nickname Nuur Dheere), was a learned religious leader and the 5th Sultan of the Habr Yunis Sultanate and later also one of the leaders behind the Dervish movement (Somali), Somali Dervish movement and Somaliland campaign, revolt (1899–1920). He was the principal agitator rallying the followers of the Kob Fardod Tariqa behind his anti- French Roman Catholic missions, Catholic Mission campaign that would become the cause of the Dervish uprising. He assisted in assembling men and arms and hosted the revolting tribesmen in his quarter at Burao in August 1899, declaring the Dervish rebellion. He fought and led the war throughout the years 1899–1904. He and his brother Geleh Ahmed (Kila Ahmed) were the main signatories of the Dervish peace treaty with the British, Ethiopians and Italian colonial powers on March 5, 1905, known as the Ilig Treaty or the Pestalozza agreement. Sultan Nur is entombed in a white-domed shrine in Taleh, the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), though both refer to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei, Malaysia and Oman are the only sovereign states which retain the title "sultan" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hahi
Hahi (, ), is a town in Oodweyne District located in western Togdheer, Somaliland. History Hahi started as a permanent well for pastoralists and became a settlement. In the 19th century, members of the Sufi Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism. Practitioners of Sufism are r ... order Dandarawiyah would establish a tariqa and jama'a (congregation) at the town. The order was founded by Sayid Mohamed al Dandarawi who was a student of Ibrahim al Rashid and their teachings spread from Arabia to Sudan before eventually reaching Somaliland via the Somali Sheikh Sayid Aadan Ahmed. It would spread to Sheikh, Somaliland, Sheikh although it remained much smaller than the established Qadiriyya or Salihiyya orders. A young Nur Ahmed Aman, Nur Ahmed would study in the tariqa of Hahi before a succession crisis would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somali Literature
Somali literature is the literature used by the ethnic Somalis of Somalia, Somaliland, Djibouti, Yemen, Eritrea, Ogadenia, and Kenya. Somali poetry Nation of Bards Due to the Somali people's passionate love for and facility with poetry, Somalia has also been called by, among others, the Canadian novelist and scholar Margaret Laurence, a "Nation of Poets" and a "Nation of Bards". The 19th-century British explorer Richard Francis Burton, who visited the Somali Peninsula, similarly recounts in his book ''First Footsteps in East Africa'' how: According to Canadian novelist and scholar Margaret Laurence, who originally coined the term "Nation of Poets" to describe the Somali Peninsular, the Eidagale sub-section of the Garhajis clan were viewed as "the recognized experts in the composition of poetry" by their fellow Somali contemporaries: Structure Somali poetry features obligatory alliteration, similar in some respects to the requirements of Germanic alliterative verse. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habr Je'lo
The Habr Je'lo (), , Full Name: ''Mūsa ibn ash-Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad,'' historically known as the Habr Toljaala () is a major Northern Somali clan of the wider Isaaq family. Its members form the Habr Habusheed () confederation along with the Imran, Sanbur and Tolje’lo. The Habr Je'lo are divided into five further sub-tribes: the Mohamed Abokor, Musa Abokor, Samane Abokor, Reer dood and Omar. Historically, the Mohamed Abokor, Samane Abokor and Reer Dood are chiefly nomadic pastoralists, whereas the Musa Abokor and Omar obtained much of their wealth via their frankincense plantations in the mountainous interior adjacent to the coastline. The Habr Je'lo played a prominent role in the livestock and frankincense trade during the pre-colonial period. The Habr Je'lo also partook in a major organised front to oppose British rule in the late 19th and early 20th centuries under the leadership of Haji Sudi, Sheikh Bashir, Haji Farah Omar, Michael Mariano and other subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
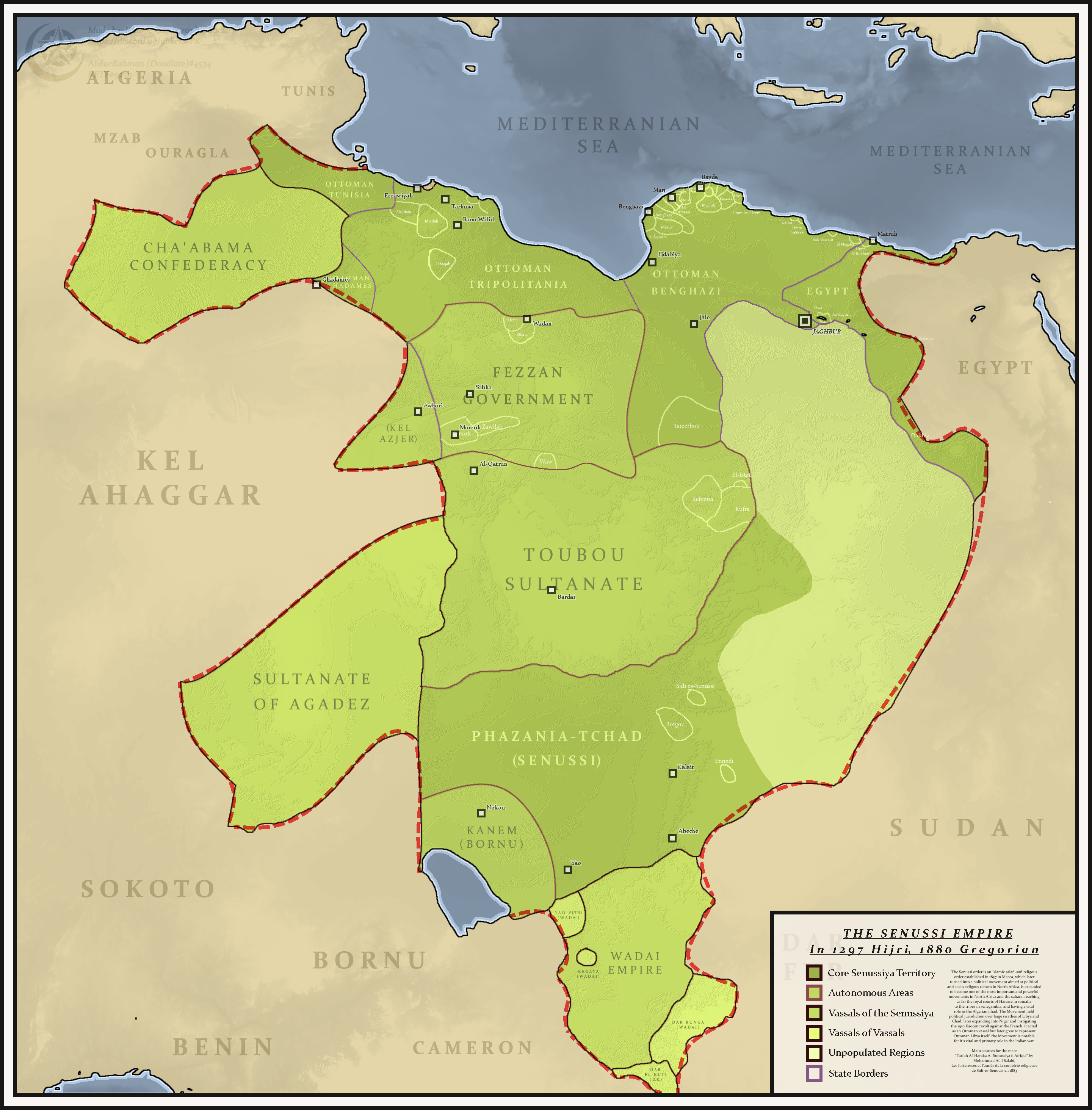
Senussi
The Senusiyya, Senussi or Sanusi () are a Muslim political-religious Sufi order and clan in Libya and surrounding regions founded in Mecca in 1837 by the Grand Sanussi ( ''as-Sanūssiyy al-Kabīr''), the Algerian Muhammad ibn Ali al-Sanusi. During World War I the Senussis fought against both Italy and Britain. During World War II, the Senussis provided support to the British Eighth Army in North Africa against Nazi and Fascist Italian forces. The Grand Senussi's grandson became King Idris I of Libya in 1951. The 1969 Libyan revolution led by Muammar Gaddafi overthrew him, ending the Libyan monarchy. The movement remained active despite sustained persecution by Gaddafi's government. The Senussi spirit and legacy continue to be prominent in today's Libya, mostly in Cyrenaica. History Beginnings: 1787–1859 The Senussi order has been historically closed to Europeans and outsiders, leading reports of their beliefs and practices to vary immensely. Though it is possible to ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ahmad
Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah bin Fahal (; 12 August 1843 – 21 June 1885) was a Sudanese religious and political leader. In 1881, he claimed to be the Mahdi and led a war against Egyptian rule in Sudan, which culminated in a remarkable victory over them in the Siege of Khartoum. He created a vast Islamic state extending from the Red Sea to Central Africa and founded a movement that remained influential in Sudan a century later. From his announcement of the Mahdist State in June 1881 until its end in 1898, Holt, P.M.: "The Mahdist State in Sudan, 1881–1898". Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1970. p. 45. the Mahdi's supporters, the Ansār, established many of its theological and political doctrines. After Muhammad Ahmad's unexpected death from typhus on 22 June 1885, his chief deputy, Abdallahi ibn Muhammad took over the administration of the nascent Mahdist State. The Mahdist State, weakened by his successor's autocratic rule and inability to unify the populace to resist the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haji Guled Center 1906
Hajji (; sometimes spelled Hajjeh, Hadji, Haji, Alhaji, Al-Hadj, Al-Haj or El-Hajj) is an honorific title which is given to a Muslim who has successfully completed the Hajj to Mecca. Etymology ''Hajji'' is derived from the Arabic ' (), which is the active participle of the verb ' ('to make the pilgrimage'; ). The alternative form ' is derived from the name of the Hajj with the adjectival suffix -''ī'' (), and this was the form adopted by non-Arabic languages. Use ''Hajji'' and its variant spellings are used as honorific titles for Muslims who have successfully completed the Hajj to Mecca. In Arab countries, ' and ' (pronunciation varies by Arabic dialect) is a commonly used manner of addressing any older person respectfully if they have performed the pilgrimage. It is often used to refer to an elder, since it can take years to accumulate the wealth to fund the travel (particularly before commercial air travel), and in many Muslim societies to a respected man as an honorific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luigi Robecchi Bricchetti
Luigi Robecchi Bricchetti (21 May 1855 – 31 May 1926) was an Italian explorer, geographer, cartographer and naturalist. Biography Robecchi Bricchetti was the illegitimate son of Ercole Robecchi, a land owner from Zerbolò, and a young seamstress, Teresa Brichetti. He grew up with his mother and used her name until his father recognized the paternity after a lengthy legal battle. In 1874 Luigi changed his family name to Robecchi Bricchetti.Perna, Alessandro Luigi (2014)"''L'avventura africana di Robecchi Bricchetti, il più grande esploratore italiano del Corno d'Africa''"''L'Huffington Post''. 03 July 2014. (in Italian). Robecchi Bricchetti enrolled at the faculty of Civil Engineering at the University of Pavia and then continued his education at the University of Zurich and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, where he eventually graduated.Exhibit "''Un esploratore pavese in Africa - Le collezioni zoologiche di Luigi Robecchi Bricchetti al Museo di Storia Naturale di Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guled Haji
Guled Haji (; 1820s–1907) was a Somali sage and the ''Aqil'' or leader of the Baha Sugule branch of the powerful Rer Ainanshe Habr Yunis. The Rer Ainashe are the traditional rulers of the Habr Yunis Sultanate. Biography Guled had completed the Hajj pilgrimage to Makkah and adopted the honorific ''Hajji'' title and was referred to as such rather than his full name. He was a grandson of the first Sultan of the Habr Yunis Sugulleh Ainashe. According to Italian explorer Enrico Baudi i Vesme, who visited Burao in 1889, Guled Haji was a prominent chief of Burao ranking second only to Sultan Awad Deria. Guled Haji has a town named after him in the Oodweyne district of Togdheer. Proverbs Guled was known for his wise speech and proverbs and he gave birth to hundreds of them in the Somali language and some are still used in the present day. what one needs for survival ( water inst.) is imperative no matter how far/hard one has to labour. a worthwhile endeavour regardless of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idrisiyya
The Idrisiyya order () is a Sufi order of Sunni Islam founded by Ahmad ibn Idris al-Fasi. It is also called the Tariqa Muhammadiyya, and it rejects following any of the four schools of Islamic jurisprudence (''taqlid''),Scott Alan Kugle, ''Sufis & Saints' Bodies: Mysticism, Corporeality, & Sacred Power'', 2007, ISBN 080783081X, p. 269-270 adopting the same methodology as Ismail Dehlavi, who remarked that the agenda of the new order known as Tariqa Muhammadiyya was to purify Islam and reject what they deemed to be ''bid'ah'' or ''shirk''.Past present: When history fails Dawn (newspaper), Published 3 March 2012, Retrieved 16 August 2018Dajani, Samer, Reassurance for the Seeker, p. 14. It is not a ''tariqa'' in the sense of an organized Sufi order, but rather a methodology, consisting of a set of beliefs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |