|
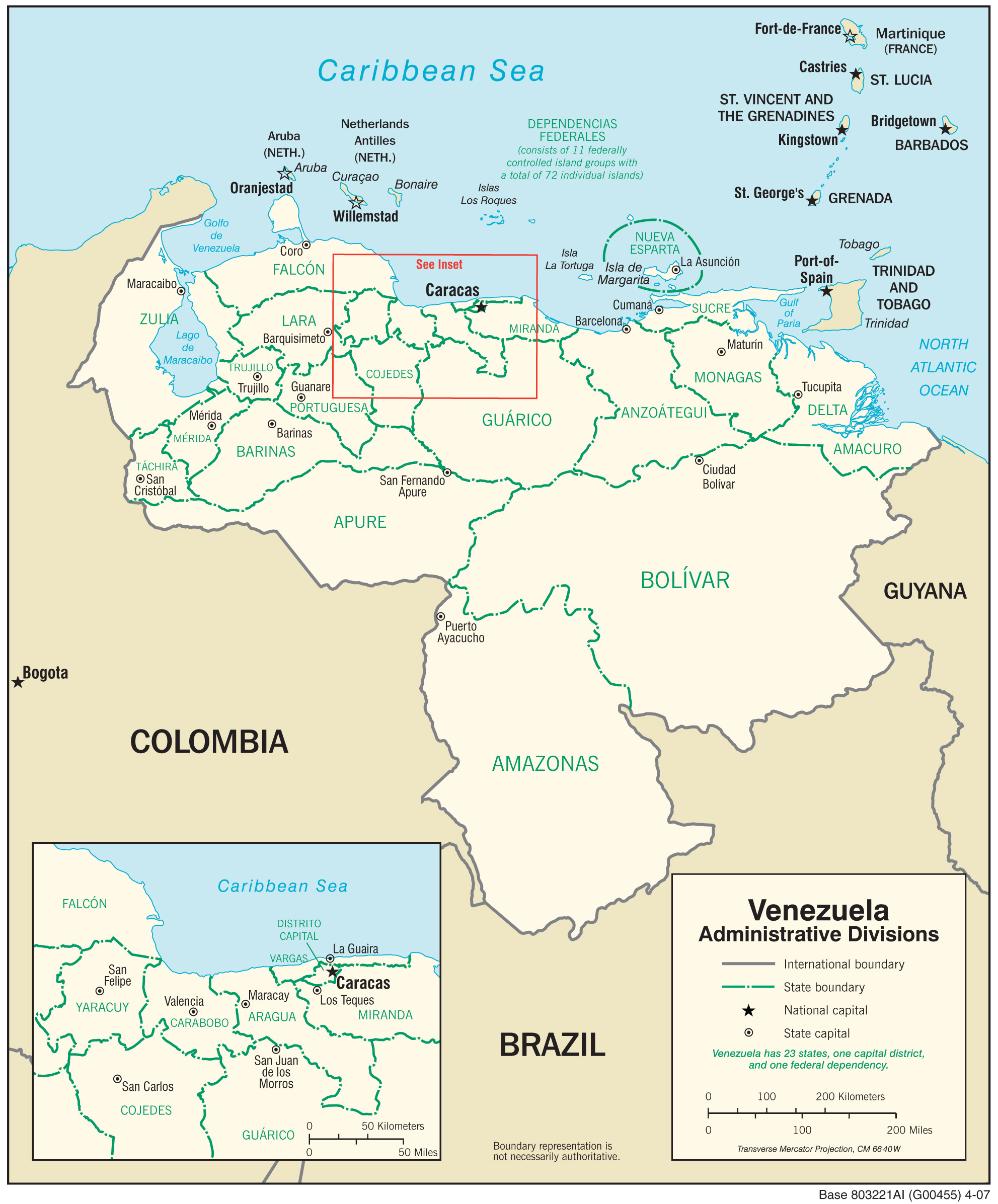
Nueva Esparta State
The Nueva Esparta State (in Spanish: ''Estado Nueva Esparta'', ) is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. It comprises Margarita Island, Coche, and the lightly inhabited Cubagua. The state is located off the northeast Caribbean coast of Venezuela. The main island of Margarita has an area of . Its capital city is La Asunción, and the main urban center is Porlamar. Etymology Its name, Nueva Esparta ("''New Sparta"''), comes from the heroism shown by its inhabitants during the Venezuelan War of Independence, deemed similar to that of the Spartan soldiers of Ancient Greece. History Spanish colonization Margarita was discovered on August 15, 1498, during Columbus' third voyage. On that trip the Admiral would also discover mainland Venezuela. That day, Columbus saw three islands, two of them small, low and arid (the current Coche and Cubagua), separated by a channel from a third, larger one, covered with vegetation and populated by indigenous people who called it ''Paraguachoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of Venezuela
The Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela is a federation made up of twenty-three states ('), a Capital District (Venezuela), Capital District (') and the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, Federal Dependencies ('), which consist of many List of islands of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. Venezuela claims the Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute, disputed Essequibo territory as one of its states, which it calls Guayana Esequiba, but the territory is controlled by Guyana as part of six of its Regions of Guyana, regions. The states and territories of Venezuela are usually organized into Regions of Venezuela, regions (), although these regions are mostly geographical entities rather than administrative entities. Historical states Prior to the Federal War (1859–1863), the country was divided into provinces rather than states (see Provinces of Venezuela). The victorious forces were supposed to grant more autonomy to the individual states, but this w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous List of Caribbean islands, islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo Municipalities of Quintana Roo#Municipalities, islands and Districts of Belize#List, Belizean List of islands of Belize, islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands Department#Islands, Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the Mainland, continental mainland of the Americas bordering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, and vessels used for piracy are called pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples of such areas include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Corsairs
Corsairs () were privateers, authorised to conduct raids on shipping of a foreign state at war with the Kingdom of France, on behalf of the French crown. Seized vessels and cargo were sold at auction, with the corsair captain entitled to a portion of the proceeds. Although not History of the French Navy, French Navy personnel, corsairs were considered legitimate combatants in France (and allied nations), provided the commanding officer of the vessel was in possession of a valid letter of marque ( or , the latter giving ''corsairs'' their name), and the officers and crew conducted themselves according to contemporary admiralty law. By acting on behalf of the French Crown, if captured by the enemy, they could in principle claim treatment as prisoners of war, instead of being considered pirates. Because corsairs gained a swashbuckling reputation, the word "corsair" is also used generically as a more romantic or flamboyant way of referring to privateers, or even to pirates. The Barbar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumaná
Cumaná () is the capital city of Venezuela's Sucre State. It is located east of Caracas. Cumaná was one of the first cities founded by Spain in the mainland Americas and is the oldest continuously-inhabited Hispanic-established city in South America. Its early history includes several successful counters by the indigenous people of the area who were attempting to prevent Spanish incursion into their land, resulting in the city being refounded several times. The municipality of Sucre, which includes the capital city, Cumaná, had a population of 358,919 at the 2011 Census; the latest estimate (as at mid 2016) is 423,546. The city is located at the mouth of the Manzanares River on the Caribbean coast, in the northeast of Venezuela. It is home to first and most important of the five campuses of the Universidad de Oriente, and is a busy maritime port, home of one of the largest tuna fleets in Venezuela. The city is close to Mochima National Park, whose beaches are a popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nueva Cádiz
Nueva Cádiz is an archaeological site and former port town on Cubagua, off the coast of Venezuela. First established in 1500 as a seasonal settlement, by 1515 it had become a year-round permanent town. it was one of the first European settlements in the Americas. The settlement was given the name Nueva Cádiz when it was incorporated as a city in 1528. History As early as 1502, rancherías were established on Cubagua, occupied for 3–4 months each year during trading. The island was of particular interest because of its rich pearl oyster beds. Eventually, the settlement became permanent and, by 1520, after the great Indian uprising, its resident population surpassed 300. On September 12, 1528 by a royal decree issued by Charles V, Nueva Cádiz was incorporated and became a city named Nueva Cádiz. It became the first Spanish town in South America. By 1530 Nueva Cádiz had a population of 223 Europeans and 700 natives. At its peak (around 1535), it had over 1500 people. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonzalo Fernández De Oviedo Y Valdés
Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés (August 1478 – 1557), commonly known as Oviedo, was a Spanish soldier, historian, writer, botanist and colonist. Oviedo participated in the Spanish colonization of the West Indies, arriving in the first few years after Christopher Columbus became the first European to arrive at the islands in 1492. Oviedo's chronicle ''Historia general de las Indias'', published in 1535 to expand on his 1526 summary ''La Natural hystoria de las Indias'' (collectively reprinted, three centuries after his death, as ''Historia general y natural de las Indias''), forms one of the few primary sources about it. Portions of the original text were widely read in the 16th century in Spanish, English, Italian and French editions, and introduced Europeans to the hammock, the pineapple, and tobacco as well as creating influential representations of the colonized peoples of the region. Early life Oviedo was born in Madrid of an Asturian lineage and educated in the cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Alonso Niño
Pedro Alonso Niño (c. 1455 – c. 1505) was known in his time as Peralonso Niño, he was a Spanish navigator and discoverer. He piloted the '' Santa María'' during Christopher Columbus's first voyage to the Americas in 1492, and accompanied him on his second voyage in 1493. Biography Niño was born in Moguer, Spain. His father was Alfon Perez Niño, a Spanish sailor. Pedro Alonso Niño was married twice, to Juana Muñiz and Leonor de Boria, and sired four children, namely Juan Niño, Francisco Niño, Isabel Quintero and Leonor Fernández. He was nicknamed "''El negro''" for his involvement in the African slave trade. He explored the west coast of Africa in his early years and many other places. Niño guided Columbus and navigated the Atlantic Ocean as he piloted the '' Santa María'' during Christopher Columbus's expedition of 1492,Alice Bache Gould, Nueva Lista Documentada De Los Tripulantes De Colon En 1492, ''Boletin de la Real Academia de la Historia'', Tomo CLXX, Nú ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbus Voyages
Between 1492 and 1504, the Italian explorer and navigator Christopher Columbus led four transatlantic crossing, transatlantic maritime expeditions in the name of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain to the Caribbean and to Central and South America. These voyages led to the widespread knowledge of the New World. This breakthrough inaugurated the period known as the Age of Exploration, which saw the colonization of the Americas, a related Columbian exchange, biological exchange, and trans-Atlantic trade. These events, the effects and consequences of which persist to the present, are often cited as the beginning of the modern era. Born in the Republic of Genoa, Columbus was a navigator who sailed in search of a westward route to India, China, Japan and the Maluku Islands, Spice Islands thought to be the East Asian source of Spice trade, spices and other precious oriental goods obtainable only through arduous Silk Road, overland routes. Columbus was partly inspired by 13th-century Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |