|
Nuclear Cratering Group
The United States Army Corps of Engineers Nuclear Cratering Group (NCG) was an organization within the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), located at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, which was involved in research on the potential uses and effects of nuclear devices for large-scale excavation and quarrying. The group's activities were focused on research for practical applications of nuclear devices, some of which were proposed for the Atomic Energy Commission's (AEC) Project Plowshare program for peaceful nuclear explosions. In particular, the NCG was directed to study excavation techniques for a sea-level canal across the Isthmus of Panama. The Nuclear Cratering Group was established in 1962. It was reorganized as the Explosive Excavation Research Laboratory under the Waterways Experiment Station in 1971. History The joint USACE/AEC program was established in May 1962 by Presidential directive, with the stated purpose of studying the use of nuclear explosive devices to aid i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart Dam
The Rampart Dam or Rampart Canyon Dam was a project proposed in 1954 by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to dam the Yukon River in Alaska for Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power. The project was planned for Rampart Canyon (also known as Rampart Gorge) just southwest of the village of Rampart, Alaska, about west-northwest of Fairbanks. The resulting dam would have created a lake roughly the size of Lake Erie, making it the largest human-made reservoir in the world. The plan for the dam itself called for a concrete structure high with a top length of about . The proposed power facilities would have consistently generated between 3.5 and 5.0gigawatts of electricity, based on the flow of the river as it differs between winter and summer. Though supported by many politicians and businesses in Alaska, the project was canceled after objections were raised. Alaska Natives, Native Alaskans in the area protested the threatened loss of nine villages that would be flooded by the dam. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Radiation Laboratory
Lawrence may refer to: Education Colleges and universities * Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States * Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States Preparatory & high schools * Lawrence Academy at Groton, a preparatory school in Groton, Massachusetts, United States * Lawrence College, Ghora Gali, a high school in Pakistan * Lawrence School, Lovedale, a high school in India * The Lawrence School, Sanawar, a high school in India Research laboratories * Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, United States * Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, United States People * Lawrence (given name), including a list of people with the name * Lawrence (surname), including a list of people with the name * Lawrence (band), an American soul-pop group * Lawrence (judge royal) (died after 1180), Hungarian nobleman, Judge royal 1164–1172 * Lawrence (musician), Lawrence Hayward (born 1961), British musi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ka Lae
Ka Lae (), also known as South Point, is the southernmost point of the Hawaii (island), Big Island of Hawaii and Extreme points of the United States, of the 50 United States. The Ka Lae area is registered as a National Historic Landmark, National Historic Landmark District under the name South Point Complex. The area is also known for its strong ocean currents and winds and is the home of a wind farm. Geography The name for the southern tip of the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii comes from ''Ka Lae'' in the Hawaiian language which means "the point". It is often spelled as one word, Kalae, or called South Point or South Cape. A confluence of ocean currents just offshore makes this spot one of Hawaii's most popular fishing spots. Both Red snapper (fish), red snapper and Giant trevally, ulua are plentiful here. Locals fish from the cliffs, some dangling perilously over the edge of steep lava ledges. Swimming here, however, is not recommended, due to the current. In fact, it is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty Island
Admiralty Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago in Southeast Alaska. It is long and wide with an area of , making it the seventh-largest island in the United States and the 132nd largest island in the world. It is one of the ABC islands in Alaska. The island is nearly cut in two by the Seymour Canal; to its east is the long, narrow Glass Peninsula. Most of Admiralty Island—955,747 acres (3,868 km2)—is protected as the Admiralty Island National Monument administered by the Tongass National Forest. The Kootznoowoo Wilderness encompasses vast stands of old-growth temperate rainforest. These forests provide some of the best habitat available to species such as brown bears, bald eagles, and Sitka black-tailed deer. Angoon, a traditional Tlingit community home to 572 people, is the only settlement on the island, although an unpopulated section of the city of Juneau comprises (6.2 percent) of the island's land area near its northern end. The island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaquina Bay
Yaquina Bay ( ) is a coastal Estuary, estuarine community found in Newport, Oregon. Yaquina Bay is a semi-enclosed body of water, approximately 8 km2 (3.2 mi2) in area, with free connection to the Pacific Ocean, but also diluted with freshwater from the Yaquina River land drainage. The Bay is traversed by the Yaquina Bay Bridge. Two small cities border the Yaquina River and Bay: Newport (population approx. 9,989), and Toledo, Oregon, Toledo (population approx. 3,459). The Yaquina Bay in Newport is a popular tourist destination along the Pacific Coast Highway. It is also an important estuary for the area's ecology and economy. History Yaquina Bay is named after the Yaquina people, Yaquina Tribe that occupied the territory along the Yaquina River. When the railroad came to the area in the late 1880s, many thought Yaquina Bay would be the commerce center for the Pacific Northwest. Wheat, lumber, and other goods were transported to Yaquina Bay as the area began to develop. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketchikan, Alaska
Ketchikan ( ; ) is a city in and the borough seat of the Ketchikan Gateway Borough on Revillagigedo Island of Alaska. It is the state's southeasternmost major settlement. Downtown Ketchikan is a National Historic Landmark District. With a population at the 2020 census of 8,192, up from 8,050 in 2010, it is the sixth-most populous city in the state, and thirteenth-most populous community when census-designated places are included. The surrounding borough, encompassing suburbs both north and south of the city along the Tongass Highway (most of which are commonly regarded as a part of Ketchikan, albeit not a part of the city itself), plus small rural settlements accessible mostly by water, registered a population of 13,948 in that same census. Incorporated on August 25, 1900, Ketchikan is the earliest extant incorporated city in Alaska, because consolidation or unification elsewhere in Alaska resulted in the dissolution of those communities' city governments. Ketchikan is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetta Inlet
Hetta Inlet is a deep embayment in the southwestern coast of Prince of Wales Island in the U.S. state of Alaska. It connects with the Pacific Ocean through Cordova Bay. The head of the inlet is separated by a divide from the West Arm of Cholmondeley Sound. The shores are abrupt from the water's edge, and the channels and inlets are deep. The precipitation is probably a little greater than at Ketchikan, and the mean annual temperature is slightly higher. The white crystalline limestone of the Wales series, striking nearly north and south, is the predominant country rock of Hetta Inlet. In it are intruded many igneous rocks, some schistose, some massive. The white limestones are closely folded and have great variation in dip. The igneous rocks, so far as determined from the small collection made, include gabbros, diorites, amphibolites, diabases, and pyroxene-syenites. All these are comparatively massive. The greenstoneschists, which occupy considerable areas, are chloritic. The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholmondeley Sound
Cholmondeley Sound is a deep bay or inlet on the southeast side of Prince of Wales Island, in the Alexander Archipelago of southeast Alaska, in Tongass National Forest and connecting to Clarence Strait. The sound's entrance lies between Chasina Point and Skin Island. It is about west of Ketchikan, Alaska. Cholmondeley Sound has several bays and inlets within it, including Kitkun Bay, Dora Bay, Brennan Bay, and Sunny Cove. At its western end Cholmondeley Sound splits into two fjord-like inlets: West Arm Chomondeley Sound, about long, and South Arm Cholmondeley Sound, about long. The full length from the entrance of the sound to the head of West Arm is about . Cholmondeley Sound and its several arms are all deep, with steep and heavily forested shorelines. Cholmondeley Sound was named by George Vancouver on 21 August 1793, for George Cholmondeley, The Earl of Cholmondeley. There was once a Haida summer village, known as Chatchini or Chat-chee-ni, used by the Kaigani Haida of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gila River
The Gila River (; O'odham ima Keli Akimel or simply Akimel, Quechan: Haa Siʼil, Maricopa language: Xiil) is a tributary of the Colorado River flowing through New Mexico and Arizona in the United States. The river drains an arid watershed of nearly that lies mostly within the U.S., but also extends into northern Sonora, Mexico. Indigenous peoples have lived along the river for at least 2,000 years, establishing complex agricultural societies before European exploration of the region began in the 16th century. European Americans did not permanently settle the Gila River watershed until the mid-19th century. During the 20th century, development in the Gila River watershed prompted the construction of large diversion and flood control structures on the river and its tributaries, and consequently the Gila contributes only a small fraction of its historic flow to the Colorado. The historic natural discharge of the river was around , but has declined to only . The engineering pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
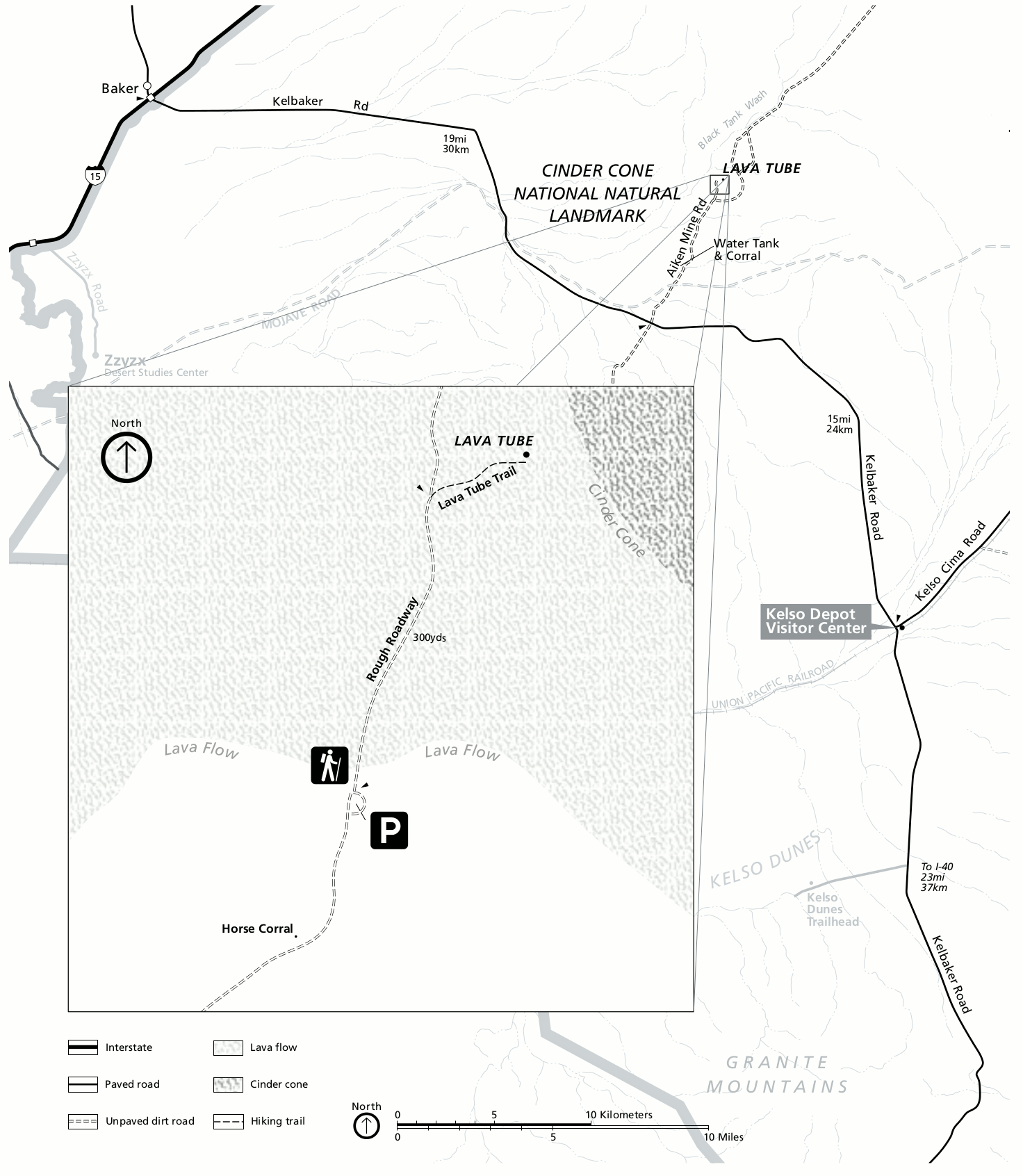
Cima Dome
Cima volcanic field is a volcanic field in San Bernardino County, California, close to the border with Nevada. The volcanic field covers a surface area of within the Mojave National Preserve west of the Cima Dome and consists of about 40 volcanic cones with about 60 lava flows. The volcanic cones range from simple cones over multi-cratered mountains to eroded hills, and lava flows are up to long. At least one lava tube exists in the field and can be visited. Volcanic activity in the field commenced in the Late Miocene and after a pause between 3 and 1 million years ago continued into the latest Pleistocene. The youngest cone is known as the Black Tank cone and formed about 15,000 years before present, although it is possible that it was formed through two separate eruption events; formerly it was considered to be of historical age. Geography and geology The Cima volcanic field lies in the eastern Mojave Desert of California, between the Shadow Valley in the northeast, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amchitka Island
Amchitka (; ;) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The island, with a land area of roughly , is about long and wide. The area has a maritime climate, with many storms, and mostly overcast skies. Amchitka was populated for more than 2,500 years by the Aleut people, but has had no permanent population since 1832. The island has been part of the United States since the Alaska Purchase of 1867. During World War II, it was used as an airfield by US forces in the Aleutian Islands Campaign. Amchitka was selected by the United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) to be the site for underground detonations of nuclear weapons. Three such tests were carried out: ''Long Shot'', an blast in 1965; ''Milrow'', a blast in 1969; and ''Cannikin'' in 1971 – at , the largest underground test ever conducted by the United States. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |