|
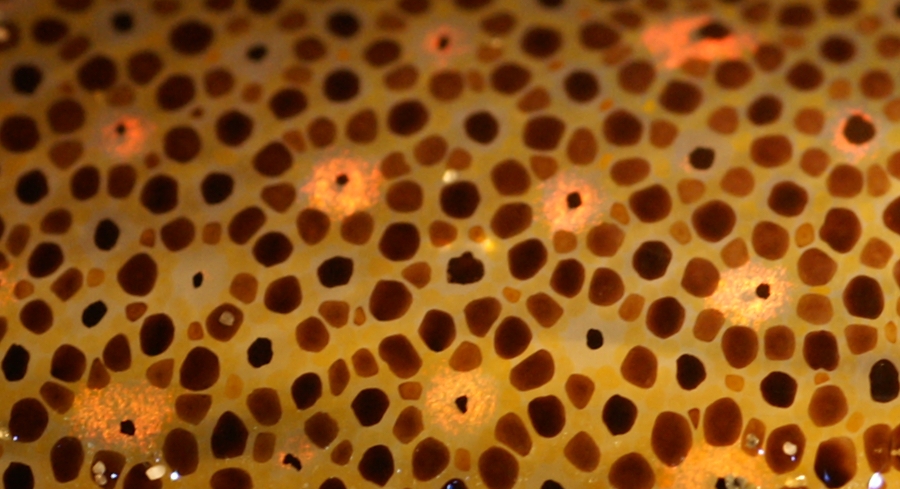
Noturus Albater
The Ozark madtom (''Noturus albater'') is a freshwater fish endemic to the United States. It is one of 29 species of madtom. Description The Ozark madtom has a stout body and small head. A dark bar can be found at the base of the caudal fin, and the caudal fin is usually straight or slightly rounded. The pectoral fin has 9 rays, and the anal fin has 13 to 16 rays. The fish has a total length of 120 mm (4 in). Distribution and habitat The Ozark madtom are found around the upper White River and the Little Red River in the Ozark Uplands in Arkansas and Missouri, United States. The Ozark madtom can by found in riffles and rocky pools, as well as cool, clear, high-gradient creeks and small to medium-sized rivers. They are found in shallow depths (usually of less than half a meter deep) and high velocity currents. During the day, they use the rocky bed bottom as cover. Diet Most of the Ozark madtom's diet consists of aquatic insects, with Diptera (flies) making up a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Fish
Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salinity of less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine conditions in many ways, especially the difference in levels of salinity. To survive fresh water, the fish need a range of physiological adaptations. 41.24% of all known species of fish are found in fresh water. This is primarily due to the rapid speciation that the scattered habitats make possible. When dealing with ponds and lakes, one might use the same basic models of speciation as when studying island biogeography. Physiology Freshwater fish differ physiologically from salt water fish in several respects. Their gills must be able to diffuse dissolved gases while keeping the salts in the body fluids inside. Their scales reduce water diffusion through the skin: freshwater fish that have lost too many scales will die. They also have well developed kidneys to reclaim salts from body fluids before e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myomere
Myomeres are blocks of skeletal muscle tissue arranged in sequence, commonly found in aquatic chordates. Myomeres are separated from adjacent myomeres by connective fascia (myosepta) and most easily seen in larval fishes or in the olm. Myomere counts are sometimes used for identifying specimens, since their number corresponds to the number of vertebrae in the adults. Location varies, with some species containing these only near the tails, while some have them located near the scapular or pelvic girdles. Depending on the species, myomeres could be arranged in an epaxial or hypaxial manner. Hypaxial refers to ventral muscles and related structures while epaxial refers to more dorsal muscles. The horizontal septum divides these two regions in vertebrates from cyclostomes to gnathostomes. In terrestrial chordates, the myomeres become fused as well as indistinct, due to the disappearance of myosepta. Shape The shape of myomeres varies by species. Myomeres are commonly zig-zag, " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1969
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Most fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lernaea
''Lernaea'' is a genus of copepod crustaceans whose members are commonly called ''anchor worms'' and are parasitic on freshwater fishes. Life cycle Anchor worms mate during the last free-swimming (copepodid) stage of development. After mating, the female burrows into the flesh of a fish and transforms into an unsegmented, wormlike form, usually with a portion hanging from the fish's body. Eggs are released from the posterior "tails" (egg sacs) into the water, where they hatch within 24 to 36 hours. The nauplii will go through three stages before molting into copepodids, which associate with fish gills. After a further five stages and mating, the male leaves the host and dies, while the female transitions into the anchored stage (may move to different fish host). Diagnosis Symptoms of anchor worm can be as follows: # Anchor worms (''Lernaea'' sp.) can be seen with the naked eye # Frequent rubbing or "flashing" # Localised redness # Inflammation on the body of the fish # Tiny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilt Darter
The gilt darter (''Percina evides'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It can be found in a number of states in the Mississippi River drainage of the United States although it has been extirpated from some river systems in which it was at one time present, mostly due to siltation and pollution problems. Males are more colorful than females and can grow to a length of about . It is a benthic fish that feeds primarily on small aquatic insect larvae. Males form territories during the breeding season in late spring and early summer. Spawning typically takes place at the upper ends of riffles with sandy and gravelly bottoms interspersed with larger cobbles. Some organisations are endeavouring to conserve populations of the gilt darter and re-introduce it to states where the fish has been extirpated but suitable habitat still exists. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Darter
The rainbow darter (''Etheostoma caeruleum'') is a small species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It is native to North America where it is found in small, fast-moving streams and small to medium-sized rivers. It grows to in length. The species is very sensitive to pollution and silt, staying in clean, pollution-free water. The rainbow darter is easily identified by three dark spots on the back, and blue and orange in the dorsal and anal fins. Life The rainbow darter lives in clean, rocky riffles from March through June. It has a lifespan of about 4 years. The males can grow up to 48 mm long, while the largest female reaches just under 43 mm. The male form is resplendent in bright oranges and iridescent blue spots, stripes, and checks. Distribution The rainbow darter is a small, benthic freshwater fish found in many creeks and small to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding Shiner
The bleeding shiner (''Luxilus zonatus'') is a freshwater ray-finned minnow in the family '' Leuciscidae'', which was recently changed to distinguish between North American and Asian minnows. It occurs in tributaries of Ozark-draining tributaries of the Missouri, and Mississippi rivers in southern Missouri and northeastern Arkansas. Its preferred habitat is rocky and sandy pools and runs of headwaters, creeks and small rivers. Taxonomy Class: Actinopterygii, Order: Cypriniformes, Family: ''Leuciscidae'', Genus: ''Luxilus'', Species: ''L. zonatus''. The bleeding shiner was originally known to be classified as the ''Alburnus zonatus'' by Agassiz in 1863. Formerly known to be in the genus ''Notropis'', but removed and added to the genus ''Luxilus'' in 1989. Originally the now distinct species of ''L. zonatus'' and ''N. Pilsbryi'' were considered to be synonymous, but after carefully observing the morphological evidence they were added to the ''Luxilus'' genus. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly "hue") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference properties. Some species can rapidly change colour through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbel (anatomy)
In fish anatomy and turtle anatomy, a barbel is a slender, whiskerlike sensory organ near the mouth. Fish that have barbels include the catfish, the carp, the goatfish, the hagfish, the sturgeon, the zebrafish, the black dragonfish and some species of shark such as the sawshark. Barbels house the taste buds of such fish and are used to search for food Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ... in murky water. The word "barbel" comes from the Middle Latin ''barbula'', for "little beard." Barbels are sometimes erroneously referred to as '' barbs'', which are found in bird feathers for flight. Barbels may be located in a variety of locations on the head of a fish. "Maxillary barbels" refers to barbels on either side of the mouth. Barbels may also be nasal, exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolk Sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development. In humans The yolk sac is the first element seen within the gestational sac during pregnancy, usually at 3 days gestation. The yolk sac is situated on the front ( ventral) part of the embryo; it is lined by extra-embryonic endoderm, outside of which is a layer of extra-embryonic mesenchyme, derived from the epiblast. Blood is conveyed to the wall of the yolk sac by the primitive aorta and after circulating through a wide-meshed capillary plexus, is returned by the vitelline veins to the tubular heart of the embryo. This constitutes the vit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnality
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as cats and ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsiers and some owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as ''Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intense sunlight. Diurnal animals, including squirrels and songbirds, are act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |