|
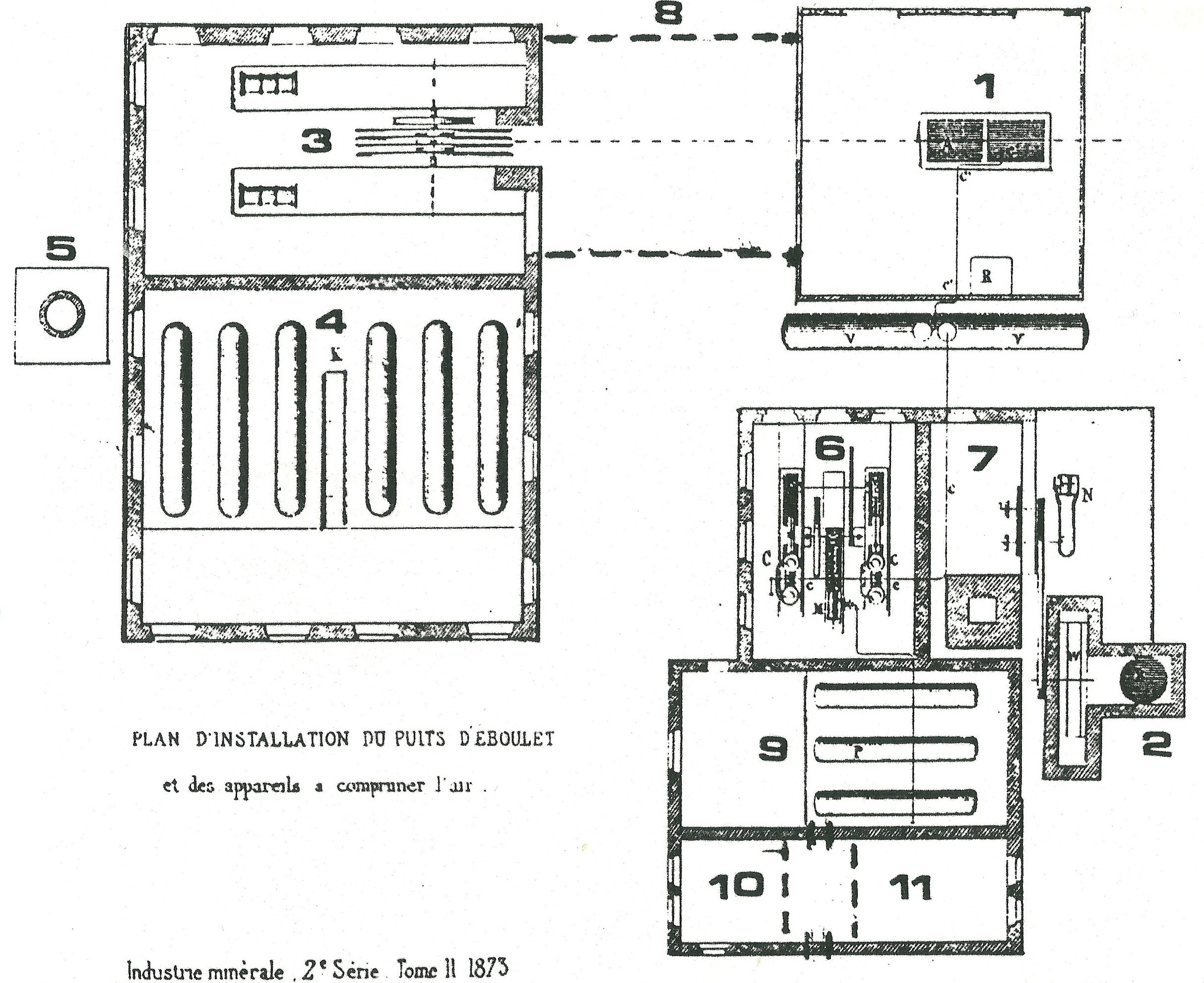
Notre-Dame Mine Shaft
The Notre-Dame (or Éboulet) Pit was one of the principal shaft mining, mine shafts of the Ronchamp coal mines, Ronchamp Mining Company (les Houillères de Ronchamp), located in North-Eastern France in the hamlet of Éboulet, the commune of Champagney, Haute-Saône, Champagney, and the department of Haute-Saône. The pit was created by a rival company, The Forge Masters (la Société des maîtres de forges), which had owned the :fr:Bassin houiller stéphanien sous-vosgien, hamlet of Éboulet's mines since 1851, fifteen years before the Ronchamp Mining Company acquired them. As its supply of coal dwindled, the mine was converted into a water well used for pumping water used in the mining process to several other nearby mines. The pit was plugged in 1958, when all the coal mines formerly owned by Ronchamp were closed by the government utility, Électricité de France. Three mining community, miner towns, a dormitory, and a reservoir of potable water were constructed around the mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champagney, Haute-Saône
Champagney () is a commune in the Haute-Saône department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. Population See also *Communes of the Haute-Saône department *Ronchamp coal mines The Ronchamp Coal Mines were an area of coal mines located in the Vosges and Jura coal mining basins, in eastern France. They covered three municipalities; Ronchamp, Champagney and Magny-Danigon. Operated for more than two centuries, from the ... * Hamlet of La Houillère References Communes of Haute-Saône {{HauteSaône-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewer
A hewer (german: Hauer or ''Häuer'') is a miner who loosens rock and minerals in a mine. In medieval mining in Europe a ''Hauer'' was the name given to a miner who had passed his test (''Hauerprüfung'') as a hewer. Training In Europe in former times, before he could become a hewer, the miner had to learn to be a "sorter boy" (''Scheidejunge''), identifying ores and separating the ore from the gangue. After that he would continue his training in the pit itself. Here, he had to learn further skills, initially as a putter (''Hundtstößer'' literally "truck pusher"), transporting material around the mine in wagons. Only afterwards could he learn the skills, as an apprentice hewer (''Lehrhäuer''), that he would later need as a hewer. This form of training, the acquisition of knowledge by experience, was practised in mining until the First World War World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur De Buyer Coal Mine
The Arthur de Buyer Coal Mine, or coal mine #11, was one of the major Ronchamp coal mines, which is in the area of the commune of Magny-Danigon in the French region of Franche-Comté. Digging started in 1894 in an attempt to ensure the future of the company, which was in a difficult position at that time. The project was directed by Leon Poussigue, director of the company since 1891. He was responsible for organizing the excavation, designing buildings and installing each machine. The seat is named as a tribute to Arthur de Buyer (the same family of the De Buyer owner), the president since 1876. He retired during the commissioning activity of the mine. Active from 1900 to the early 1950s, it was 1010 meters deep, making it the deepest mine in France in the early 20th century and the first to pass the symbolic depth of 1,000 meters. After it had produced coal for almost half a century, there were, up to the 21st century, several conversion attempts. Today only ruins remain. A pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Roof
A hip roof, hip-roof or hipped roof, is a type of roof where all sides slope downwards to the walls, usually with a fairly gentle slope (although a tented roof by definition is a hipped roof with steeply pitched slopes rising to a peak). Thus, a hipped roof has no gables or other vertical sides to the roof. A square hip roof is shaped like a pyramid. Hip roofs on houses may have two triangular sides and two trapezoidal ones. A hip roof on a rectangular plan has four faces. They are almost always at the same pitch or slope, which makes them symmetrical about the centerlines. Hip roofs often have a consistent level fascia, meaning that a gutter can be fitted all around. Hip roofs often have dormer slanted sides. Construction Hip roofs are more difficult to construct than a gabled roof, requiring more complex systems of rafters or trusses. Hip roofs can be constructed on a wide variety of plan shapes. Each ridge is central over the rectangle of the building below it. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles De Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Republic from 1944 to 1946 in order to restore democracy in France. In 1958, he came out of retirement when appointed President of the Council of Ministers (Prime Minister) by President René Coty. He rewrote the Constitution of France and founded the Fifth Republic after approval by referendum. He was elected President of France later that year, a position to which he was reelected in 1965 and held until his resignation in 1969. Born in Lille, he graduated from Saint-Cyr in 1912. He was a decorated officer of the First World War, wounded several times and later taken prisoner at Verdun. During the interwar period, he advocated mobile armoured divisions. During the German invasion of May 1940, he led an armoured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanois Coal Mine
The Chanois coal mine is one of the main shafts of the Ronchamp coal mines, in the French Communes of France, commune of Ronchamp, within the Haute-Saône department, belonging to the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region. It was the center of Ronchamp's coal mining operations from the late 19th century until the mines closed in 1958. It was therefore chosen as the site for the coal mine's ancillary facilities, including a coal preparation plant, a Coke plant (fuel plant), coking plant, and a Ronchamp thermal power station, power station. It succeeded the Saint-Joseph Coal Mine, Saint Joseph shaft in 1895 and ceased mining in 1951. At the beginning of the 21st century, many remnants of these facilities (ruins, a large concrete hopper, converted buildings, and two imposing spoil tips) remain. Excavation Before 1873, the Ronchamp coal mining company operated in the center of the Ronchamp and Champagney coalfields. But the Shaft sinking, shafts used for this task reached the end of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puits Notre-Dame 1900
Puits () is a commune in the Côte-d'Or department in eastern France. Population See also *Communes of the Côte-d'Or department The following is a list of the 698 communes of the Côte-d'Or department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Côte-d'Or {{CôteOr-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Perforation Puits Notre-Dame
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by animals and people, by natural forces such as wind and water, and by chemical, thermal, or electrical power, and include a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems. Renaissance natural philosophers identified six simple machines which were the elementary devices that put a load into motion, and calculated the ratio of output force to input force, known today as mechanical advantage. Modern machines are complex systems that consist of structural elements, mechanisms and control component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Joseph Coal Mine
The Saint-Joseph Coal Mine is one of the main shafts of the Ronchamp coal mine, in the Ronchamp commune, within the French region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. It was one of the most productive coal mines in the Ronchamp coal mines, Ronchamp coalfield during the second half of the 19th century. Throughout this period, it was the center of activity for the List of mining companies, mining company, with the installation of a Coke (fuel), coking plant and a Coal preparation plant, coal-washing plant, before being replaced by the Chanois Coal Mine, Chanois shaft. The Saint Joseph shaft was hit by several disasters. On August 10, 1859, a firedamp explosion killed twenty-nine people. On May 8, 1860, another explosion destroyed the underground tunnels and the roof of the surface recette building. After the closure of the Saint-Joseph shaft in 1895, the buildings were demolished and replaced by a small sawmill, whose buildings, now used as shops for building materials, still exist into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris-Est–Mulhouse-Ville Railway
The railway from Paris-Est to Mulhouse-Ville is a 491-kilometre long railway line, that connects Paris to Mulhouse via Troyes, Chaumont and Belfort, France. The railway was opened in several stages between 1848 and 1858. Route The Paris–Mulhouse railway leaves the Gare de l'Est in Paris in eastern direction. At Noisy-le-Sec, where the Paris–Strasbourg railway branches off, it turns south. It crosses the river Marne at Nogent-sur-Marne, and turns southeast. Near Gouaix it reaches the river Seine, and follows this river upstream, until Nogent-sur-Seine on its right bank, then on its left bank, roughly southeastward. At Troyes it crosses the Seine again, and turns east. It enters the Aube valley near Jessains, and continues upstream along Bar-sur-Aube. It leaves the Aube and enters the upper Marne valley at Chaumont. It passes Langres and the railway junction Culmont-Chalindrey, where it crosses the line Nancy–Dijon. It reaches the river Saône at Jussey, and follows it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |