|
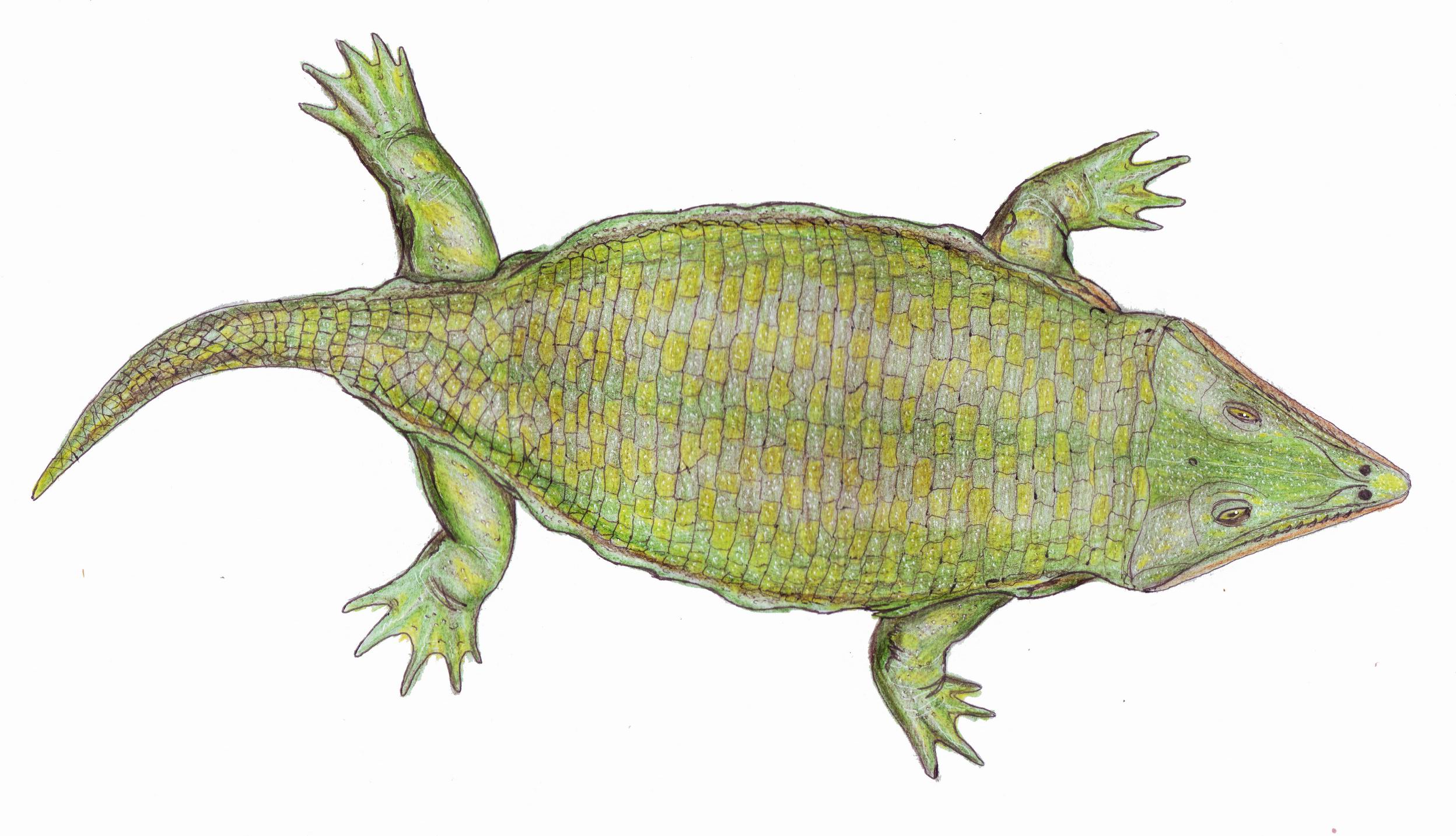
Notobrachyops
''Notobrachyops'' is a genus of brachyopid temnospondyl amphibian. It is known from a skull roof impression found in the Ashfield Shale (Late Triassic) of Mortdale, New South Wales, Australia. The Ashfield Shale has also yielded a shark species, a lungfish species, six species of paleoniscid fish, a species of holostean fish, a subholostean fish, and the labyrinthodont amphibian '' Paracyclotosaurus davidi''. See also * List of prehistoric amphibians * Prehistoric amphibian This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... References Stereospondyls Triassic amphibians of South America Fossil taxa described in 1973 {{Temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashfield Shale
Ashfield Shale is part of the Wianamatta group of sedimentary rocks in the Sydney Basin. It lies directly on contemporaneously eroded Hawkesbury sandstone or the Mittagong formation. These rock types were formed in the Triassic Period. It is named after the Sydney suburb of Ashfield. Some of the early research was performed at the old Ashfield Brickworks Quarry. This rock type is often associated with the Inner West and North Shore of the city. However, it has also been recorded at Penrith, Revesby, Bilpin and Mount Irvine. Description Ashfield Shale comprises black mudstones and grey shales with frequent sideritic clay ironstone bands. The thickness ranges between 45 and 64 metres. It is 20 metres thick at the Sydney Olympic Site. The chemistry of the rock is typical of shales, with high iron levels, and some iron sulphide and low calcium levels. The geology of the shale lenses within the Hawkesbury Sandstone is chemically similar to the Ashfield Shale. At Tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachyopidae
Brachyopidae is an extinct family of temnospondyl labyrintodonts. They evolved in the early Mesozoic and were mostly aquatic. A fragmentary find from Lesotho, Africa is estimated to have been long, the largest amphibian ever known to have lived besides ''Prionosuchus''.Steyer, J.S. & Damiani, R. (2005): A giant brachyopoid temnospondyl from the Upper Triassic or Lower Jurassic of Lesotho. ''Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France'', no. 3: pp 243-248.abstract/ref> Brachyopids were the only group of temnospondyls to survive into the Jurassic aside from their sister family Chigutisauridae. With records of the family from the Jurassic of Asia. List of genera *'' Banksiops'' *'' Batrachosaurus'' *'' Batrachosuchoides'' *'' Batrachosuchus'' *'' Brachyops'' *'' Gobiops'' *'' Notobrachyops'' *'' Platycepsion'' *'' Sinobrachyops'' *'' Vanastega'' *''Xenobrachyops ''Xenobrachyops'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Triassic of Australia, describi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1973 In Paleontology
Pinophyta Arthropods Insects Conodonts Archosauromorphs Newly named crurotarsins Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Newly named pterosaurs References {{portal, Paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fos ... Paleontology 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by a single living species, the bowfin ('' Amia calva''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Lepisosteidae), represented by seven living species in two genera ('' Atractosteus'', ''Lepisosteus''). The earliest members of the clade appeared during the Early Triassic, over 250 million years ago. Holostei was thought to be regarded as paraphyletic. However, a recent study provided evidence that the Holostei are the closest living relates of the Teleostei, both within the Neopterygii. This was found from the morphology of the Holostei, for example presence of a paired vomer. Holosteans are closer to teleosts than are the chondrosteans, the other group intermediate between teleosts and cartilaginous fish, which are regarded as (at the nearest) a sister group to the Neopterigii. The spiracles of holosteans are reduced to vesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospondyls
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Classification and anatomy The group was first defined by Zittel (1888) on the recognition of the distinctive vertebral anatomy of the best known stereospondyls of the time, such as ''Mastodonsaurus'' and ''Metoposaurus''. The term 'stereospondylous' as a descriptor of vertebral anatomy was coined the following year by Fraas, referring to a vertebral position consisting largely or entirely of the intercentrum in addition to the neural arch. While the name 'Stereospondyli' is derived from the stereospondylous vertebral condition, there is a diversity of vertebral morphologies among stereospondyls, including the diplospondylous (' tupilakosaurid') co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Amphibian
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published ('' nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracyclotosaurus
''Paracyclotosaurus'' (meaning "Near Wheeled Lizard") is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian, which would have appeared similar to today's salamander – but much larger, measuring up to long and weighing between . It lived in the Middle Triassic period, about 235 million years ago, and fossils have been found in Australia, India, and South Africa. Although they could live on dry land, ''Paracyclotosaurus'' probably spent most of its time in water. They had flattened bodies and elongated heads, almost long, that vaguely resembled those of modern crocodiles. Discovery and naming The type species ''P. davidi'' is only known from one complete specimen recovered from Australia. It was discovered by quarry miners in a brick pit in St. Peters in Sydney, New South Wales. The discovery, made in 1910, was from a large ironstone nodule within Ashfield Shale which contained the nearly complete skeleton. The reconstruction was finished in July 1914, and was initially determined t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodont
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoniscidae
Palaeoniscidae is an extinct family of ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) ascribed to the order Palaeonisciformes. The family includes the genus ''Palaeoniscum'' and potentially other Palaeozoic and Mesozoic early actinopterygian genera. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek words παλαιός (''palaiós'', ancient) and ὀνίσκος (''oniskos'', 'cod-fish' or woodlouse). Historic background The family was first named "Palaeoniscini" by Charles Lucien Bonaparte in 1846, and "Palaeonisciden" by Carl Vogt in 1851. Later, the family name was standardized to Palaeoniscidae. The authorship of the family Palaeoniscidae is variably attributed to either Bonaparte or Vogt in the literature. Vogt ascribed the following genera to Palaeoniscidae: ''Palaeoniscum'', ''Platysomus'' (misspelled as ''Platysemius''), ''Amblypterus'', '' Eurynotus'', '' Pygopterus'', and '' Acrolepis''. With the exception of ''Palaeoniscum'', these genera were later placed in separate families ( P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)