|
Northern Xia
Xia (), known in historiography as Hu Xia (胡夏), Northern Xia (北夏), Helian Xia (赫連夏) or the Great Xia (大夏), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Helian clan of Tiefu-Xiongnu ethnicity during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. Prior to establishing the Xia, the imperial clan existed as a tribal entity known as the Tiefu (). All rulers of the Xia declared themselves "emperors". Both the Tiefu and Xia were based in the Ordos Desert, and during the reign of Helian Bobo, they constructed their capital of Tongwan, a heavily fortified and state-of-the-art city that served as a frontier garrison until the Song dynasty. Its ruins were discovered during the Qing dynasty and can still be seen in present-day Inner Mongolia. At its peak, the Xia also controlled the Guanzhong region in modern-day central Shaanxi. Due to their mix Xiongnu and Xianbei ethnicity, the Tiefu were initially known as a group of Wuhuan, which in the 4th century, was another term for "miscellanous '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), to fully autocratic (absolute monarchy), and may have Political representation, representational, Executive (government), executive, legislative, and judicial functions. The Order of succession, succession of monarchs has mostly been Hereditary monarchy, hereditary, often building dynasties; however, monarchies can also be elective monarchy, elective and Self-proclaimed monarchy, self-proclaimed. Aristocracy (class), Aristocrats, though not inherent to monarchies, often function as the pool of persons from which the monarch is chosen, and to fill the constituting institutions (e.g. Diet (assembly), diet and Royal court, court), giving many monarchies oligarchic elements. The Legitimacy (political)#Monarchy, political legitim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
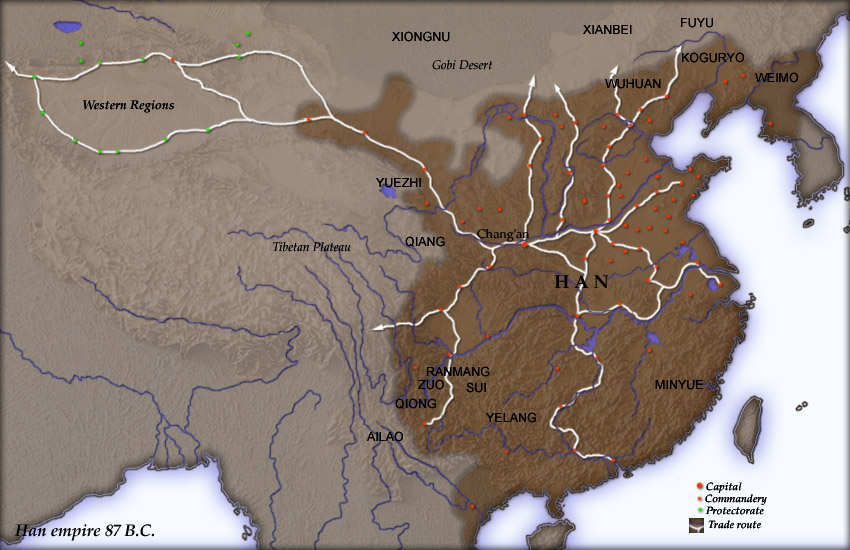
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiangqu
Qiangqu (; r. 179–188 AD) was the Western Wise Prince, successor to Huzheng, and ''chanyu'' of the Southern Xiongnu from 179 to 188 AD. Qiangqu's reign coincided with a troublesome time for the Han Empire, and few records address Chinese relations with the Southern Xiongnu. In 187 AD Qiangqu sent Southern Xiongnu cavalry troops under command of the Eastern Tuqi Prince (Wise Prince) to aid the governor of Yuzhou province against the former governor, Zhongshan province, Zhang Chun, who had rebelled in alliance with the Wuhuan. This caused discontent among the elders, who were alarmed by the frequency with which Qiangqu sent their men off to battle for the Han dynasty. In 188 AD, the Xiuchuge people rose in rebellion in the Hetao region of Bing province and killed the provincial inspector after invading Xihe Commandery. The Southern Xiongnu dissidents, led by the Xiluo clan of the Right Division, formed an alliance with the Xiuchuge, and together they killed Qiangqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 AD. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Tujue leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentrala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luandi
The Luandi (; alternatively written as Xulianti ) was the ruling clan of the Xiongnu that flourished from the 3rd century BCE to 4th century CE. The form Luandi comes from the '' Book of Han'', while the form Xulianti comes from the '' Book of Later Han''. Etymology Lanhai Wei and Hui Li reconstruct the Old Chinese pronunciation of 挛鞮 as *lyuan-tlïγ, evolving from an earlier 虚连题 (*Hala-yundluγ), as a result of a historical sound shift involving the initial dropping of *h- by demonstrating its occurrence in several historical sources. Furthermore, the conjugation of the roots *hala, meaning colorful; *yund meaning horse, *-luγ as the participle suffix would have resulted in the semantic meaning "tribe with skewbald horses" in an early Turkic dialect, allowing it to be further identified with the historical Ulayundluğ tribe. Moreover, the authors argue that the conquest of the same clan by the Xue in the 4th century CE eventually gave birth to the Xueyantuo. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qubei
Qubei (; pinyin: Qùbēi, 195–216) was a leader of the Southern Xiongnu and supervisor of the Five Divisions who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. An uncle to the last ''chanyu'' of the Southern Xiongnu, Huchuquan, Qubei was appointed by the Chinese court to supervise the Five Divisions of Xiongnu after his nephew was detained in Ye in 216. He was also the ancestor of two prominent non-Chinese clans; the Helian, who founded the Xia dynasty during the Sixteen Kingdoms period, and the Dugu. Life According to the ''Book of Wei'', Qubei was a member of the imperial Luandi clan of the Southern Xiongnu. The ''History of the Northern Dynasties'' specifies that he was the brother of the ''chanyu'', Qiangqu, but a much later and dubious account from the ''New Book of Tang'' instead claims that he was the son of Wuli, a descendant of a Han dynasty prince-turned-Xiongnu noble, Liu Jinbo. When Huchuquan ascended as ''chanyu'' in 195, Qubei was bestowed the title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Five Barbarians", their descendants founded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty (; ) is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, it was established by the legendary figure Yu the Great, after Emperor Shun, Shun, the last of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, and they are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, the earliest oracle bone inscriptions dating from the Late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the ''Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hu (people)
Hu (; IPA: ) also Huren (胡人, "Hu people") or Huzu (胡族, "Hu tribes"), was a rather vague term to designate ancient groups of people, namely populations beyond the Central Plains, generally to the north and west of the Huaxia ''Huaxia'' is a historical concept representing the Chinese nation, and came from the self-awareness of a common cultural ancestry by ancestral populations of the Han people. Etymology The earliest extant authentic attestation of the ''H ... realm. The Hu were usually horse-mounted nomads. According to Hill (2009): Ancient Chinese dynasties such as the Shang dynasty and Zhou dynasty, into the Spring and Autumn period, recount of numerous encounters with the nomadic tribes of the northern steppes and other alien tribes. At that time, the preferred term to designate them was the "Four Barbarians" ( zh, c=四夷, p=sìyí), each was named for a cardinal direction: the ''Dongyi'' (東夷, "Eastern Barbarians"), ''Nanman'' (南蠻, "Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', < (c. 78 BCE): *''ʔâ-wân'' < *''Awar'') were a Proto-MongolicPulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Press p. 452 of pp. 411–466. or |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols (who spoke either pre-Proto-Mongolic,, quote: "The Xianbei confederation appears to have contained speakers of Pre-Proto-Mongolic, perhaps the largest constituent linguistic group, as well as former Xiongnu subjects, who spoke other languages, Turkic almost certainly being one of them."Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Pressp. 452of pp. 411–466. or Para-Mongolic languages), and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |