|
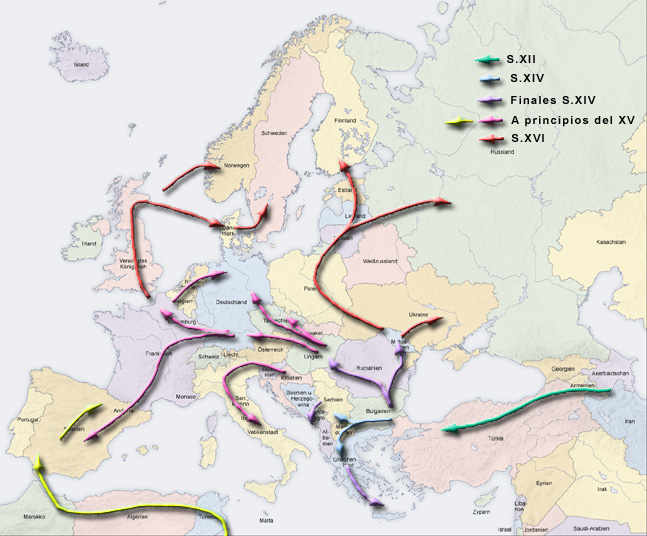
Northern Romani Dialects
Northern Romani dialects are a group of dialects of the Romani language Romani ( ; also Romanes , Romany, Roma; ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani people. The largest of these are Vlax Romani language, Vlax Romani (about 500,000 speakers), Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Roma ... spoken in various Northern, North-Western, North- Central and North- Eastern European countries. The first grammatical outline of the Romani language was done on the Sinti variety. Dialects Elšík uses this classification and dialect examples (geographical information from Matras): References Romani in Europe {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
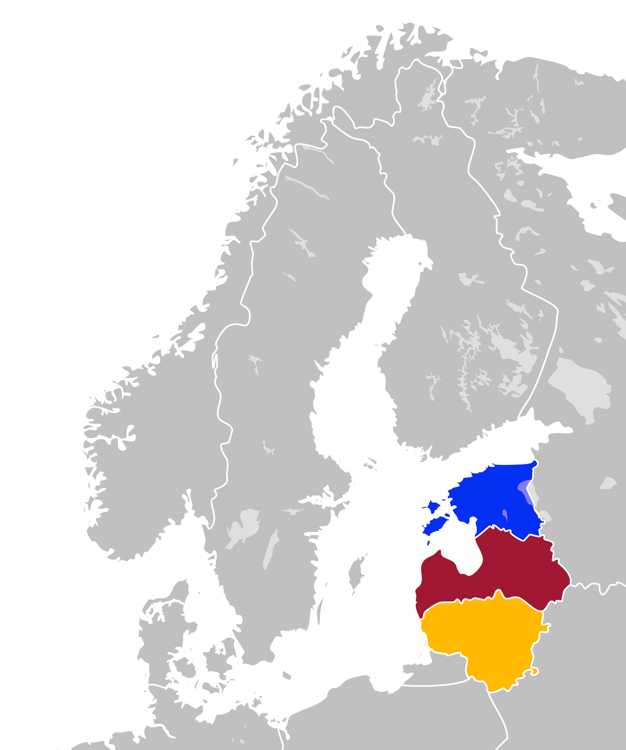
Baltic States
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. The term "Balticum" is sometimes used to describe the region comprising the three states; see e.g All three Baltic countries are classified as World Bank high-income economy, high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. Etymology The term ''Baltic'' stems from the name of the Baltic Sea – a hydronym dating back to at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology. Climate The climate is mainly Oceanic climate (Cfb), Humid continental climate (Dfb), Subarctic climate (Dfc and Dsc) and Tundra (ET). Geography Northern Europe might be defined roughly to include some or all of the following areas: British Isles, Fennoscandia, the peninsula of Jutland, the Baltic region, Baltic plain that lies to the east, and the many islands that lie offshore from mainland northern Europe and the main European continent. In some cases, Greenland is also included, although it is only politically European, comprising part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and not considered to be geographically in Europe. The area is partly mountainous, including the northern volcanic islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marburg
Marburg (; ) is a college town, university town in the States of Germany, German federal state () of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf Districts of Germany, district (). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has a population of approximately 76,000. Having been awarded town privileges in 1222, Marburg served as capital of the Landgrave, landgraviate of Hessen-Marburg during periods of the 15th to 17th centuries. The University of Marburg was founded in 1527 and dominates the public life in the town to this day. Marburg is a historic centre of the pharmaceutical industry in Germany, and there is a plant in the town (by BioNTech) to produce vaccines to tackle Covid-19. History Founding and early history Like many settlements, Marburg developed at the crossroads of two important early medieval highways: the trade route linking Cologne and Prague and the trade route from the North Sea to the Alps and on to Italy, the former crossing the river La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
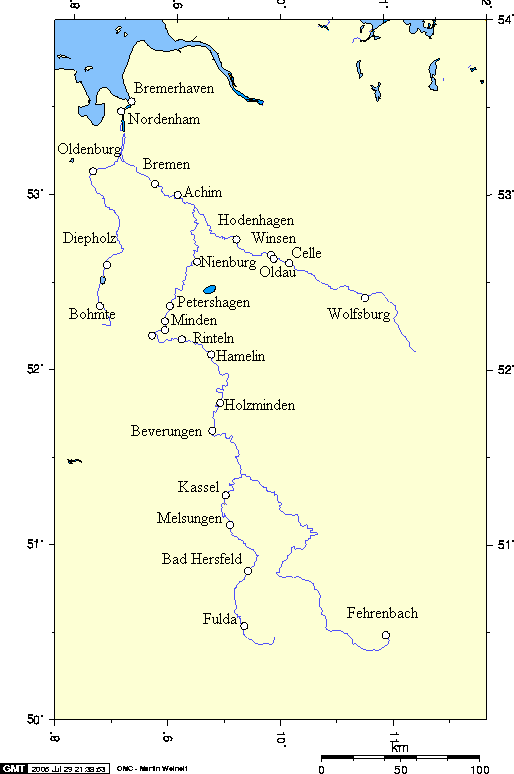
Hamelin
Hameln ( ; ) is a town on the river Weser in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Hameln-Pyrmont and has a population of roughly 57,000. Hamelin is best known for the tale of the Pied Piper of Hamelin. History Hameln started with a monastery, which was founded as early as 851 AD; its surrounding village became a town by the 12th century. The incident involving the "Pied Piper" (see below) is said to have occurred in 1284 and may be based on a true event, although somewhat different from the traditional tale. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Hamelin was a minor member of the Hanseatic League. In June 1634, during the Thirty Years' War, Lothar Dietrich, Freiherr of Bönninghausen, a general in the Imperial Army of the Holy Roman Emperor, lost the Battle of Oldendorf to the Swedish General Kniphausen, after Hamelin had been besieged by the Swedish army. The era of the town's greatest prosperity began in 1664, when Hamelin became a fortified border town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinte Romani
Sinte Romani (also known as Sintitikes, Manuš) is the variety of Romani spoken by the Sinti people in Germany, France, Austria, Belgium, the Netherlands, some parts of Northern Italy and other adjacent regions. Sinte Romani is characterized by significant German influence and is not mutually intelligible with other forms of Romani. The language is written in the Latin script. Overview The name Romani derives from ''řom'', the historical self-designation of speakers of the Romani language group. Romani is sometimes written as Romany (in English), but native speaking people use the word Romani for the language. Historically, Romani people have been known for being nomadic, but today only a small percentage of Romani people are unsettled due to forced assimilation and government interventions. Sinte Romani is a dialect of Romani and belongs to the Northwestern Romani dialect group, Sinti is the self-designation of a large Romani population that began leaving the Balkans earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Kalo Language
Kalo, Kàlo or the Finnish Romani language () is a variety of the Romani language spoken by the Kaale subgroup of the Romani people in Finland and Sweden. The language is related to but not mutually intelligible with Scandoromani or Angloromani. Kalo has 6,000–10,000 speakers and many young people do not know the language. The majority of speakers are from older generations and about two-thirds of the Romani in Finland still speak the language. There have been some revival efforts. Dictionaries and grammar books have been produced and some universities offer Kalo as a course. It has some similarities to the Romani languages in Hungary, where stress is placed on the first syllable of the word. This may be related to the fact that both Finnish and Hungarian words have fixed word-initial stress, a feature that would have diffused to the Romani languages. Kalo has been taught in schools since the late 1980s, with some courses available as early as the 1970s. Current situation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Kale
The Kaale (; ; , ''Suomen romanit;'' also known as Finnish Romani, Finnish Roma, Finnish Kale are a Romani subgroup who live primarily in Finland but also in Sweden. Their main languages are Finnish, Swedish and Kalo. History From the 1500s to World War II The first Roma arrived in southwest Finland and Åland in the 16th century from the area that is now Sweden. In the following centuries, Finland's Roma population was supplemented by traveling groups from the Baltic and Russia. A seemingly settled Roma group was known to have travelled in Finland’s wilderness areas around the turn of the 16th and 17th centuries, but there is no surviving information about their relations with the majority population. In the Swedish part of the kingdom, "Tattares" are said to have arrived to Sweden and Stockholm for the first time in 1512, when people referred to as "Tattares" were traveling through the country. According to the minutes of the Stockholm city council, a group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angloromani Language
Angloromani or Anglo-Romani (literally "English Romani"; also known as Angloromany, Rummaness, or ) is a Para-Romani dialect spoken by the Romanichal, a subgroup of the Romani people in the United Kingdom and other parts of the English-speaking world. It is characterised by the presence of Romani vocabulary and syntax in the English used by Romanichal. Romanichal used the Romani language from their arrival in the 16th century up until the late 19th century, when it was replaced, for the most part, by English as their everyday and family language. This resulted in the formation of Angloromani. This differs from the presence of loanwords (such as that used locally in Edinburgh and Northumberland) from the Romani language, such as (originally a toffee apple), (originally Romani 'brother'), and (originally 'boy'). Documentation A document from about the seventeenth century titled the ''Winchester Confessions'' indicates that the English Romani language was itself a dialect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanichal
The Romanichal ( ; more commonly known as English Gypsies) are a Romani people, Romani subgroup in the United Kingdom. Many Romanichal speak Angloromani, a mixed language that blends Romani language, Romani vocabulary with English syntax. Romanichal residing in England, Scotland, and Wales are part of the Gypsy, Roma and Traveller people (UK), Gypsy (Romani), Roma, and Traveller community. Genetic, cultural, and linguistic findings indicate that the Romani people trace their origins to South Asia, likely in the regions of present-day Punjab, Rajasthan, and Sindh. Etymology The word "Romanichal" is derived from ''Romani chal'', where ''chal'' is Angloromani language, Angloromani for "fellow".Oxford English Dictionary Second Edition 1989, "Romany3, n. and a." Distribution Nearly all Romanichal in Great Britain live in England, with smaller communities in South Wales, Northeast Wales, and the Scottish Borders. The Romani diaspora, Romanichal diaspora emigrated from Great Britai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Romani Language
The Welsh Romani language is a variety of the Romani language spoken by the Kale subgroup of the Romani people, who have been present in Wales since the 16th century. Welsh Romani is one of the many Northern Romani dialects. The majority of the vocabulary is of Romani origin but there are a number of loanwords from other languages. Welsh loanwords include ''melanō'' ("yellow", from ''melyn''), ''grīga'' ("heather", from ''grug'') and ''kraŋka'' ("crab", from ''cranc''). There are also English loanwords such as ''vlija'' ("village"), ''spīdra'' ("spider") and ''bråmla'' ("bramble"). Historically the variants of Welsh Romani and Angloromani (spoken by the Romanichal) constituted the same variant of Romani, known as British Romani. Welsh Romani is closely related to Angloromani, Scandoromani (spoken by Romanisæl in Sweden and Norway), Scottish Cant (spoken by Scottish Lowland Romani in Lowland Scotland) and Kalo (Spoken by Kaale in Finland and Sweden). Kale, Romanichal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kale (Welsh Roma)
The Kale (also Kalé, Kalá, Valshanange; ) are a Romani subgroup predominantly found in northwestern Wales, specifically in the Welsh-speaking areas. Roma have been present in Wales since the 16th century. The Kale were traditionally renowned musicians, and are reported to have introduced the fiddle to Wales. They were also known for their distinctive styles of clothing, dance, poetry and storytelling. The Kale are closely related to the Romanichal, Romanisael, Kaale and Scottish Lowland Roma. They are considered part of the Gypsy (Romani), Roma and Traveller (GRT) community. Romanichal are present in South Wales (in and around Cardiff, Swansea and Newport) and North East Wales (in and around Wrexham as well as in parts of Wales close to Liverpool and Chester). The Romani people can trace their origins to South Asia, likely in the regions of present-day Punjab, Rajasthan and Sindh.Hübschmannová, Milena (1995). "Romaňi čhib – romština: Několik základních inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |