|
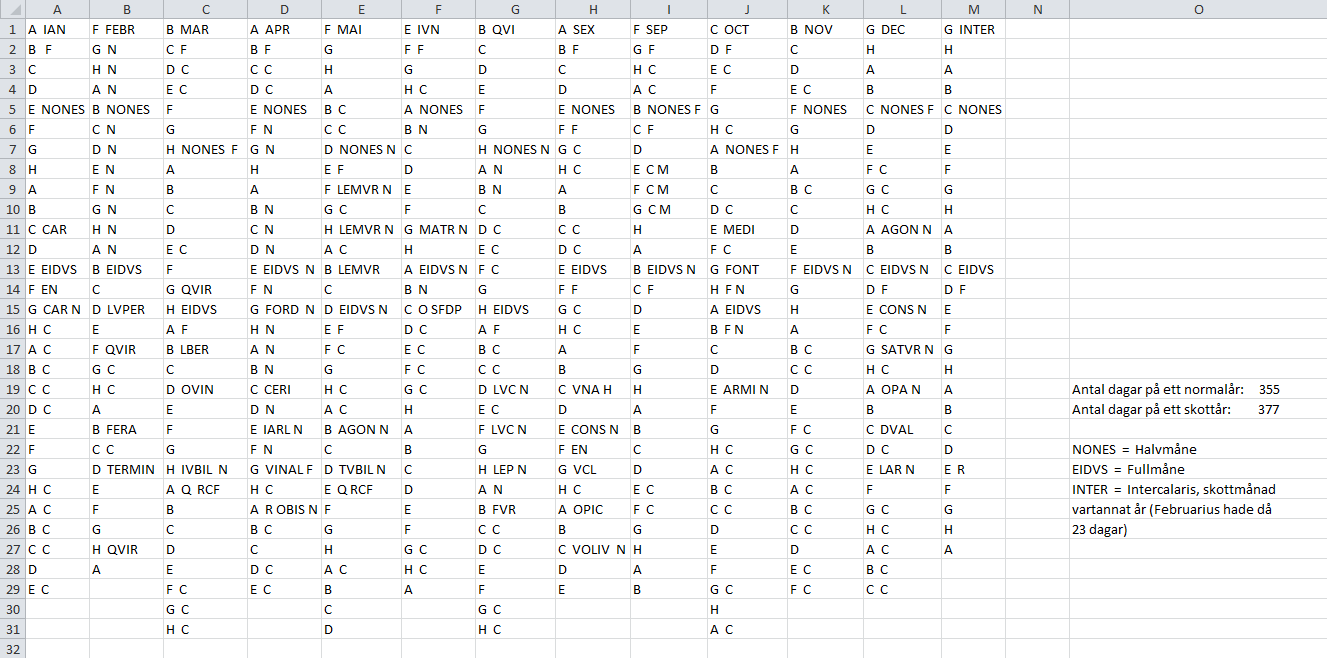
Nonae
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the dictator Julius Caesar and emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones, and ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly before the middle of the month (the ides), and eight days—nine, counting inclusively—before this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Februarius
''Februarius'', fully ''Mensis Februarius'' ("month of Februa"), was the shortest month of the Roman calendar from which the Julian and Gregorian month of February derived. It was eventually placed second in order, preceded by '' Ianuarius'' ("month of Janus", January) and followed by ''Martius'' ("month of Mars", March). In the oldest Roman calendar, which the Romans believed to have been instituted by their legendary founder Romulus, March was the first month, and the calendar year had only ten months in all. ''Ianuarius'' and ''Februarius'' were supposed to have been added by Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, originally at the end of the year. It is unclear when the Romans reset the course of the year so that January and February came first. ''Februarius'' was the only month in the pre-Julian calendar to have an even number of days, numbering 28. This was mathematically necessary to permit the year itself to have an odd number of days. Ancient sources derived ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ianuarius
''Ianuarius'', fully ''Mensis Ianuarius'' ("month of Janus"), was the first month of the ancient Roman calendar, from which the Julian and Gregorian month of January derived. It was followed by ''Februarius'' (" February"). In the calendars of the Roman Republic, ''Ianuarius'' had 29 days. Two days were added when the calendar was reformed under Julius Caesar in 45 BCE. In the oldest Roman calendar, which the Romans believed to have been instituted by their legendary founder Romulus, the first month was ''Martius'' ("month of Mars", March), and the calendar year had only ten months. ''Ianuarius'' and ''Februarius'' were supposed to have been added by Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, originally at the end of the year. It is unclear when the Romans reset the course of the year so that January and February came first. ''Ianuarius'' is conventionally thought to have taken its name from Janus, the dual-faced god of beginnings, openings, passages, gates and doorways, but ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
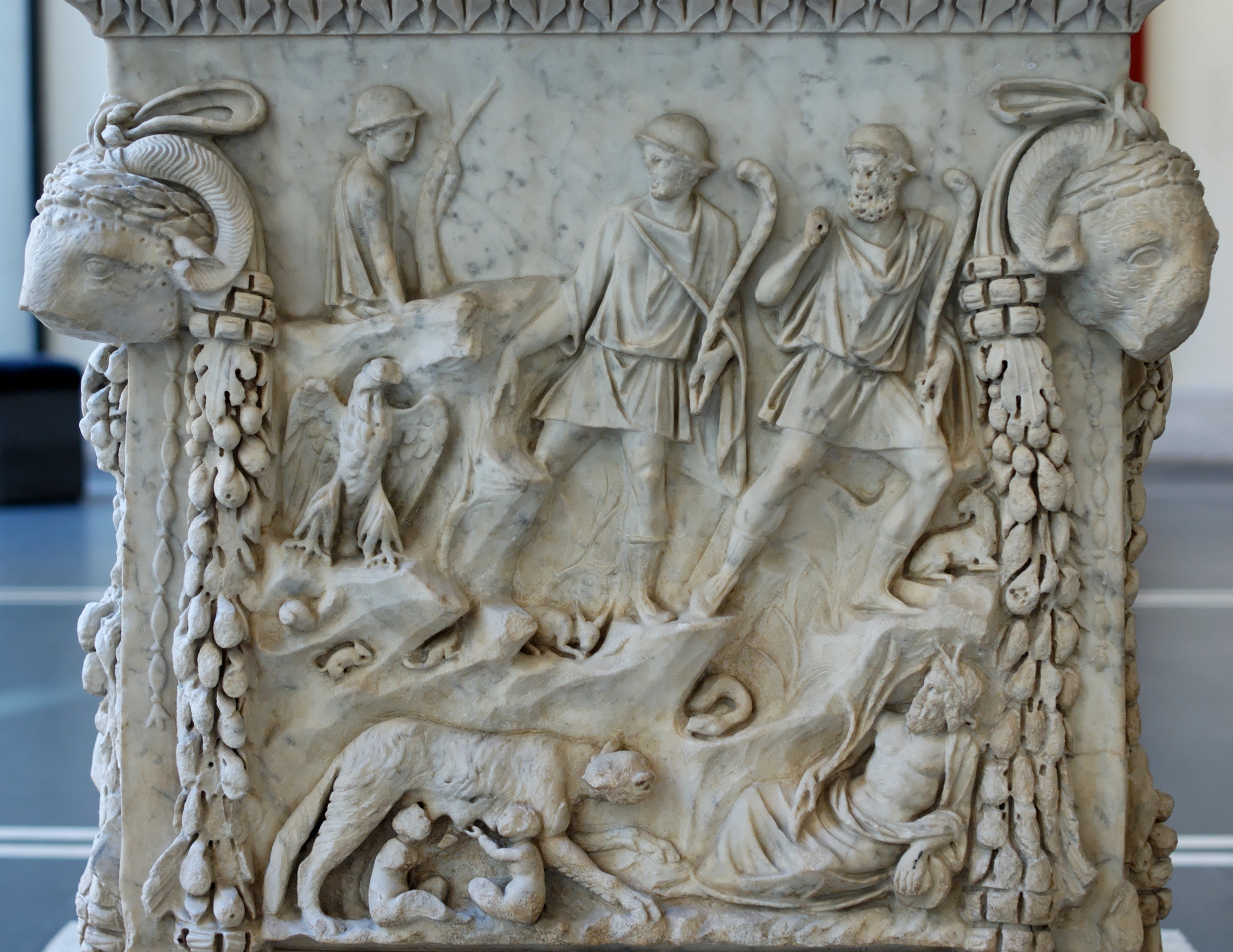
Roman Legend
Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, ''Roman mythology'' may also refer to the modern study of these representations, and to the subject matter as represented in the literature and art of other cultures in any period. Roman mythology draws from the mythology of the Italic peoples and ultimately from Proto-Indo-European mythology. Roman mythology also draws directly on Greek mythology, potentially as early as Rome's protohistory, but primarily during the Hellenistic period of Greek influence and through the Roman conquest of Greece, via the artistic imitation of Greek literary models by Roman authors. The Romans identified their own gods with those of the ancient Greeks—who were closely historically related in some cases, such as Zeus and Jupiter—and reinterpreted myths about Greek deities under the names of their Roman counterparts. Greek and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nones (calendar)
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the dictator Julius Caesar and emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones, and ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly before the middle of the month (the ides), and eight days—nine, counting inclusively—before this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ides (calendar)
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the Roman dictator, dictator Julius Caesar and Roman emperor, emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones (calendar), nones, and ides (calendar), ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's Egyptian calendar, former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the Byzantine Empire, later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Del Teatro Romano De Caesaraugusta
Museo may refer to: * Museo, 2018 Mexican drama heist film *Museo (Naples Metro) Museo is a station on line 1 of the Naples Metro. It was opened on 5 April 2001 as the eastern terminus of the section of the line between Vanvitelli and Museo. On 27 March 2002 the line was extended to Dante Dante Alighieri (; – 14 Se ..., station on line 1 of the Naples Metro * Museo, Seville, neighborhood of Seville, Spain {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numa Pompilius
Numa Pompilius (; 753–672 BC; reigned 715–672 BC) was the legendary second king of Rome, succeeding Romulus Romulus () was the legendary foundation of Rome, founder and King of Rome, first king of Ancient Rome, Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus ... after a one-year interregnum. He was of Sabine origin, and many of Rome's most important religious and political institutions are attributed to him, such as the Roman calendar, Vestal Virgins, the cult of Mars, the cult of Jupiter, the cult of Romulus, and the office of ''pontifex maximus''. Genealogy According to Plutarch, Numa was the youngest of Pomponius's four sons, born on the day of Rome's founding (traditionally, 21 April 753 BC). He lived a severe life of discipline and banished all luxury from his home. Titus Tatius, king of the Sabines and a colleague of Romulus, gave in marriage his only daughter, Tatia (wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romulus
Romulus () was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of these traditions incorporate elements of folklore, and it is not clear to what extent a historical figure underlies the mythical Romulus, the events and institutions ascribed to him were central to the myths surrounding Rome's origins and cultural traditions. Traditional account The myths concerning Romulus involve several distinct episodes and figures, including the miraculous birth and youth of Romulus and his twin brother, Remus; Remus' murder and the founding of Rome; the Rape of the Sabine Women, and the subsequent war with the Sabines; a period of joint rule with Titus Tatius; the establishment of various Roman institutions; the death or apotheosis of Romulus, and the succession of Numa Pompilius. Romulus and Remus According to Roman my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of Rome
The Roman Kingdom (also referred to as the Roman monarchy, or the regal period of ancient Rome) was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began with the city's founding 753 BC, with settlements around the Palatine Hill along the river Tiber in central Italy, and ended with the overthrow of the kings and the establishment of the Republic 509 BC. Little is certain about the kingdom's history as no records and few inscriptions from the time of the kings survive. The accounts of this period written during the Republic and the Empire are thought largely to be based on oral tradition. Origin The site of the founding of the Roman Kingdom (and eventual Republic and Empire) had a ford where one could cross the river Tiber in central Italy. The Palatine Hill and hills surrounding it provided easily defensible positions in the wide fertile plain surrounding them. Each of these features c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Week
A week is a unit of time equal to seven days. It is the standard time period used for short cycles of days in most parts of the world. The days are often used to indicate common work days and rest days, as well as days of worship. Weeks are often mapped against yearly calendars, but are typically not the basis for them, as weeks are not based on astronomy. The modern seven-day week can be traced back to the Babylonians, who used it within their calendar. Other ancient cultures had different week lengths, including ten in Egypt and an eight-day week for Etruscans. The Etruscan week was adopted by the Ancient Romans, but they later moved to a seven-day week, which had spread across Western Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean. In 321 AD, Emperor Constantine officially decreed a seven-day week in the Roman Empire, including making Sunday a public holiday. This later spread across Europe, then the rest of the world. In English, the names of the days of the week are Monday, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nundinae
The nundinae (), sometimes anglicized to nundines,. were the market days of the ancient Roman calendar, forming a kind of weekend including, for a certain period, rest from work for the ruling class ( patricians). The nundinal cycle, market week, or 8-day week ( la, nundinum. or ') was the cycle of days preceding and including each nundinae. These were marked on fasti using from A to H. The earliest form of the Roman calendar is sometimes said to have included exactly 38 such cycles, running for 304 days from March to December before an unorganized expanse of about 50 winter days. The lengths of the Republican and Julian calendars, however, were not evenly divisible by 8; under these systems, the nundinae fell on a different letter each year. These letters formed the basis of the later Christian dominical letters. Name The name ' was apparently formed from an early form of ' ("ninth") and ' ("day"), a root related to ' and ultimately the Proto-Indo-European root reconstruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |