|
Nixonomics
Nixonomics, a portmanteau of the words "Nixon" and "economics", refers either to the performance of the U.S. economy under U.S. President Richard Nixon (i.e. the expansions in 1969 and from 1970 to 1973 during the broader Post–World War II economic expansion and the recessions from 1969 to 1970 and from 1973 to 1975) or the Nixon administration's economic policies. Nixon is the first president to have his surname combined with the word "economics". Nixon won a weak economy from President Lyndon B. Johnson. In 1969, a tax bill passed that held several Nixon ideas, including a repeal of the investment tax credit and removal of two million of the nation's poor from the tax rolls. After a year it was becoming obvious that the plan wasn't working. Nixon gave his budget plan to congress in 1971 in which he was to use a $11.6 billion deficit. Nixon then publicly agreed with Keynesian economic principles which stated that government expenditure could take the nation out of their recess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Stabilization Act Of 1970
The Economic Stabilization Act of 1970 (Title II of , formerly codified a12 U.S.C. § 1904 was a United States law that authorized the President to stabilize prices, rents, wages, salaries, interest rates, dividends and similar transfers as part of a general program of price controls within the American domestic goods and labor markets. It established standards to serve as a guide for determining levels of wages, prices, etc., which would allow for adjustments, exceptions and variations to prevent inequities, taking into account changes in productivity, cost of living and other pertinent factors. The Pay Board and the Price Commission were created on October 22, 1971, when President Nixon appointed 22 members between the boards, as agencies to create and administer economic controls in Phase II of the Economic Stabilization Program (ESP), with Donald Rumsfeld newly acting as the executive director of the Cost of Living Council responsible for establishing the overall goals of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nixon Edited Transcripts
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was the 36th vice president from 1953 to 1961 under President Dwight D. Eisenhower. His five years in the White House saw reduction of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War, détente with the Soviet Union and China, the first manned Moon landings, and the establishment of the Environmental Protection Agency and Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Nixon's second term ended early, when he became the only president to resign from office, as a result of the Watergate scandal. Nixon was born into a poor family of Quakers in a small town in Southern California. He graduated from Duke Law School in 1937, practiced law in California, then moved with his wife Pat to Washington in 1942 to work for the federal government. After active duty in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Connally
John Bowden Connally Jr. (February 27, 1917June 15, 1993) was an American politician. He served as the 39th governor of Texas and as the 61st United States secretary of the Treasury. He began his career as a Democratic Party (United States), Democrat and later became a Republican Party (United States), Republican in 1973. Born in Floresville, Texas, Connally pursued a legal career after graduating from the University of Texas at Austin. During World War II, he served on the staff of James Forrestal and Dwight D. Eisenhower before transferring to the Asiatic-Pacific Theater. After the war, he became an aide to Senator Lyndon B. Johnson. When Johnson assumed the vice presidency in 1961, he convinced President John F. Kennedy to appoint Connally to the position of United States Secretary of the Navy. Connally left the Kennedy Administration in December 1961 to run for Governor of Texas, and he held that position from 1963 to 1969. In 1963, Connally was riding in the presidential limo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time (magazine)
''Time'' (stylized in all caps) is an American news magazine based in New York City. For nearly a century, it was published Weekly newspaper, weekly, but starting in March 2020 it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on March 3, 1923, and for many years it was run by its influential co-founder, Henry Luce. A European edition (''Time Europe'', formerly known as ''Time Atlantic'') is published in London and also covers the Middle East, Africa, and, since 2003, Latin America. An Asian edition (''Time Asia'') is based in Hong Kong. The South Pacific edition, which covers Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands, is based in Sydney. Since 2018, ''Time'' has been published by Time USA, LLC, owned by Marc Benioff, who acquired it from Meredith Corporation. History ''Time'' has been based in New York City since its first issue published on March 3, 1923, by Briton Hadden and Henry Luce. It was the first weekly news magazine in the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidenomics
The economic policy of the Joe Biden administration, colloquially named Bidenomics, is characterized by relief measures and vaccination efforts to address the COVID-19 pandemic, investments in infrastructure, and strengthening the safety net, funded by tax increases on higher-income individuals and corporations. Other goals include: increasing the national minimum wage and expanding worker training; narrowing income inequality; expanding access to affordable healthcare; and forgiveness of student loan debt. The March 2021 enactment of the American Rescue Plan to provide relief from the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was the first major element of the policy. Biden's Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act was signed into law in November 2021 and contains about $550 billion in additional investment. His Inflation Reduction Act was enacted in August 2022. Biden's first year in office saw strong growth in real GDP, wages, employment, and stock market returns, coupled with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
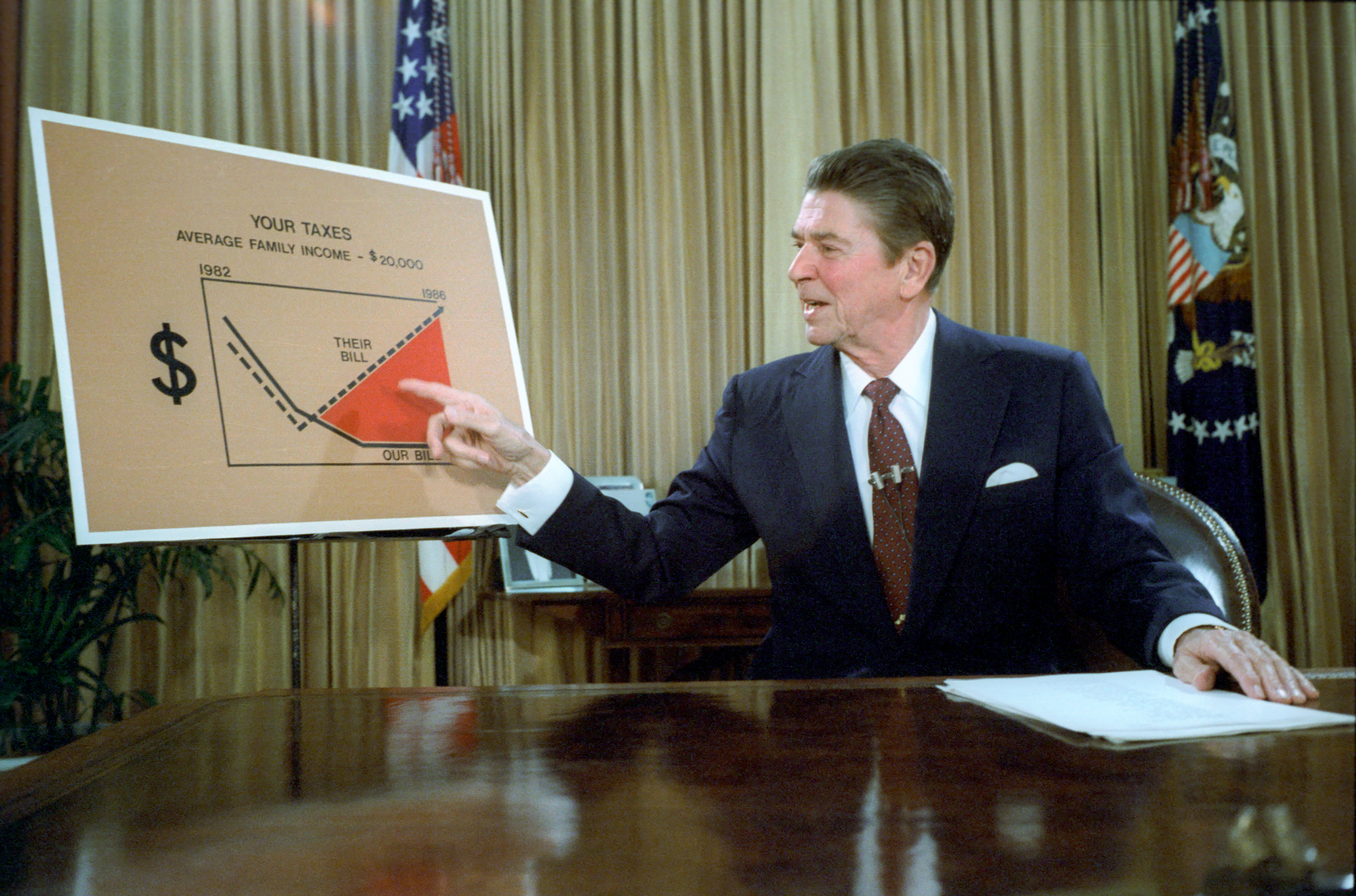
Reaganomics
Reaganomics (; a portmanteau of ''Reagan'' and ''economics'' attributed to Paul Harvey), or Reaganism, refers to the neoliberal economic policies promoted by U.S. President Ronald Reagan during the 1980s. These policies are commonly associated with and characterized as supply-side economics, trickle-down economics, or "voodoo economics" by opponents, while Reagan and his advocates preferred to call it free-market economics. The pillars of Reagan's economic policy included increasing defense spending, balancing the federal budget and slowing the growth of government spending, reducing the federal income tax and capital gains tax, reducing government regulation, and tightening the money supply in order to reduce inflation. The results of Reaganomics are still debated. Supporters point to the end of stagflation, stronger GDP growth, and an entrepreneurial revolution in the decades that followed. Critics point to the widening income gap, what they described as an atmosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Of Oil
The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel () of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level. The global price of crude oil was relatively consistent in the nineteenth century and early twentieth century. This changed in the 1970s, with a significant increase in the price of oil globally. There have been a number of structural drivers of global oil prices historically, including oil supply, demand, and storage shocks, and shocks to global economic growth affecting oil prices. Notable events driving significant price fluctuations include the 1973 OPEC oil embargo targeting nations that had supported Israel during the Yom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)