|
Nitroxinil
Nitroxinil is an anthelmintic, a veterinary medicine against parasitic worms in sheep and cattle. The substance is active against the liver fluke the ''Fasciola hepatica'' and to a lesser extent against thread worms in the gastrointestinal tract. Brand names include Fluconix, Dovenix and Trodax. Nitroxynil is also used against strains of the red gum worm (Haemonchus contortus) that have become resistant to benzimidazoles. Nitroxinil was invented by May & Baker in the mid 1960s as part of a program into investigation of derivatives of p-hydroxybenzonitrile. In addition to Nitroxynil, the herbicides ioxynil (3,5-diiodo) and bromoxynil Bromoxynil is an organic compound with the formula HOBr2C6H2CN. It is classified as a nitrile herbicide, and as such sold under many trade names. It is a white solid. It works by inhibiting photosynthesis. It is moderately toxic to mammals. ... (3,5-dibromo) were also invented by the same company. Nitroxynil has a nitro group in addition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthelmintic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic, antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may also be called vermifuges (those that stun) or vermicides (those that kill). Anthelmintics are used to treat people who are infected by helminths, a condition called helminthiasis. These drugs are also used to treat infected animals. Pills containing anthelmintics are used in mass deworming campaigns of school-aged children in many developing countries. The drugs of choice for soil-transmitted helminths are mebendazole and albendazole; for schistosomiasis and tapeworm, tapeworms it is praziquantel. Types Antiparasitics that specifically target worms of the genus ''Ascaris'' are called ascaricides. * Benzimidazoles: ** Albendazole – effective against Strongyloides stercoralis, threadworms, roundworms, whipworms, tapeworms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
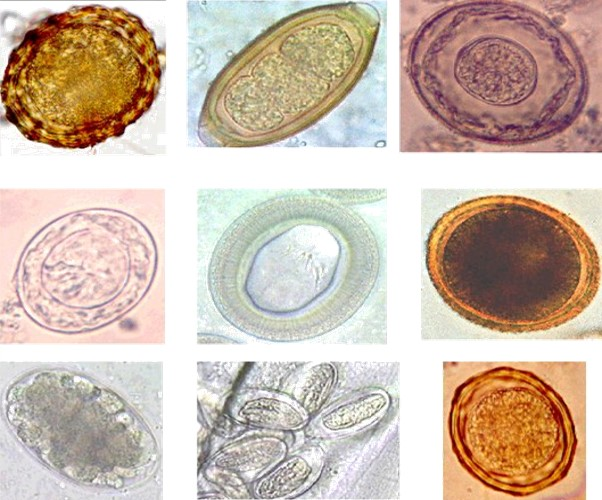
Parasitic Worms
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large Parasitism#Basic concepts, macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted helminth, soil-transmitted and intestinal parasite infection, infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are Parasitism#Basic concepts, endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living host (biology), hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Fluke
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes. They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also in bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver parenchyma. In these organs, they produce pathological lesions leading to parasitic diseases. They have complex life cycles requiring two or three different hosts, with free-living larval stages in water. Biology The body of liver flukes is leaf-like and flattened. The body is covered with a tegument. They are hermaphrodites having complete sets of both male and female reproductive systems. They have simple digestive systems and primarily feed on blood. The anterior end is the oral sucker opening into the mouth. Inside, the mouth leads to a small pharynx which is followed by an extended intestine that runs through the entire length of the body. The intestine is heavily branched a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola Hepatica
''Fasciola hepatica'', also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitism, parasitic trematode (fluke or flatworm, a type of helminth) of the class (biology), class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans, and is transmitted by sheep and cattle to humans the world over. The disease caused by the fluke (flatworm), fluke is called fasciolosis or fascioliasis, which is a type of helminthiasis and has been classified as a neglected tropical disease. Fasciolosis is currently classified as a plant/food-borne trematode infection, often acquired through eating the parasite's Trematode life cycle stages, metacercariae encysted on plants. ''F. hepatica'', which is distributed worldwide, has been known as an important parasite of sheep and cattle for decades and causes significant economic losses in these livestock species, up to £23 million in the UK alone. Because of its relatively large size and economic impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemonchus Contortus
''Haemonchus contortus'', also known as the barber's pole worm, is a very common parasite and one of the most pathogenic nematodes of ruminants. Adult worms attach to abomasum, abomasal mucosa and feed on the blood. This parasite is responsible for anemia, oedema, and death of infected sheep and goats, mainly during summer in warm, humid climates. Females may lay over 10,000 eggs a day, which pass from the host animal in the faeces. After hatching from their eggs, ''H. contortus'' larvae ecdysis, molt several times, resulting in an L3 form that is infection, infectious for the animals. The host ingests these larvae when grazing. The L4 larvae, formed after another molt, and adult worms suck blood in the abomasum of the animal, potentially giving rise to anaemia and oedema, which eventually can lead to death. The infection, called haemonchosis, causes large economic losses for farmers around the world, especially for those living in warmer climates. Anthelminthics are used to prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazoles
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a colorless solid. Preparation Benzimidazole is produced by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid,. or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate: :C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH 2-substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation.Robert A. Smiley "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions Benzimidazole is a base: :C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → 6H4(NH)2CHsup>+ It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases: :C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li 6H4N2CH + H2 The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry. The most prominent benzimidazole complex features ''N''-ribosyl-dimethylbenzimidazole as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May & Baker
May & Baker was a British chemical company founded by John May and William Gerrard Baker in Wandsworth, London in 1839. They initially specialized in the manufacture of chemicals derived from mercury and bismuth. Over the years they diversified into other chemical fields including photographic chemicals, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and chemicals for research and development. The company was bought by Établissements Poulenc Frères (later to become Société des Usines Chimiques Rhône-Poulenc) in 1922, and subsequently moved to Dagenham, Essex, although it continued to trade under the May & Baker name. During this time May & Baker branched into pharmaceuticals, with one of their major discoveries being sulphapyridine (M&B 693), first produced in 1937. This compound, May & Baker's most famous product, was one of the first generation of sulfonamide antibiotics. During WW2, M&B 693 saved many thousands of lives, including Sir Winston Churchill who was treated with it for pn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoxynil
Bromoxynil is an organic compound with the formula HOBr2C6H2CN. It is classified as a nitrile herbicide, and as such sold under many trade names. It is a white solid. It works by inhibiting photosynthesis. It is moderately toxic to mammals. Production and use It is produced by bromination of 4-hydroxybenzonitrile. It is a post-emergence to control annual broadleaved weeds.Franz Müller and Arnold P. Applebyki "Weed Control, 2. Individual Herbicides" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2010 Degradation Bromoxynil decomposes with a half life of approximately two weeks in soil. Persistence increases in soils with elevated clay or organic matter content, suggesting the compound has somewhat limited bioavailability to microorganisms in these environments. Under aerobic conditions in soils or pure cultures, products of bromoxynil degradation often retain the original bromine groups. The herbicide, and one of its common degradation products (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiparasitic Agents
Antiparasitics are a class of medications which are indicated for the treatment of parasitic diseases, such as those caused by helminths, amoeba, ectoparasites, parasitic fungi, and protozoa, among others. Antiparasitics target the parasitic agents of the infections by destroying them or inhibiting their growth; they are usually effective against a limited number of parasites within a particular class. Antiparasitics are one of the antimicrobial drugs which include antibiotics that target bacteria, and antifungals that target fungi. They may be administered orally, intravenously or topically. Broad-Spectrum antiparasitics, analogous to broad-spectrum antibiotics for bacteria, are antiparasitic drugs with efficacy in treating a wide range of parasitic infections caused by parasites from different classes. Types Broad-spectrum * Nitazoxanide Antiprotozoals * Melarsoprol (for treatment of sleeping sickness caused by '' Trypanosoma brucei'') * Eflornithine (for sleeping si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |