|
Nitrogen Fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment, or hand-tool methods. Historically, fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations, and byproducts of human-nature industries (e.g. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from animal slaughter). However, starting in the 19th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manure Spreading Hlokozi 2007 11 29
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the soil fertility, fertility of soil by adding organic matter and nutrients, such as nitrogen, that are utilised by bacteria, fungus, fungi, and other organisms in the soil. Higher organisms then feed on the fungi and bacteria in a chain of life that comprises the soil food web. Types There are in the 21st century three main classes of manures used in soil management: Animal manure Most animal manure consists of feces. Common forms of animal manure include farmyard manure (or farm slurry (liquid manure). Farmyard manure also contains plant material (often straw), which has been used as bedding for animals and has absorbed the feces and urine. Agricultural manure in liquid form, known as slurry, is produced by more intensive livestock rearing systems where concrete or slats are used instead of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food System
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition, food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a population: growing, harvesting, processing, packaging, transporting, marketing, consumption, distribution, and disposal of food and food-related items. It also includes the inputs needed and outputs generated at each of these steps. Food systems fall within agri-food systems, which encompass the entire range of actors and their interlinked value-adding activities in the primary production of food and non-food agricultural products, as well as in food storage, aggregation, post-harvest handling, transportation, processing, distribution, marketing, disposal, and consumption. A food system operates within and is influenced by social, political, economic, technological and environmental contexts. It also requires human resources that provide labor, research a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Impact Of Agriculture
The environmental impact of agriculture is the effect that different farming practices have on the ecosystems around them, and how those effects can be traced back to those practices. The environmental impact of agriculture varies widely based on practices employed by farmers and by the scale of practice. Farming communities that try to reduce environmental impacts through modifying their practices will adopt sustainable agriculture practices. The negative impact of agriculture is an old issue that remains a concern even as experts design innovative means to reduce destruction and enhance eco-efficiency. Animal agriculture practices tend to be more environmentally destructive than agricultural practices focused on fruits, vegetables and other biomass. The emissions of ammonia from cattle waste continue to raise concerns over environmental pollution. When evaluating environmental impact, experts use two types of indicators: "means-based", which is based on the farmer's production m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species. Definition The word pesticide derives from the Latin ''pestis'' (plagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is agriculture, farming in sustainability, sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an understanding of ecosystem services. There are many methods to increase the sustainability of agriculture. When developing agriculture within the sustainable food systems, it is important to develop flexible business processes and farming practices. Agriculture has an enormous environmental impact of agriculture, environmental footprint, playing a significant role Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, in causing climate change (food systems are responsible for one third of the anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions), water scarcity, water pollution, land degradation, deforestation and other processes; it is simultaneously causing environmental changes and being impacted by these changes. Sustainable agriculture consists of environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Contamination
Soil contamination, soil pollution, or land pollution as a part of land degradation is caused by the presence of xenobiotic (human-made) chemicals or other alteration in the natural soil environment. It is typically caused by industrial activity, agricultural chemicals or improper disposal of waste. The most common chemicals involved are petroleum hydrocarbons, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (such as naphthalene and benzo(a)pyrene), solvents, pesticides, lead, and other heavy metals. Contamination is correlated with the degree of industrialization and intensity of chemical substance. The concern over soil contamination stems primarily from health risks, from direct contact with the contaminated soil, vapour from the contaminants, or from secondary contamination of water supplies within and underlying the soil. Mapping of contaminated soil sites and the resulting clean ups are time-consuming and expensive tasks, and require expertise in geology, hydrology, chemistry, computer m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
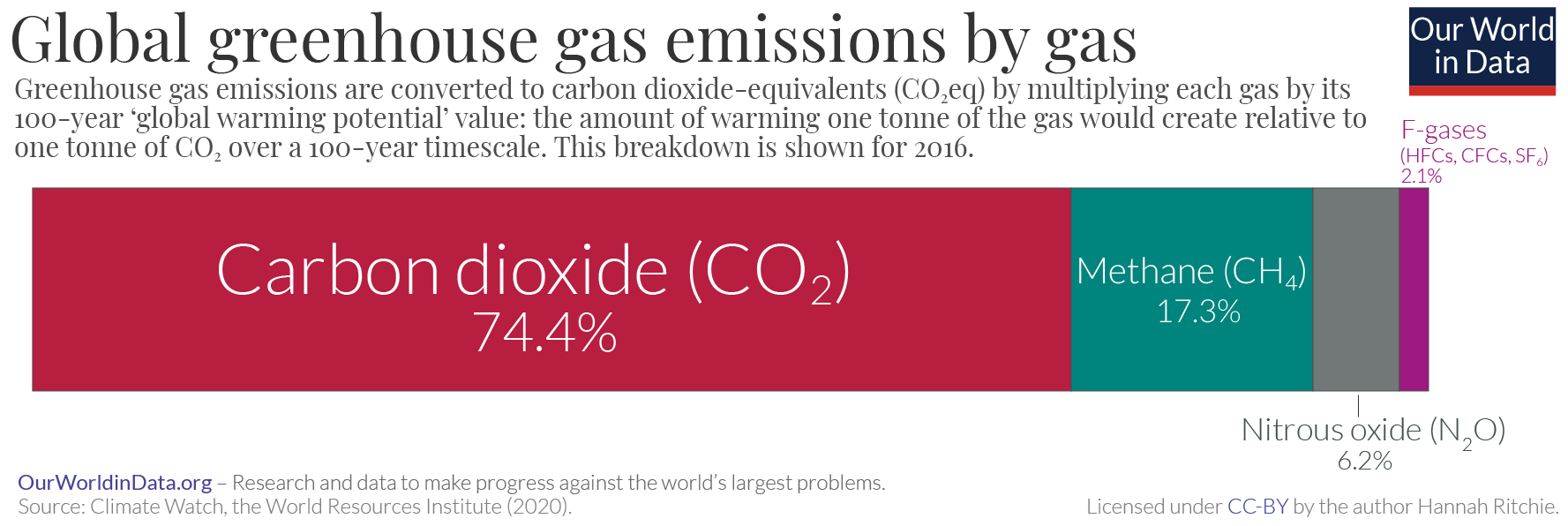
Carbon Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the surface of a river, lake, etc., often because chemicals that are used to help crops grow have been carried there by rain. Eutrophication may occur naturally or as a result of human actions. Manmade, or cultural, eutrophication occurs when sewage, Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater, fertilizer runoff, and other nutrient sources are released into the environment. Such nutrient pollution usually causes algal blooms and bacterial growth, resulting in the depletion of dissolved oxygen in water and causing substantial environmental degradation. Many policies have been introduced to combat eutrophication, including the United Nations Development Program (UNDP)'s sustainability development goals. Approaches for prevention and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants mix with these water bodies. Contaminants can come from one of four main sources. These are sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. Water pollution may affect either surface water or groundwater pollution, groundwater. This form of pollution can lead to many problems. One is the environmental degradation, degradation of aquatic ecosystems. Another is spreading Waterborne diseases, water-borne diseases when people use polluted water for drinking or irrigation. Water pollution also reduces the ecosystem services such as drinking water provided by the Water resources, water resource. Sources of water pollution are either p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
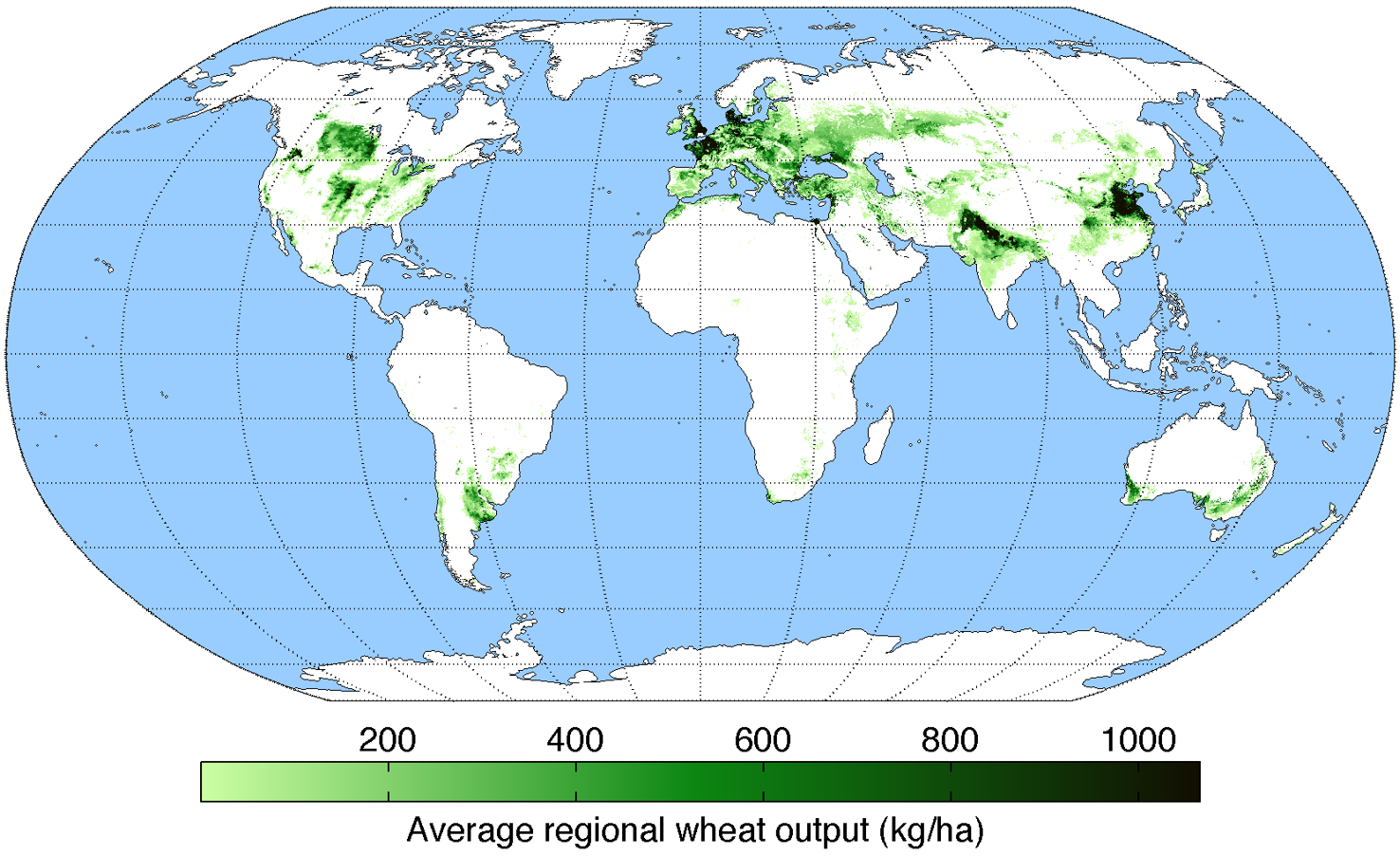
Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , developed countries in the early 20th century and subsequently spread globally until the late 1980s. In the late 1960s, farmers began incorporating new technologies, including High-yielding variety, high-yielding varieties of cereals, particularly dwarf wheat and rice, and the widespread use of Fertilizer, chemical fertilizers (to produce their high yields, the new seeds require far more fertilizer than traditional varieties), Pesticide , pesticides, and controlled irrigation. At the same time, newer methods of cultivation, including mechanization, were adopted, often as a package of practices to replace traditional agricultural technology. This was often in conjunction with loans conditional on policy changes being made by the Developing coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Food Systems
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition, Human food, food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a population: growing, harvesting, processing, Food packaging, packaging, transporting, Agricultural marketing, marketing, consumption, Food distribution, distribution, and disposal of food and food-related items. It also includes the inputs needed and outputs generated at each of these steps. Food systems fall within agri-food systems, which encompass the entire range of actors and their interlinked value-adding activities in the primary production of food and non-food agricultural products, as well as in food storage, aggregation, post-harvest handling, transportation, processing, distribution, marketing, disposal, and consumption. A food system operates within and is influenced by social, political, economic, technological and environmental co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haber Process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely divided iron metal as a catalyst: \ce \qquad This reaction is exothermic but disfavored in terms of entropy because four equivalents of reactant gases are converted into two equivalents of product gas. As a result, high pressures and temperatures that are not too high are needed to Le_Chatelier's_principle, drive the reaction forward. The German chemists Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch developed the process in the first decade of the 20th century, and its improved efficiency over existing methods such as the Birkeland–Eyde process, Birkeland-Eyde and Frank–Caro process, Frank-Caro processes was a major advancement in the industrial production of ammonia. The Haber process can be combined with steam reforming to produce ammonia with just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |