|
Nikon Z6III
The Nikon Z6III is a mid-range full-frame mirrorless camera produced by Nikon. The camera was announced on June 17, 2024. Features Image sensor The Z6III features a 24.5-megapixel, partially stacked CMOS sensor, which enables the camera to match the 120fps burst ( DX format, 10MP only) capability of the Nikon Z8 and Z9 cameras with fully stacked CMOS sensors. Due to this, Z6III has the fastest readout speed in its class as of June 2024. Image processor The Z6III uses the EXPEED 7 image processor, which are also used in Nikon Zf, Z8, Z9, and Z50II. Video capability For videographers, the Z6III supports 6K video recording at 60 frames per second. Additionally, it offers 4K recording at 120 frames per second and Full HD at 240 frames per second. The camera includes features such as focus peaking, zebra patterns, and customizable picture profiles to aid in achieving professional-grade video quality. Autofocus and subject detection The Z6 III's autofocus system util ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon Nikkor Z 24-120 Mm F/4 S
The Nikon Nikkor Z 24-120 mm S is a full-frame standard zoom lens with a constant aperture of , manufactured by Nikon for use on Nikon Z-mount mirrorless cameras. Introduction The lens was introduced on October 28, 2021 (along with the Nikkor Z 100-400 mm VR S and FTZ II mount adapter). The lens comes with a bayonet-type lens hood (HB-102). Features * 24-120 mm focal length (approximately equivalent field of view of a 36-180 mm lens when used on a DX format camera) * Nikon Z-mount#Z-mount lenses, S-Line lens * Autofocus using dual stepping motors (STM), dedicated focus-by-wire manual focus ring (at the front of the lens) * 16 elements in 13 groups (including 3 ED, 1 aspherical ED glass, 3 aspherical lens elements, elements with Nano Crystal Coat and ARNEO Coat, and a fluorine-coated front lens element) * 9-blade rounded diaphragm * Internal focusing (IF lens) * One customizable control ring at the back (aperture, ISO and exposure compensation functions c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ProRes RAW
Apple ProRes is a high quality, "visually lossless" lossy video compression format developed by Apple Inc. for use in post-production that supports video resolution up to 8K. It is the successor of the Apple Intermediate Codec and was introduced in 2007 with Final Cut Studio 2. Much like the H.26x and MPEG standards, the ProRes family of codecs use compression algorithms based on the discrete cosine transform (DCT). ProRes is widely used as a final format delivery method for HD broadcast files in commercials, features, Blu-ray and streaming. Overview ProRes is a line of intermediate codecs, which means they are intended for use during video editing, and not for practical end-user viewing. This is achieved by only using intra-frame compression, where each frame is stored independently and can be decoded with no dependencies on other frames. The benefit of an intermediate codec is that it offers excellent random access performance in post-production applications, and retains highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
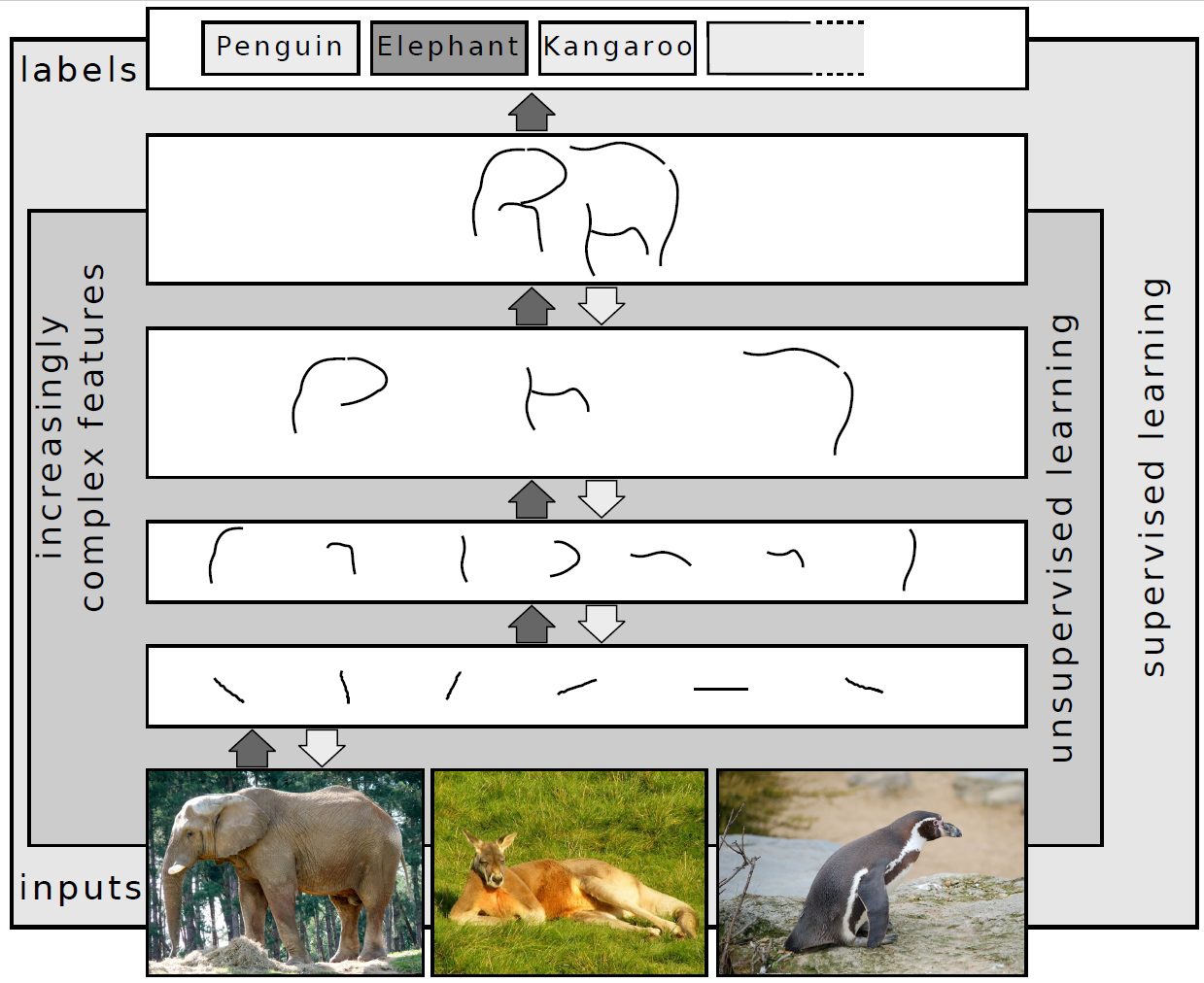
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autofocus
An autofocus (AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication. Autofocus methods are distinguished as active, passive or hybrid types. Autofocus systems rely on one or more sensors to determine correct focus. Some AF systems rely on a single sensor, while others use an array of sensors. Most modern SLR cameras use through-the-lens optical sensors, with a separate sensor array providing light metering, although the latter can be programmed to prioritize its metering to the same area as one or more of the AF sensors. Through-the-lens optical autofocusing is usually speedier and more precise than manual focus with an ordinary viewfinder, although more precise manual focus can be achieved with special accessories such as focusing magnifiers. Autofocus accur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus Peaking
Focus peaking is a focusing aid in live preview or electronic viewfinder An electronic viewfinder (EVF) is a camera viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is displayed on a small screen (usually LCD or OLED) which the photographer can look through when composing their shot. It differs from a live preview sc ...s on digital cameras that places a white or coloured highlight on in-focus edges (contours) within an image using an edge detect filter. It was initially only common on video cameras, as the feature is incompatible with the optical viewfinders found on DSLRs. Some external monitors and some image organisation programs can also perform focus peaking separately from the camera body. It is sometimes referred to as "focus assist" or "peaking highlights". Focus peaking is fast but it is considered to be inferior to digitally zooming in, and is not recommended when taking pictures with either a very narrow or very wide depth of field. References {{photography-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon Zf
The Nikon Zf is a Mirrorless camera, mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera with the Nikon Z-mount with a list price of $1999 body only, in the US. History The camera was announced on 20 September 2023 and was shipped out to customers in Japan on 27 October 2023 (others unknown). On 25 September 2023, Nikon announced that the Zf is expected for delayed delivery for some customers due to unexpected order volume. __TOC__ Features The Zf is a full-frame camera believed to use the same 24.5MP BSI-CMOS sensor used in the Nikon Z6II, as its official specifications are the same. It has a 273-point phase-detection autofocus system and can shoot up to 10 frames per second in normal mode, and 14 frames per second in expanded mode. Although it closely resembles the Nikon Zfc, which was also based on the design of Nikon's classic Nikon FM2, FM2 with almost the same internals of Nikon Z50, there are number of upgrades on the Zf, even in comparison to the Z6II on which the camera internals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss ", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type semiconductor, p-type and n-type semiconductor, n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including Nonvolatile BIOS memory, CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data conversion, data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1948, Bardeen and Brattain patented an insulated-gate transistor (IGFET) with an inversion layer. Bardeen's concept forms the basis of CMOS technology today. The CMOS process was presented by Fairchild Semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon Z9
The Nikon Z9 is a flagship full-frame mirrorless camera produced by Nikon. The camera was announced on October 28, 2021. It is the eighth Z-mount camera body and the sixth full-frame Z-mount body. The Z9 has the same 45.7 MP resolution as the Z7 and Z7II cameras, but uses a much faster stacked CMOS sensor which improves autofocus and continuous shooting performance. The Z9 introduced the EXPEED 7 image processor, which provides an improvement of 10 times over the image processing speed of the EXPEED 6 predecessor, which was used in the previous Nikon full-frame Z6II and Z7II cameras. The continuous shooting capabilities of the Z9 significantly exceed those of Nikon's previous Nikon D6 while providing more than double the resolution. The Z9 is the first Nikon Z camera to support 8K video, which can be recorded internally at 60 fps in 12-bit N-RAW. The Z9 is the first flagship full-frame camera without a mechanical shutter. In January of 2024, Nikon revealed that NASA la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon Z8
The Nikon Z8 is a high-end full-frame mirrorless camera produced by Nikon. The camera was announced on May 10, 2023. It is the tenth Z-mount camera body and the seventh full-frame Z-mount body. Features The Z8 has the same 45.7 MP stacked CMOS sensor as the Z9, with identical autofocus and video capabilities to the Z9, but in an around 30% smaller body, comparable to that of the D850, but approximately 100 grams lighter. Aircraft (civilian and military) were added to the subject detection autofocus. The camera utilizes an electronic shutter with speeds up to 1/32000 sec and includes 5-axis in-body image stabilization. The battery is the same EN-EL15 series used in the Z5/6/7 and various DSLRs; the much larger EN-EL18 batteries for the Z9 and D4/5/6 DSLRs cannot be used. HEIF was added as a recording format. The magnesium alloy and a new material developed by Teijin give it the same dust and water resistance as the D850. Firmware version 2.0 introduced Auto Capture (automati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon DX Format
The Nikon DX format is an alternative name used by Nikon corporation for APS-C image sensor format being approximately 24x16 mm. Its dimensions are about (29 mm vs 43 mm diagonal, approx.) those of the 35mm format. The format was created by Nikon for its digital SLR cameras, many of which are equipped with DX-sized sensors. DX format is very similar in size to sensors from Pentax, Sony and other camera manufacturers. All are referred to as APS-C, including the Canon cameras with a slightly smaller sensor. Nikon has produced 23 lenses for the DX format, from macro to telephoto lenses. 35mm format lenses can also be used with DX format cameras, with additional advantages: less vignetting, less distortion and often better border sharpness. Disadvantages of 35mm lenses include generally higher weight and incompatible features such as autofocus with some lower-end DX cameras. Nikon has also produced digital SLRs that feature the larger Nikon FX format sensor that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back-illuminated Sensor
Comparison of simplified back-illuminated and front-illuminated pixel cross-sections A back-illuminated (BI) sensor, also known as back-side illumination (BSI) sensor, is a type of digital image sensor that uses a novel arrangement of the imaging elements to increase the amount of light captured and thereby improve low-light performance. The technique was used for some time in specialized roles like low-light security cameras and astronomy sensors, but was complex to build and required further refinement to become widely used. Sony was the first to reduce these problems and their costs sufficiently to introduce a 5-megapixel 1.75 μm BI CMOS sensor at general consumer prices in 2009.''Sony'', 2009 BI sensors from OmniVision Technologies have since been used in consumer electronics from other manufacturers as in the HTC EVO 4G Android smartphone, and as a major selling point for the camera in Apple's iPhone 4.''Apple'', 2010 Description A traditional, front-illuminated di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirrorless Camera
A mirrorless camera (sometimes referred to as a mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera (MILC) or digital single-lens mirrorless (DSLM)) is a digital camera which, in contrast to DSLRs, does not use a mirror in order to ensure that the image presented to the photographer through the viewfinder is identical to that taken by the camera. They have come to replace DSLRs, which have historically dominated interchangeable lens cameras. Other terms include electronic viewfinder interchangeable lens (EVIL) and compact system camera (CSC). When compared to similar DSLRs, these cameras can be smaller, lighter, and quieter. In cameras with mirrors, light from the lens is directed to either the image sensor or the viewfinder. This is done using a mechanical movable mirror which sits behind the lens. By contrast, in a mirrorless camera, the lens always shines light onto the image sensor, and what the camera sees is displayed on a screen for the photographer. Some mirrorless cameras also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |