|
Nikon 1 J1
The Nikon 1 J1 is a Nikon 1 series high-speed mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera with 1" sensor size launched by Nikon on September 21, 2011. It is a new model that focuses on high-performance, portability and versatility. Nikon lists the estimated selling price of the Nikon 1 J1 One-Lens Kit in the United States at $649.95. Released on October 20, 2011, this kit comes with the 1 NIKKOR VR 10-30mm f/3.5-5.6 lens. This camera integrates many new technologies and is designed for ease of use, sporting only four shooting modes: Still Images, Moving Images, Motion Snapshot and Smart Photo Selector and only two buttons for Power, Shutter and Record. Nikon 1 J1 has an all-new Nikon 1 lens mount, which has made lens changes simpler and quicker. The successor is the J2. Features The Nikon 1 J1 uses interchangeable lenses with Nikon 1 mount. It features a 2.7x lens focal length and 10.1 million pixels. The camera has 1080p Full HD movie capability, as well as slow motion movie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon
(, ; ) is a Japanese optics and photographic equipment manufacturer. Nikon's products include cameras, camera lenses, binoculars, microscopes, ophthalmic lenses, measurement instruments, rifle scopes, spotting scopes, and equipment related to Semiconductor device fabrication, semiconductor fabrication, such as Stepper, steppers used in the photolithography steps of such manufacturing. Nikon is the world's second largest manufacturer of such equipment. Since July 2024, Nikon has been headquartered in Nishi-Ōi, Shinagawa, Shinagawa, Tokyo where the plant has been located since 1918. The company is the eighth-largest chip equipment maker as reported in 2017. Also, it has diversified into new areas like 3D printers, 3D printing and regenerative medicine to compensate for the shrinking digital camera market. Among Nikon's many notable product lines are Nikkor imaging lenses (for Nikon F-mount, F-mount cameras, large format photography, photographic enlargers, and other applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
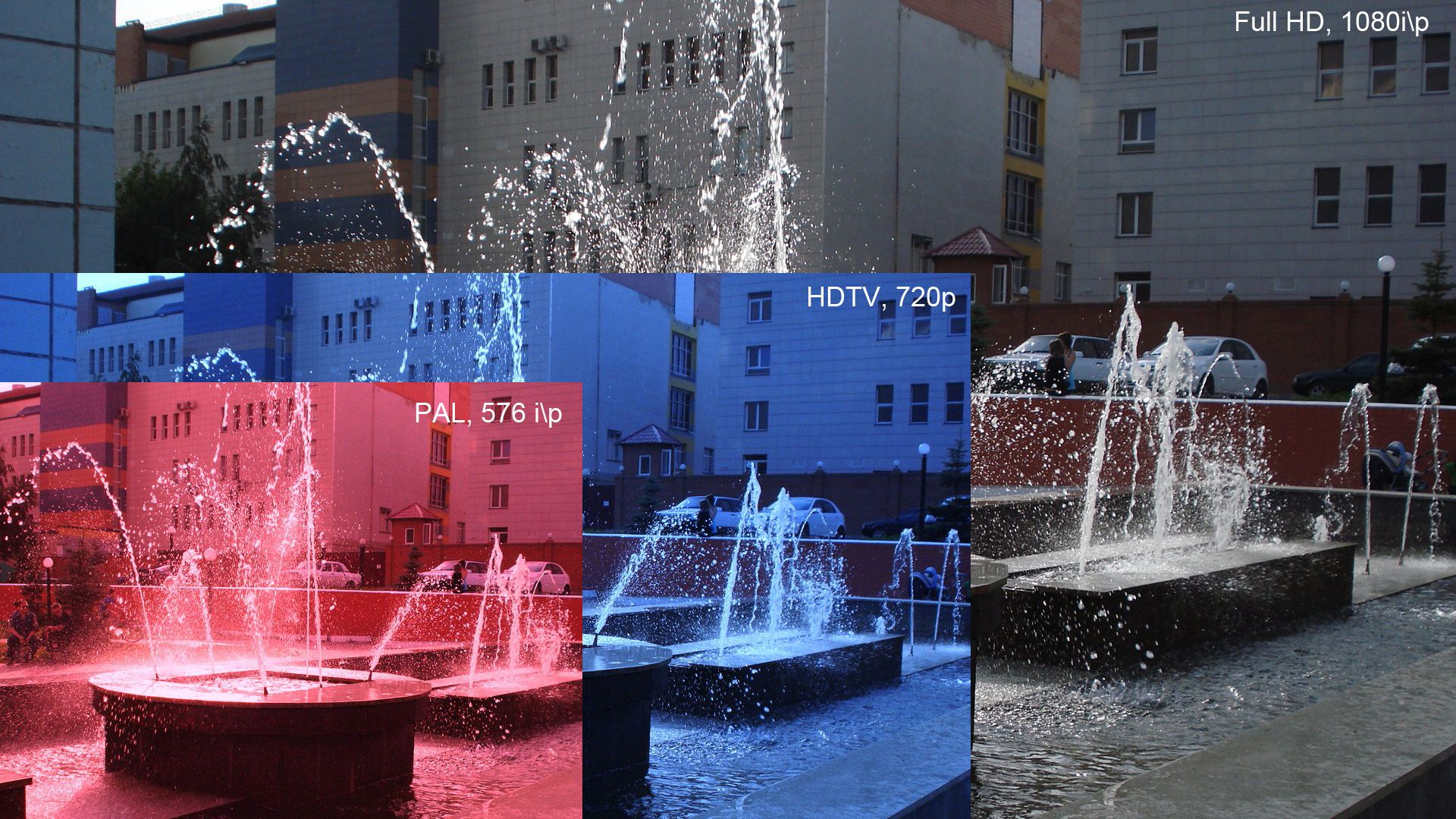
1080p
1080p (1920 × 1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non- interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes referred to as 2K resolution (meaning having a horizontal resolution of approximately 2,000 pixels), other sources differentiate between 1080p and (true) 2K resolution. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taipeh Imbiss
, nickname = The City of Azaleas , image_map = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Taiwan#Asia#Pacific Ocean#Earth , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Taiwan , established_title = Settled , established_date = 1709 , established_title1 = Renamed Taihoku , established_date1 = 17 April 1895 , established_title2 = Provincial city (Taiwan), Provincial city status , established_date2 = 25 October 1945 , established_title3 = Retreat of the government of the Republic of China to Taiwan, Provisional national capital , established_date3 = 7 December 1949 , established_title4 = Reconstituted as a Yuan-controlled municipality , established_date4 = 1 July 1967 , capital_type = City seat , capital = Xinyi District, Taipei, Xinyi District , largest_settlement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposure Value
In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera's shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure (photography), exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance). Exposure value is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale, with a difference of 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop. The EV concept was developed by the German shutter manufacturer Friedrich Deckel in the 1950s (#CITEREFGebele1958, Gebele 1958; #CITEREFRay2000, Ray 2000, 318). Its intent was to simplify choosing among equivalent camera exposure settings by replacing combinations of shutter speed and f-number (e.g., 1/125 s at ) with a single number (e.g., 15). On some lenses with Shutter (photography)#Diaphragm shutter, leaf shutters, the process was further simplified by allowing the shutter and aperture controls to be linked such that, when one w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochrome Photography
Monochrome photography is photography where each position on an image can record and show a different ''amount'' of light (Value (color), value), but not a different color (hue). The majority of monochrome photographs produced today are black-and-white, either from a gelatin silver process, or as digital photography. Other hues besides grey can be used to create monochrome photography, but brown and Sepia (color), sepia tones are the result of older processes like the albumen print, and cyan tones are the product of cyanotype prints. As monochrome photography provides an inherently less accurate reproduction than color photography, it is mostly used for artistic purposes and certain Imaging, technical imaging applications. Description Although methods for color photography, photographing in color emerged slowly starting in the 1850s, monochrome imagery dominated photography until the mid–twentieth century. From the start, photographic recording processes such as the dague ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Photography
Color photography (also spelled as colour photography in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is photography that uses media capable of capturing and reproducing colors. By contrast, black-and-white or gray-monochrome photography records only a single channel of luminance (brightness) and uses media capable only of showing shades of gray. In color photography, electronic sensors or light-sensitive chemicals record color information at the time of exposure (photography), exposure. This is usually done by analyzing the spectrum of colors into three channels of information, one dominated by red, another by green and the third by blue, in imitation of the way the normal color vision#Physiology of color perception, human eye senses color. The recorded information is then used to reproduce the original colors by mixing various proportions of red, green and blue light (RGB color, used by video displays, digital projectors and some historical photographic proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close-up
A close-up or closeup in filmmaking, television production A television show, TV program (), or simply a TV show, is the general reference to any content produced for viewing on a television set that is broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, and cable, or distributed digitally on streaming plat ..., photography, still photography, and the comic strip medium is a type of shot (filmmaking), shot that tightly film frame, frames a person or object. Close-ups are one of the standard shots used regularly with medium and long shots (cinematic techniques). Close-ups display the most detail, but they do not include the broader scene. Moving toward or away from a close-up is a common type of zooming (filmmaking), zooming. A close up is taken from head to neck, giving the viewer a detailed view of the subject's face. History Most early filmmakers, such as Thomas Edison, Auguste and Louis Lumière and Georges Méliès, tended not to use close-ups and preferred to frame their s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Digital Camera Modes
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of ''The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processing Engine
An image processor, also known as an image processing engine, image processing unit (IPU), or image signal processor (ISP), is a type of media processor or specialized digital signal processor (DSP) used for image processing, in digital cameras or other devices. Image processors often employ parallel computing even with SIMD or MIMD technologies to increase speed and efficiency. The digital image processing engine can perform a range of tasks. To increase the system integration on embedded devices, often it is a system on a chip with multi-core processor architecture. Function Bayer transformation The photodiodes employed in an image sensor are color-blind by nature: they can only record shades of grey. To get color into the picture, they are covered with different color filters: red, green and blue (RGB) according to the pattern designated by the Bayer filter. As each photodiode records the color information for exactly one pixel of the image, without an image processor there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EXPEED
The Nikon Expeed image processor, image/video processors (often styled ''EXPEED'') are media processors for Nikon dslr, Nikon's digital cameras. They perform a large number of tasks: * Bayer filtering * demosaicing * image sensor corrections/dark-frame subtraction * image noise noise reduction, reduction * Unsharp masking, image sharpening * image scaling * gamma correction * image enhancement/Active D-Lighting * colorspace conversion * chroma subsampling * framerate conversion * image distortion, lens distortion/chromatic aberration correction * image compression/JPEG encoding * video compression * Electronic visual display, display/HDMI, video interface driving * digital image editing * face detection * Audio signal processing, audio processing/Audio compression (data)#Audio, compression/MP3, encoding and * computer data storage/data transmission. Expeed's Multiprocessor, multi-processor system on a chip solution integrates an image processor in multi-core processor architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Rate
Frame rate, most commonly expressed in frame/s, or FPS, is typically the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images (Film frame, frames) are captured or displayed. This definition applies to film and video cameras, computer animation, and motion capture systems. In these contexts, frame rate may be used interchangeably with and refresh rate, which are expressed in hertz. Additionally, in the context of computer graphics performance, FPS is the rate at which a system, particularly a GPU, is able to generate frames, and refresh rate is the frequency at which a display shows completed frames. In electronic camera specifications frame rate refers to the maximum possible rate frames could be captured, but in practice, other settings (such as exposure time) may reduce the actual frequency to a lower number than the frame rate. Human vision The temporal sensitivity and resolution of human vision varies depending on the type and characteristics of visual stimulus, and it differs betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Plane
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the '' focal points'', the principal points, and the nodal points; there are two of each. For ''ideal'' systems, the basic imaging properties such as image size, location, and orientation are completely determined by the locations of the cardinal points. For simple cases where the medium on both sides of an optical system is air or vacuum four cardinal points are sufficient: the two focal points and either the principal points or the nodal points. The only ideal system that has been achieved in practice is a plane mirror, however the cardinal points are widely used to the behavior of real optical systems. Cardinal points provide a way to analytically simplify an optical system with many components, allowing the imaging characteristics of the system to be approximately determined with simple calculations. Explanation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |