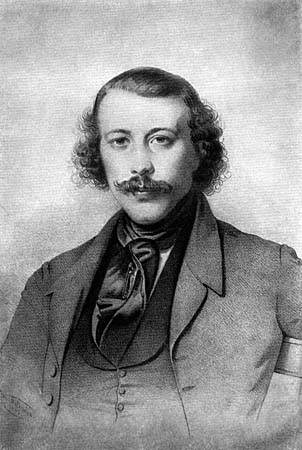|
Nikolay Speshnev
Nikolay Alexandrovich Speshnev (Russian: Николай Александрович Спе́шнев; 6 October 1821, Kursk – 29 March 1882, St. Petersburg) was a 19th-century Russian aristocrat and political activist, best known for his involvement with the pro-socialist literary discussion group the Petrashevsky Circle. He formed a secret revolutionary society from among the members of the circle, which included the young Fyodor Dostoevsky. After the government of Tsar Nicholas I arrested the members of the Petrashevsky Circle in 1849, Speshnev was interrogated, threatened with torture, and eventually sentenced, along with Dostoevsky, Petrashevsky and others, to execution by firing squad. The sentence was commuted to hard labour in Siberia, but the prisoners were only informed of this after enduring a mock execution. Dostoevsky drew on his experiences with Speshnev's secret society and the Petrashevsky Circle when writing his socio-political satire ''Demons''. The novel's central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memoirs Illustrating The History Of Jacobinism
''Memoirs Illustrating the History of Jacobinism'' (French: ''Mémoires pour servir à l’histoire du Jacobinisme'') is a book by Abbé Augustin Barruel, a French Jesuit priest. It was written and published in French in 1797–98, and translated into English in 1799. In the book, Barruel claims that the French Revolution was the result of a deliberate conspiracy or plot to overthrow the throne, altar and aristocratic society in Europe. The plot was allegedly hatched by a coalition of philosophes, Freemasons and the Order of the Illuminati. The conspirators created a system that was inherited by the Jacobins who operated it to its greatest potential. The ''Memoirs'' purports to expose the Revolution as the culmination of a long history of subversion. Barruel was not the first to make these charges but he was the first to present them in a fully developed historical context and his evidence was on a quite unprecedented scale. Barruel wrote each of the first three volumes of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
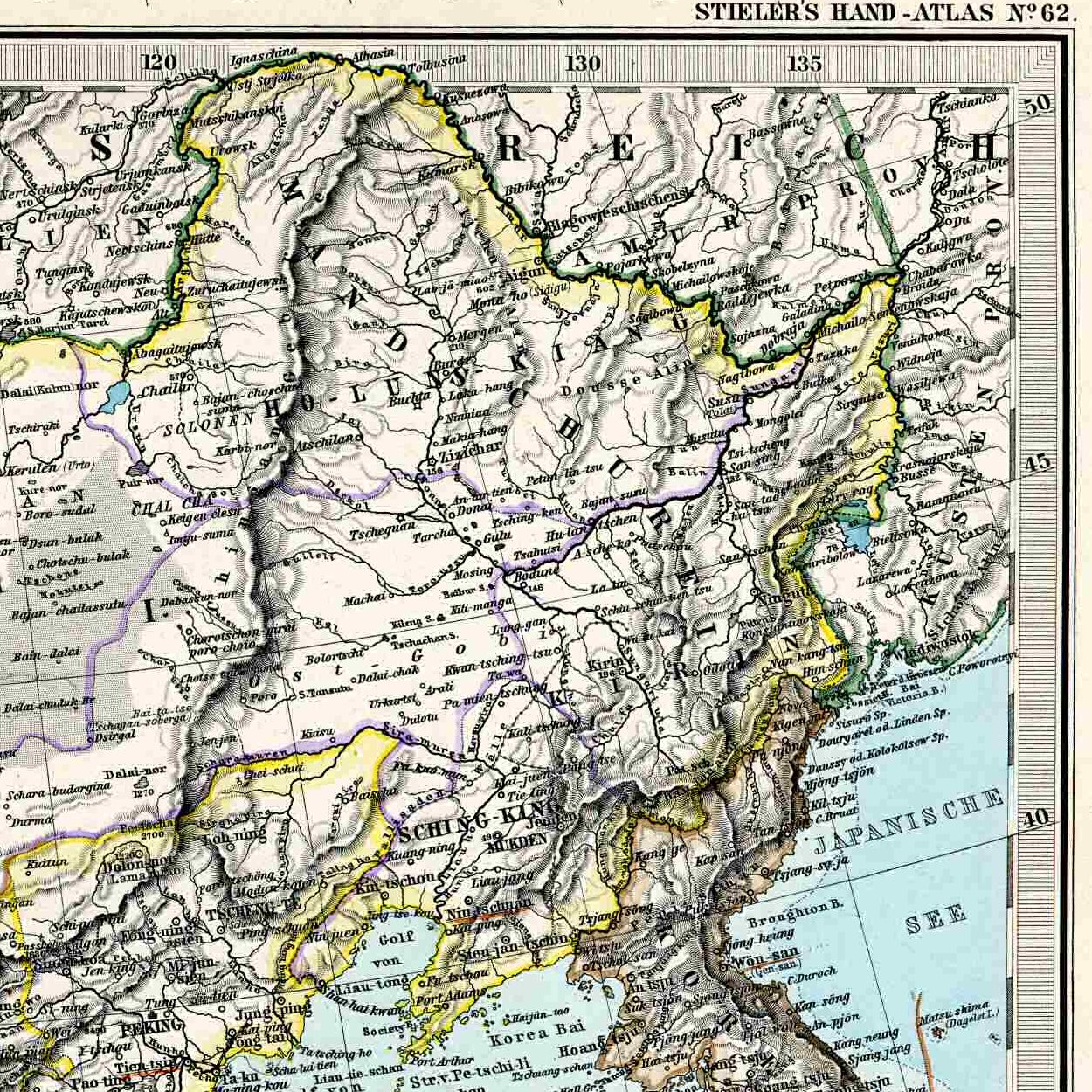
Amur River
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ''proper'' is long, and has a drainage basin of .Амур (река в Азии) If including its main stem , the Argun, the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Herzen
Alexander Ivanovich Herzen (; ) was a Russian writer and thinker known as the precursor of Russian socialism and one of the main precursors of agrarian populism (being an ideological ancestor of the Narodniki, Socialist-Revolutionaries, Trudoviks and the agrarian American Populist Party). With his writings, many composed while exiled in London, he attempted to influence the situation in Russia, contributing to a political climate that led to the emancipation of the serfs in 1861. He published the important social novel '' Who is to Blame?'' (1845–46). His autobiography, '' My Past and Thoughts'' (written 1852–1870), is often considered one of the best examples of that genre in Russian literature. Life Herzen (or Gertsen) was an illegitimate son of a rich Russian landowner, Ivan Yakovlev, and Henriette Wilhelmina Luisa Haag from Stuttgart. Yakovlev gave his son the surname Herzen because he was a "child of his heart" (German ''Herz''). He was first cousin to Count Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin. Sometimes anglicized to Michael Bakunin. ( ; – 1 July 1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist. He is among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major figure in the revolutionary socialist, social anarchist, and collectivist anarchist traditions. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing the Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. After participating in the 1848 Prague and 1849 Dresden uprisings, Bakunin was imprisoned, tried, sentenced to death, and extradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky
Count Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky (also spelled as Nikolai Nikolaevich Muraviev-Amurskiy; ; – ) was a Russian general, statesman and diplomat, who played a major role in the expansion of the Russian Empire into the Amur River basin and to the shores of the Sea of Japan. The surname Muravyov has also been transcribed as Muravyev or Murav'ev. Early life and career Nikolay Muravyov was born in Saint Petersburg and graduated from the Page Corps in 1827. He participated in the Siege of Varna in the Russo-Turkish War in 1828–1829, and later in suppression of the November Uprising in Poland in 1831. For health reasons, he retired from the military in 1833 and returned home to manage his father's estate. However, he returned to active duty in 1838, as General Golovin's aide-de-camp, to serve in the Caucasus region. During one of the campaigns against the mountain people Muravyov was wounded. . In 1840, Muravyov was assigned to command one of the sections of the Bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, 25th-largest city in Russia by population, the fifth-largest in the Siberian Federal District, and one of the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, cities in Siberia. Located in the south of the eponymous oblast, the city proper lies on the Angara River, a tributary of the Yenisei River, Yenisei, about 850 kilometres (530 mi) to the south-east of Krasnoyarsk and about 520 kilometres (320 mi) north of Ulaanbaatar. The Trans-Siberian Highway (Federal M53 and M55 Highways) and Trans-Siberian Railway connect Irkutsk to other regions in Russia and Mongolia. Many distinguished Russians were sent into exile in Irkutsk for their part in the Decembrist revolt of 1825, and the city became an exile-post for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerchinsky District
Nerchinsky District () is an administrativeRegistry of the Administrative-Territorial Units and the Inhabited Localities and municipalLaw #316-ZZK district (raion), one of the thirty-one in Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia. It is located in the center of the krai, and borders with Tungokochensky District in the north, Chernyshevsky District in the east, Baleysky District in the south, and with Shilkinsky District in the west. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Nerchinsk Nerchinsk (; , ''Nershüü''; , ''Nerchüü''; mnc, m=, v=Nibcu, a=Nibqu) is a town and the administrative center of Nerchinsky District in Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia, located on the left bank of the Nercha River, above its confluence with th .... Population: 30,694 ( 2002 Census); The population of Nerchinsk accounts for 52.6% of the district's total population. History The district was established on January 4, 1926. References Notes Sources * * * {{Use mdy d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobolsk
Tobolsk (, ) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1587, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, and was the historic capital of the Siberia region. Population: History Origins The town was founded on the site of the Tatar town of Bitsik-tura. In 1580, a group of Yermak Timofeyevich's Cossacks initiated the Russian conquest of Siberia, pushing eastwards on behalf of the Tsardom of Russia. After a year of Tatar attacks, Yermak prepared for the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir and a campaign to take the Khanate's capital city, Qashliq. The Cossacks conquered the city on 26 October 1582, sending Kuchum into retreat. Despite the conquest, Kuchum regrouped his remaining forces and formed a new army, launching a surprise attack on 6 August 1584, killing Yermak. There were a series of battles over Qashliq, which passed between Tatar and Cossack control, before the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter And Paul Fortress
The Peter and Paul Fortress () is the original citadel of Saint Petersburg, Russia, founded by Peter the Great in 1703 and built to Domenico Trezzini's designs from 1706 to 1740 as a star fortress. Between the first half of the 1700s and early 1920s it served as a prison for political criminals. It has been a museum since 1924. History From foundation until 1917 The fortress was established by Peter the Great on , on small Hare Island by the north bank of the Neva River. From around 1720, the fort served as a base for the city garrison and also as a prison for high-ranking or political prisoners. Russian Revolution and beyond During the February Revolution of 1917, it was attacked by mutinous soldiers of the Pavlovsky Life Guards Regiment on February 27 (O.S.) and the prisoners were freed. Under the Provisional Government, hundreds of Tsarist officials were held in the Fortress. The tsar was threatened with being incarcerated at the fortress on his return from Mogile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantons Of Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the Federated state, member states of the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the . Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms ('Eight Cantons'; from 1353 to 1481) and ('Thirteen Cantons', from 1513 to 1798).rendered "the 'confederacy of eight'" and "the 'Thirteen-Canton Confederation'", respectively, in: Each canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy, formerly also ('lieu/locality', from before 1450), or ('estate', from ), was a fully sovereignty, sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848, with a brief period of centralised government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). The term has been widely used since the 19th century. "" The number of canton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonderbund War
The Sonderbund War (, , ) of November 1847 was a civil war in Switzerland, then still a relatively loose confederacy of cantons. It ensued after seven Catholic cantons formed the ("separate alliance") in 1845 to protect their interests against a centralization of power. The war concluded with the defeat of the Sonderbund. It resulted in the emergence of Switzerland as a federal state, concluding the period of political "restoration and regeneration" in Switzerland. The Sonderbund consisted of the cantons of Lucerne, Fribourg, Valais, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Zug, all predominantly Catholic and governed by conservative administrations. The cantons of Ticino and Solothurn, also predominantly Catholic but governed by liberal administrations, did not join the alliance. After the (Federal Diet) declared the Sonderbund unconstitutional (October 1847) and ordered it dissolved by force, General Guillaume Henri Dufour led the federal army of 100,000 and defeated the Sonderbund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |