|
Niehove
Niehove (old name: ''Suxwort'') is a village in the municipality of Westerkwartier in Groningen, Netherlands. The village was located on the island of in the former Lauwerszee from 800 until 1500. It is a ''terp'' (artificial living hill) village with two ring roads and the church in the middle. The village is a protected site. In 2019, ''Elsevier Weekblad'' named Niehove the most beautiful village of the Netherlands. History Niehove has been permanently inhabited since at least the 2nd century BC. It used to be known as Suxwort. It is a ''terp'' (artificial living hill) village with a radial structure. The church is located in the middle at a height of . There are two ring roads around the ''terp'', and the houses and farms were built along the roads. Paths run down the hill like spokes in a wheel. Around 800, the Lauwerszee, a bay in the Wadden Sea, started to form and Suxwort found itself on a little island called Humsterland. Around 1200, the frequency of floods started to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
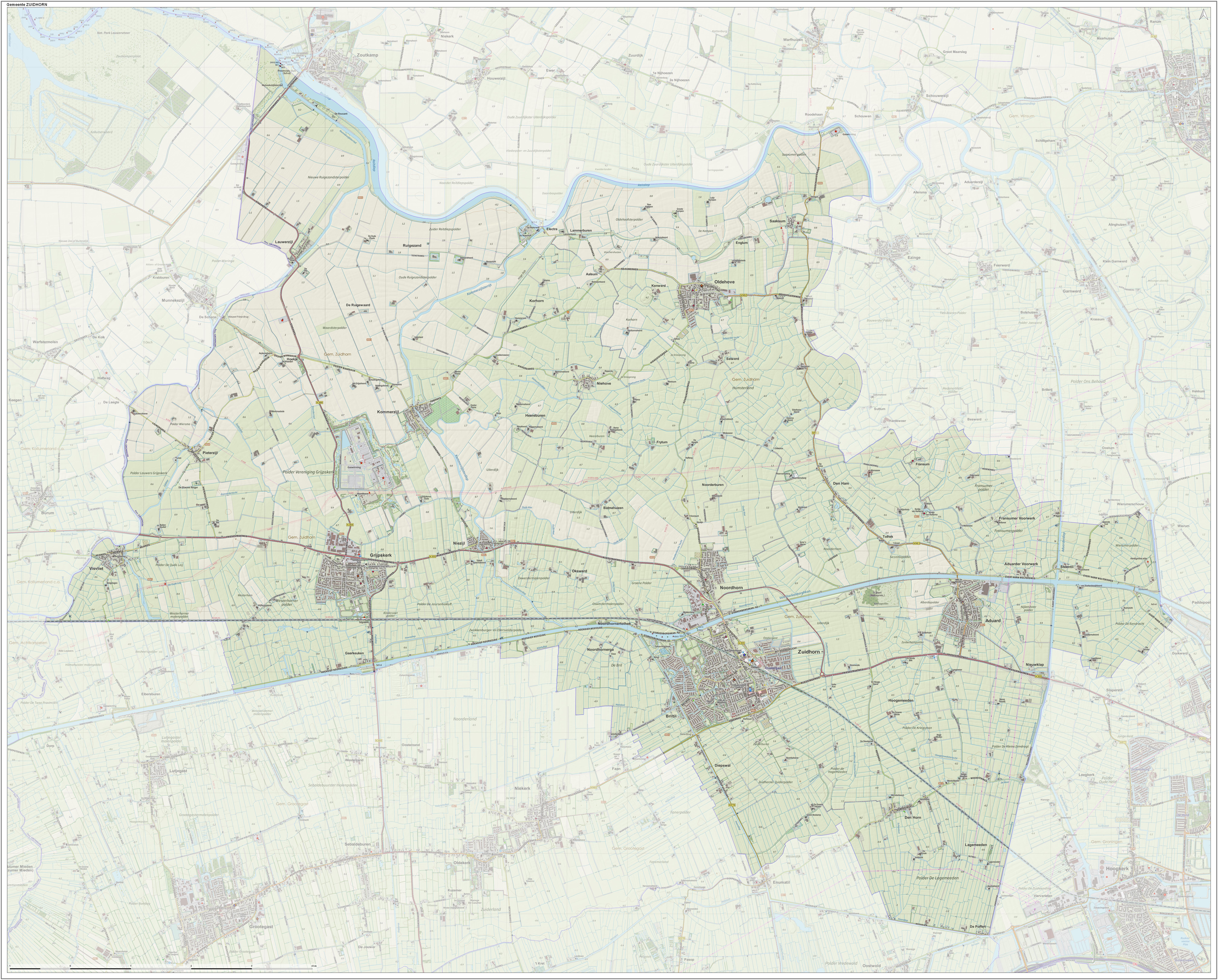
Zuidhorn
Zuidhorn (; ) is a town and former Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the northeastern Netherlands. The town largely depends on the city of Groningen (city), Groningen. A railway line, operated by Arriva, connects the town with Leeuwarden in Friesland and Groningen. Due to a municipal reorganisation in 1990, Zuidhorn municipality was extended when it merged with, though not physically connected to Oldehove (Groningen), Oldehove, Grijpskerk and Aduard. On 1 January 2019, the municipality was dissolved and merged into the municipality of Westerkwartier (municipality), Westerkwartier. Transport Zuidhorn has two train stations: Zuidhorn railway station, Zuidhorn and Grijpskerk railway station, Grijpskerk. At least once an hour a train runs between Groningen (city), Groningen and Leeuwarden. On weekdays, trains stop twice an hour in Zuidhorn. Until 1991 there used to be a third station on this line, Visvliet railway stop, Visvliet. Nature In the center of Zuidhorn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terp
A ''terp'', also known as a ''wierde, woerd, warf, warft, werf, werve, wurt'' or ''værft'', is an artificial dwelling mound found on the North European Plain that has been created to provide safe ground during storm surges, high tides and sea or river flooding. The various terms used reflect the regional dialects of the North European region. These mounds occur in the coastal parts of the Netherlands (in the provinces of Zeeland, Friesland and Groningen (province), Groningen), in southern parts of Denmark and in the north-western parts of Germany where, before Dyke (construction), dykes were made, floodwater interfered with daily life. These can be found especially in the region East Frisia, Ostfriesland and Kreis Nordfriesland (district), Nordfriesland in Germany. In Kreis Nordfriesland on the Halligen, people still live on terps unprotected by dykes. Terps also occur in the Rhine and Meuse River, Meuse river plains in the central part of the Netherlands. Furthermore, ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyke (embankment)
A levee ( or ), dike (American English), dyke (British English; see spelling differences), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is an elevated ridge, natural or artificial, alongside the banks of a river, often intended to protect against flooding of the area adjoining the river. It is usually earthen and often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastlines. Naturally occurring levees form on river floodplains following flooding. Sediment and alluvium are deposited on the banks and settle, forming a ridge that increases the river channel's capacity. Alternatively, levees can be artificially constructed from fill, designed to regulate water levels. In some circumstances, artificial levees can be environmentally damaging. Ancient civilizations in the Indus Valley, ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and China all built levees. Today, levees can be found around the world, and failures of levees due to erosion or other causes can be major disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transepts
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") churches, in particular within the Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architectural traditions, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept. Description The transept of a church separates the nave from the sanctuary, apse, choir, chevet, presbytery, or chancel. The transepts cross the nave at the crossing, which belongs equally to the main nave axis and to the transept. Upon its four piers, the crossing may support a spire (e.g., Salisbury Cathedral), a central tower (e.g., Gloucester Cathedral) or a crossing dome (e.g., St Paul's Cathedral). Since the altar is usually located at the east end of a church, a transept extends to the north and south. The north and south end walls often hold decorated windows of stained glass, such as rose windows, in stone tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludger
Ludger (; also Lüdiger or Liudger) ( – 26 March 809) was a missionary among the Frisians and Saxons, founder of Werden Abbey and the first Bishop of Münster in Westphalia. He has been called the "Apostle of Saxony". Early life to ordination Ludger's parents, Thiadgrim and Liafburg, were wealthy Christian Frisians of noble descent. In 753 Ludger saw the great Apostle of Germany, Boniface, which, together with the subsequent martyrdom of the saint, made a deep impression on him. At his own request he was sent to the Utrecht Cathedral School (''Martinsstift''), founded by Gregory of Utrecht in 756 or 757, and made good progress. In 767 Gregory, who did not wish to receive episcopal consecration himself, sent Alubert, who had come from England to assist him in his missionary work, to York to be consecrated bishop. Ludger accompanied him to be ordained into the diaconate (as he duly was, by Ethelbert of York) and to study under Alcuin, but after a year he returned to Utrecht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willehad
Willehad or Willihad (); 745 AD 8 November 789) was a Christian missionary and the Bishop of Bremen from 787 AD. Life Willehad was born in Northumbria and probably received his education at York under Ecgbert. He was a friend of Alcuin. He was ordained, and about the year 766, he went to Frisia, preaching at Dokkum and in Overijssel, to continue the missionary work of Boniface who had been martyred by the Frisians in 754. At an assembly in Paderborn in 777, Saxony was divided into missionary zones. The zone between the Weser and the Elbe, called ''Wigmodia'', was given to Willehad. From 780 Willehad preached in the region of the lower Weser River on commission from Charlemagne. He barely escaped with his life when the Frisians wanted to kill him and he returned to the area around Utrecht. Once again he and his fellow missionaries barely escaped with their lives when the local pagans wanted to kill them for destroying some temples. Finally, in 780, Charlemagne sent him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dokkum
Dokkum is a Dutch fortified city in the municipality of Noardeast-Fryslân in the province of Friesland. It has 12,669 inhabitants (February 8, 2020). The fortifications of Dokkum are well preserved and are known as the ''bolwerken'' (bulwarks). It is the fifth most popular shopping city in Friesland. It also had the smallest hospital in the Netherlands. __TOC__ History The best-known event in Dokkum's history is the martyrdom of the Anglo-Saxon missionary Saint Boniface in 754. Oliver of Cologne preached the Fifth Crusade in Dokkum in 1214 and Dokkum sent a contingent; the crescent in the coat of arms of Dokkum refers to this event. Dokkum acquired city rights in 1298. In 1572 Dokkum was sacked by the Spaniards after it had joined the Dutch Revolt. In 1597, the Admiralty of Friesland was established in Dokkum. However, it was moved to Harlingen in 1645. In 1971 the city was included in the list of Dutch 'Urban and village conservation areas'. In 1923, when Catholics in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB (born Wynfreth; 675 –5 June 754) was an English Benedictines, Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of the Catholic Church in Germany, church in Germany and was made Elector of Mainz, Archbishop of Mainz by Pope Gregory III. He was martyred in Frisia in 754, along with 52 others, and his remains were returned to Fulda, where they rest in a sarcophagus which remains a site of Christian pilgrimage. Boniface's life and death as well as his work became widely known, there being a wealth of material available — a number of , especially the near-contemporary , legal documents, possibly some sermons, and above all his correspondence. He is venerated as a saint in the Christian church and became the patron saint of Germania, known as the "Apostle to the Germans". Norman Cantor notes the three roles Boniface played that made him "one of the truly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrology, hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as levee, dikes. The three types of polder are: # Land reclamation, Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed # Floodplain, Flood plains separated from the sea or river by a dike # Marshes separated from the surrounding water by a dike and subsequently drained; these are also known as ''koogs'', especially in Germany The ground level in drained marshes subsidence, subsides over time. All polders will eventually be below the surrounding water level some or all of the time. Water enters the low-lying polder through infiltration (hydrology), infiltration and water pressure of groundwater, or rainfall, or transport of water by rivers and canals. This usually means that the polder has an excess of water, which is pumped out or drained by opening sluices at low tide. Care must be taken not to set the internal water level too low. Pold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aduard Abbey
Aduard Abbey (, ''Abdij Sint-Bernardus in Aduard'') is a former Cistercian abbey in the village of Aduard about 8 kilometres to the north-west of Groningen in the Netherlands, founded in 1192 and dissolved in 1580. History The monastery was founded in 1192 at Klaarkamp Abbey near Dokkum (of the filiation of Clairvaux Abbey, Clairvaux). Aduard Abbey in its turn founded Ihlow Abbey in East Frisia in 1231. In 1259 Aduard took over Termunten Abbey, at that time still in Menterna, previously a Rule of St. Benedict, Benedictine double monastery (the nuns were dispatched to a separate establishment, the short-lived Midwolde Abbey). Aduard Abbey was considered one of the richest, largest and best-known monasteries in the northern Low Countries. From 1245, it had an abbey school. At the end of the 14th century discipline relaxed for a time, but was re-established. In the abbey's heyday under Abbot Henricus van Rees, in the second half of the 15th century, some 300 monks lived there and pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly influential Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Bernard of Clairvaux, Saint Bernard, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of their cowl, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme Abbey, Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098. The first three abbots were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and Stephen Harding. Bernard helped launch a new era when he entered the monastery in the early 1110s with 30 companions. By the end of the 12th century, the ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldehove, Groningen
Oldehove is a village in the Dutch province of Groningen. It is located in the municipality of Westerkwartier, about 16 km northwest of the city of Groningen Groningen ( , ; ; or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. Dubbed the "capital of the north", Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of .... The town has a notable skyline with two windmills and two of its three churches visible from almost every angle, the third church (De Zaaier) being obscured from vision by houses and trees because it doesn't have the traditional tower associated with most churches in similar villages. Oldehove was a separate municipality until 1990, when it was merged with Zuidhorn. The Town Hall still exists neighboring the oldest church in the centre of town. The building is owned by private owners and functions as a home. Oldehove is also one of the few villages in the region left wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |