|
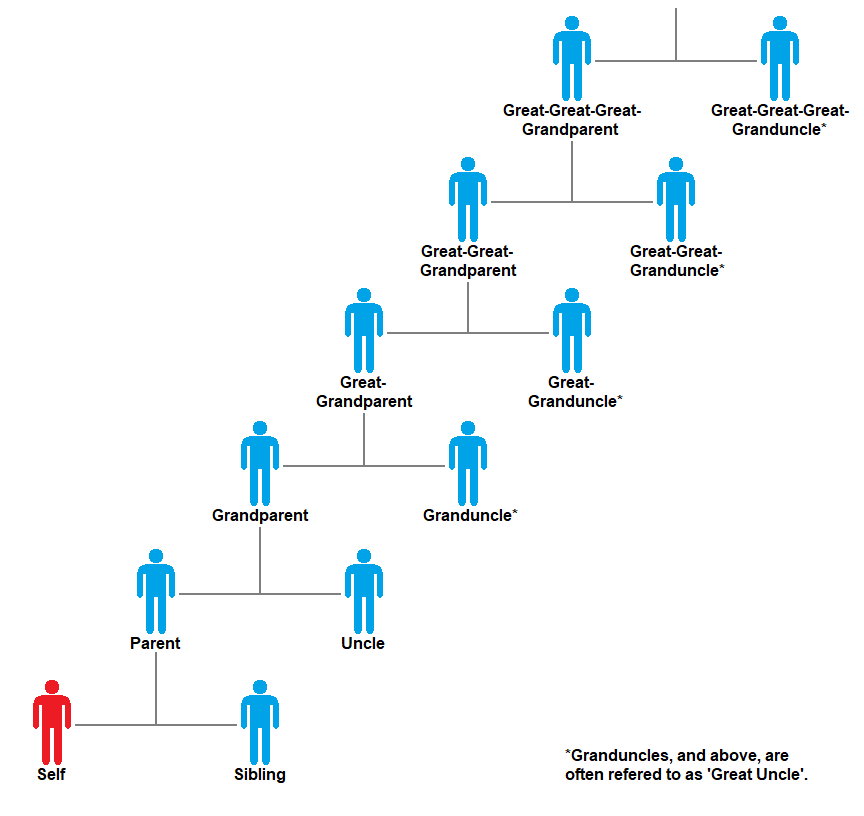
Niece
In the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a niece or nephew is a child of an individual's sibling or sibling-in-law. A niece is female and a nephew is male, and they would call their parents' siblings aunt or uncle. The gender-neutral term nibling has been used in place of the common terms, especially in specialist literature. As aunt/uncle and niece/nephew are separated by one generation, they are an example of a second-degree relationship. Unless related by marriage, they are 25% or more related by blood if the aunt/uncle is a full sibling of one of the parents, or 12.5% if they are a half-sibling. Lexicology The word nephew is derived from the French word which is derived from the Latin . The term ''nepotism'', meaning familial loyalty, is derived from this Latin term. ''Niece'' entered Middle English from the Old French word , which also derives from Latin . The word ''nibling'', derived from ''sibling'', is a neologism suggested by Samue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-degree Relative
The coefficient of relationship is a measure of the degree of consanguinity (or biological relationship) between two individuals. The term coefficient of relationship was defined by Sewall Wright in 1922, and was derived from his definition of the coefficient of inbreeding of 1921. The measure is most commonly used in genetics and genealogy. A coefficient of inbreeding can be calculated for an individual, and is typically one-half the coefficient of relationship between the parents. In general, the higher the level of inbreeding the closer the coefficient of relationship between the parents approaches a value of 1, expressed as a percentage, and approaches a value of 0 for individuals with arbitrarily remote common ancestors. Coefficient of relationship The coefficient of relationship r between two people B and C is obtained by a summation of coefficients calculated for every line by which they are connected to their identical ancestors point, common ancestors. Each such line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aunt
An aunt is a woman who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Aunts who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. Alternate terms include auntie or aunty. Aunt, auntie, and aunty also may be titles bestowed by parents and children to close friends of one or both parents who assume a sustained caring or nurturing role for the children. Children in some cultures and families may refer to the cousins of their parents as aunt or uncle due to the age and generation gap. The word comes from via Old French ''ante'' and is a family">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''ante'' and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. The male counterpart of an aunt is an uncle, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a niece and nephew, nephew or niece. The gender-neutral term pibling, a shortened form of ''parent's sibling'', may refer to eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cousin
A cousin is a relative who is the child of a parent's sibling; this is more specifically referred to as a first cousin. A parent of a first cousin is an aunt or uncle. More generally, in the kinship system used in the English-speaking world, cousins are in a type of relationship in which the two cousins are two or more generations away from their most recent common ancestor. In this usage, "degrees" and "removals" are used to specify the relationship more precisely. "Degree" measures how distant the relationship is from the most recent common ancestor(s), starting with one for first cousins and increasing with every subsequent generation. If the cousins do not come from the same generation, "removal" expresses the difference in generations between the two cousins. When no removal is not specified, no removal is assumed. Various governmental entities have established systems for legal use that can precisely specify kinship with common ancestors any number of generations i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cousins
A cousin is a relative who is the child of a parent's sibling; this is more specifically referred to as a first cousin. A parent of a first cousin is an aunt or uncle. More generally, in the kinship system used in the English-speaking world, cousins are in a type of relationship in which the two cousins are two or more generations away from their most recent common ancestor. In this usage, "degrees" and "removals" are used to specify the relationship more precisely. "Degree" measures how distant the relationship is from the most recent common ancestor(s), starting with one for first cousins and increasing with every subsequent generation. If the cousins do not come from the same generation, "removal" expresses the difference in generations between the two cousins. When no removal is not specified, no removal is assumed. Various governmental entities have established systems for legal use that can precisely specify kinship with common ancestors any number of generations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncle
An uncle is usually defined as a male relative who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent, as well as the parent of the cousins. Uncles who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. The female counterpart of an uncle is an aunt, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a nephew or niece. The word comes from , the diminutive of ''avus'' (grandfather), and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. A popular colloquial term in English is Unc. In some cultures and families, children may refer to the cousins of their parents as uncle (or aunt). It is also used as a title of respect for older relatives, neighbours, acquaintances, family friends, and even total strangers in some cultures, for example Aboriginal Australian elders. Using the term in this way is a form of fictive kinship. Any social institution where a special relationship exists between a man and his sisters' children is known as an avunculate (or avunculism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consanguinity
Consanguinity (from Latin '':wikt: consanguinitas, consanguinitas'' 'blood relationship') is the characteristic of having a kinship with a relative who is descended from a common ancestor. Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are closely related by blood from Consanguine marriage, marrying or having sexual relations with each other. The degree of relationship, degree of consanguinity that gives rise to this prohibition varies from place to place. On the other hand, around 20% of the global population lives in areas where some consanguinous marriages are preferred. The degree of relationships are also used to determine heirs of an estate according to statutes that govern intestacy, intestate succession, which also vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. In some communities and time periods, cousin marriage is allowed or even encouraged; in others, it is taboo, and considered to be incest. The degree of relative consanguinity can be illustrated with a ''consanguinity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibling-in-law
A sibling-in-law is the spouse of one's sibling or the sibling of one’s spouse. More commonly, a sibling-in-law is referred to as a brother-in-law for a male sibling-in-law and a sister-in-law for a female sibling-in-law. Sibling-in-law also refers to the reciprocal relationship between a person's spouse and their sibling's spouse. In Indian English this can be referred to as a co-sibling (specifically a co-sister, for the wife of one's sibling-in-law, or co-brother, for the husband of one's sibling-in-law). Relationships Siblings-in-law are related by a type of kinship called ''affinity'' like all in-law relationships. All of these are relations which do not relate to the person directly by blood.Cambridge Dictionaries Online.Family: non-blood relations. Just like the children of one's siblings, the children of one's siblings-in-law are called simply ''nieces'' and ''nephews'' – if necessary, specified whether "by marriage", as opposed to " by blood" or "by adoption". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepotism
Nepotism is the act of granting an In-group favoritism, advantage, privilege, or position to Kinship, relatives in an occupation or field. These fields can include business, politics, academia, entertainment, sports, religion or health care. In concept it is similar to cronyism. The term originated with the assignment of nephews, sons, or other relatives to important positions by Catholic popes and bishops. It has often been witnessed in Autocracy, autocracies, whereby Aristocracy, traditional aristocracies usually contested amongst themselves in order to obtain leverage, status, etc. Nepotism has been criticized since ancient history by philosophers including Aristotle, Thiruvalluvar, Valluvar, and Confucius, condemning it as both evil and unwise. Origins The term comes from Italian word ''nepotismo'',"Nepotism." Dictionary.com. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibling
A sibling is a relative that shares at least one parent with the other person. A male sibling is a brother, and a female sibling is a sister. A person with no siblings is an only child. While some circumstances can cause siblings to be raised separately (such as foster care or adoption), most societies have siblings grow up together. This causes the development of strong emotional bonds, with siblinghood considered a unique type of relationship. The emotional bond between siblings is often complicated and is influenced by factors such as parental treatment, birth order, personality, and personal experiences outside the family. Medically, a full-sibling is a first-degree relative and a half-sibling is a second-degree relative as they are related by 50% and 25%, respectively. Definitions The word ''sibling'' was reintroduced in 1903 in an article in '' Biometrika'', as a translation for the German ''Geschwister'', having not been used since Middle English, specifically 142 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Martin (linguist)
Samuel Elmo Martin (29 January 1924 – 28 November 2009) was an American linguist known for seminal work on the languages of East Asia, a professor at Yale University, and the author of many works on the Korean language, Korean and Japanese language, Japanese languages. Biography Martin was born in Pittsburg, Kansas on 29 January 1924, and grew up in Emporia, Kansas. During World War II he was trained as a Japanese Language Officer, and was stationed in Japan at the end of the war. After the war, he enrolled at the University of California, Berkeley, where he majored in Oriental Languages. He graduated in 1947, but stayed on at Berkeley to study for a master's degree in linguistics under Chao Yuen Ren, which he completed in 1949. He then went to Yale University to study for a PhD in Japanese Linguistics under Bernard Bloch (linguist), Bernard Bloch. He completed his dissertation on Japanese morphophonemics in 1950 (published as a monograph by the Linguistic Society of America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-sibling
A sibling is a relative that shares at least one parent with the other person. A male sibling is a brother, and a female sibling is a sister. A person with no siblings is an only child. While some circumstances can cause siblings to be raised separately (such as foster care or adoption), most societies have siblings grow up together. This causes the development of strong emotional bonds, with siblinghood considered a unique type of relationship. The emotional bond between siblings is often complicated and is influenced by factors such as parental treatment, birth order, personality, and personal experiences outside the family. Medically, a full-sibling is a first-degree relative and a half-sibling is a second-degree relative as they are related by 50% and 25%, respectively. Definitions The word ''sibling'' was reintroduced in 1903 in an article in '' Biometrika'', as a translation for the German ''Geschwister'', having not been used since Middle English, specifically 142 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Etymology Dictionary
Etymonline, or ''Online Etymology Dictionary'', sometimes abbreviated as OED (not to be confused with the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', which the site often cites), is a free online dictionary that describes the etymology, origins of English language, English words, written and compiled by Douglas R. Harper. Description Douglas R. Harper is an American Civil War historian and copy editor for LNP Media Group. He compiled the etymology dictionary to record the history and evolution of more than 50,000 words, including slang and technical terms. The core of its etymology information stems from ''The Barnhart Dictionary of Etymology'' by Robert Barnhart, Ernest Klein's ''Comprehensive Etymology Dictionary of the English Language'', ''The Middle English Compendium'', ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', and the 1889–1902 ''Century Dictionary''. Harper also researches on digital archives. On the ''Etymonline'' homepage, Harper says that he considers himself "essentially and for the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |