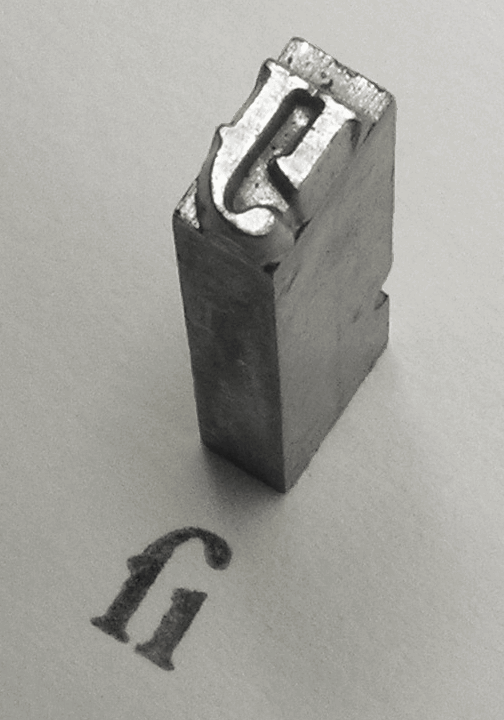|
Nicolas Jenson
Nicholas (or Nicolas) Jenson (c. 1420–1480) was a French engraver, pioneer, printer and type designer who carried out most of his work in Venice, Italy. Jenson acted as Master of the French Royal Mint at Tours and is credited with being the creator of one of the finest early Roman typefaces. Nicholas Jenson has been something of an iconic figure among students of early printing since the nineteenth century when the artist William Morris praised the beauty and perfection of his roman font. Jenson is an important figure in the early history of printing and a pivotal force in the emergence of Venice as one of the first great centers of the printing press. History In October 1458, while acting as Master of the French Royal Mint, Jenson was sent to Mainz, by King Charles VII, to study the art of metal movable type. By the time Jenson arrived in Mainz, there were a number of established printers under which he could have been apprenticed. Jenson left Mainz in 1461. Some hypothesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sommevoire
Sommevoire () is a commune in the Haute-Marne department in north-eastern France. See also *Communes of the Haute-Marne department The following is a list of the 426 communes in the French department of Haute-Marne. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Communes of Haute-Marne {{HauteMarne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serif
In typography, a serif () is a small line or stroke regularly attached to the end of a larger stroke in a letter or symbol within a particular font or family of fonts. A typeface or "font family" making use of serifs is called a serif typeface (or serifed typeface), and a typeface that does not include them is sans-serif. Some typography sources refer to sans-serif typefaces as "grotesque" (in German language, German, ) or "Gothic" (although this often refers to blackletter type as well). In German usage, the term Antiqua (typeface class), Antiqua is used more broadly for serif types. Serif typefaces can be broadly classified into one of four subgroups: Serif#Old-style, Old-style, Serif#Transitional, Transitional, Serif#Didone, Didone, and Serif#Slab serif, Slab serif, in order of first emergence. Origins and etymology Serifs originated from the first official Greek writings on stone and in Latin alphabet with Roman square capitals, inscriptional lettering—words carved into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1420s Births
Fourteen or 14 may refer to: * 14 (number), the natural number following 13 and preceding 15 * one of the years 14 BC, AD 14, 1914, 2014 Music * 14th (band), a British electronic music duo * ''14'' (David Garrett album), 2013 *''14'', an unreleased album by Charli XCX * "14" (song), a 2007 song by Paula Cole from ''Courage'' * "Fourteen", a 2000 song by The Vandals from '' Look What I Almost Stepped In...'' Other uses * ''Fourteen'' (film), a 2019 American film directed by Dan Sallitt * ''Fourteen'' (play), a 1919 play by Alice Gerstenberg * ''Fourteen'' (manga), a 1990 manga series by Kazuo Umezu * ''14'' (novel), a 2013 science fiction novel by Peter Clines * '' The 14'', a 1973 British drama film directed by David Hemmings * Fourteen, West Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community * Lot Fourteen, redevelopment site in Adelaide, South Australia, previously occupied by the Royal Adelaide Hospital * "The Fourteen", a nickname for NASA Astronaut Group 3 * Fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Rogers (typographer)
Bruce Rogers (May 14, 1870 – May 21, 1957) was an American typographer and type designer, acclaimed by some as among the greatest book designers of the twentieth century. Rogers was known for his "allusive" typography, rejecting modernism, seldom using asymmetrical arrangements, rarely using sans serif type faces, often favoring faces such as Bell (at the time known only as Brimmer), Caslon, his own Montaigne, a Jensonian precursor to his masterpiece of type design Centaur. His books can fetch high sums at auction. Early life Born Albert Bruce Rogers in Linwood, now part of Lafayette, Indiana, he never used the name Albert and was known to associates as "BR." Rogers received a B.S. from Purdue University in 1890. He enrolled at age 16, and was quickly recognized in his studies of illustration, allowing him to work with University catalogs, lettering for the yearbook, and the ''College Quarterly Magazine''. At Purdue, he worked with political cartoonist John T. McCutcheon on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Jenson
Adobe Jenson is an old-style serif typeface drawn for Adobe Systems by its chief type designer Robert Slimbach. Its Roman styles are based on a text face cut by Nicolas Jenson in Venice around 1470, and its italics are based on those created by Ludovico Vicentino degli Arrighi fifty years later. Jenson is an organic design, with a low x-height. It is considered a highly readable typeface and is accordingly often used in book design for body text. Development Adobe Jenson was first released in 1996 as a multiple master font. It was created using sophisticated interpolation or multiple-master technology, to create a range of weights and optical sizes suitable for different text sizes. This partial automation of font creation was intended to allow a gradual trend in styles from solid, chunky designs for caption-size small print to more graceful and slender designs for headings. It is now sold in the standard OpenType font format under the name Adobe Jenson Pro. Jenson's type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typeface
A typeface (or font family) is a design of Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers and other symbols, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., 24 point), weight (e.g., light, bold), slope (e.g., italic), width (e.g., condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font. There are list of typefaces, thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly. The art and craft of designing typefaces is called type design. Designers of typefaces are called type designers and are often employed by type foundry, type foundries. In desktop publishing, type designers are sometimes also called "font developers" or "font designers" (a typographer is someone who ''uses'' typefaces to design a page layout). Every typeface is a collection of glyphs, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Western Typography
Modern typographers view typography as a craft with a very long History of printing, history tracing its origins back to the first punches and dies used to make Seal (emblem), seals and coinage currency in Ancient history, ancient times. The basic elements of typography are at least as old as civilization and the earliest writing systems—a series of key developments that were eventually drawn together into one systematic craft. While woodblock printing and movable type had History of typography in East Asia, precedents in East Asia, typography in the Western world developed after the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the mid-15th century. The initial Global spread of the printing press, spread of printing throughout Germany and Italy led to the enduring legacy and continued use of blackletter, Roman type, roman, and italic types. Medieval design roots Typography, type-founding, and typeface design began as closely related crafts in mid-15th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bembo
Bembo is a serif typeface created by the British branch of the Monotype Imaging, Monotype Corporation in 1928–1929 and most commonly used for body text. It is a member of the "Serif#Old-style, old-style" of serif fonts, with its regular or roman type, roman style based on a design cut around 1495 by Francesco Griffo for Venice, Venetian printer Aldus Manutius, sometimes generically called the "Aldine roman". Bembo is named after Manutius's first publication with it, a small 1496 book by the poet and cleric Pietro Bembo. The italic type, italic is based on work by Giovanni Antonio Tagliente, a calligrapher who worked as a printer in the 1520s, after the time of Manutius and Griffo. Monotype created Bembo during a period of renewed interest in the printing of the Italian Renaissance, under the influence of Monotype executive and printing historian Stanley Morison. It followed a previous more faithful revival of Manutius's work, Poliphilus, whose reputation it largely eclipsed. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is called a naturalist or natural historian. Natural history encompasses scientific research but is not limited to it. It involves the systematic study of any category of natural objects or organisms, so while it dates from studies in the ancient Greco-Roman world and the mediaeval Arabic world, through to European Renaissance naturalists working in near isolation, today's natural history is a cross-discipline umbrella of many specialty sciences; e.g., geobiology has a strong multidisciplinary nature. Definitions Before 1900 The meaning of the English term "natural history" (a calque of the Latin ''historia naturalis'') has narrowed progressively with time, while, by contrast, the meaning of the related term "nature" has widened (see also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strozzi Family
The House of Strozzi is the name of an ancient (later noble) Florentine family, who like their great rivals the House of Medici, began in banking before moving into politics. Until its exile from Florence in 1434, the Strozzi family was by far the richest in the city, and was rivaled only by the Medici family, who ultimately took control of the government and ruined the Strozzi both financially and politically. This political and financial competition was the origin of the Strozzi-Medici rivalry. Later, while the Medici ruled Florence, the Strozzi family ruled Siena, which Florence attacked, causing great animosity between the two families. Soon afterward, the Strozzi married into the Medici family, essentially giving the Medici superiority. History Palla Strozzi (1372–1462) neglected the family bank, but played an important part in the public life of Florence, and founded the first public library in Florence in the monastery of Santa Trinita, as well as commissioning the impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |