|
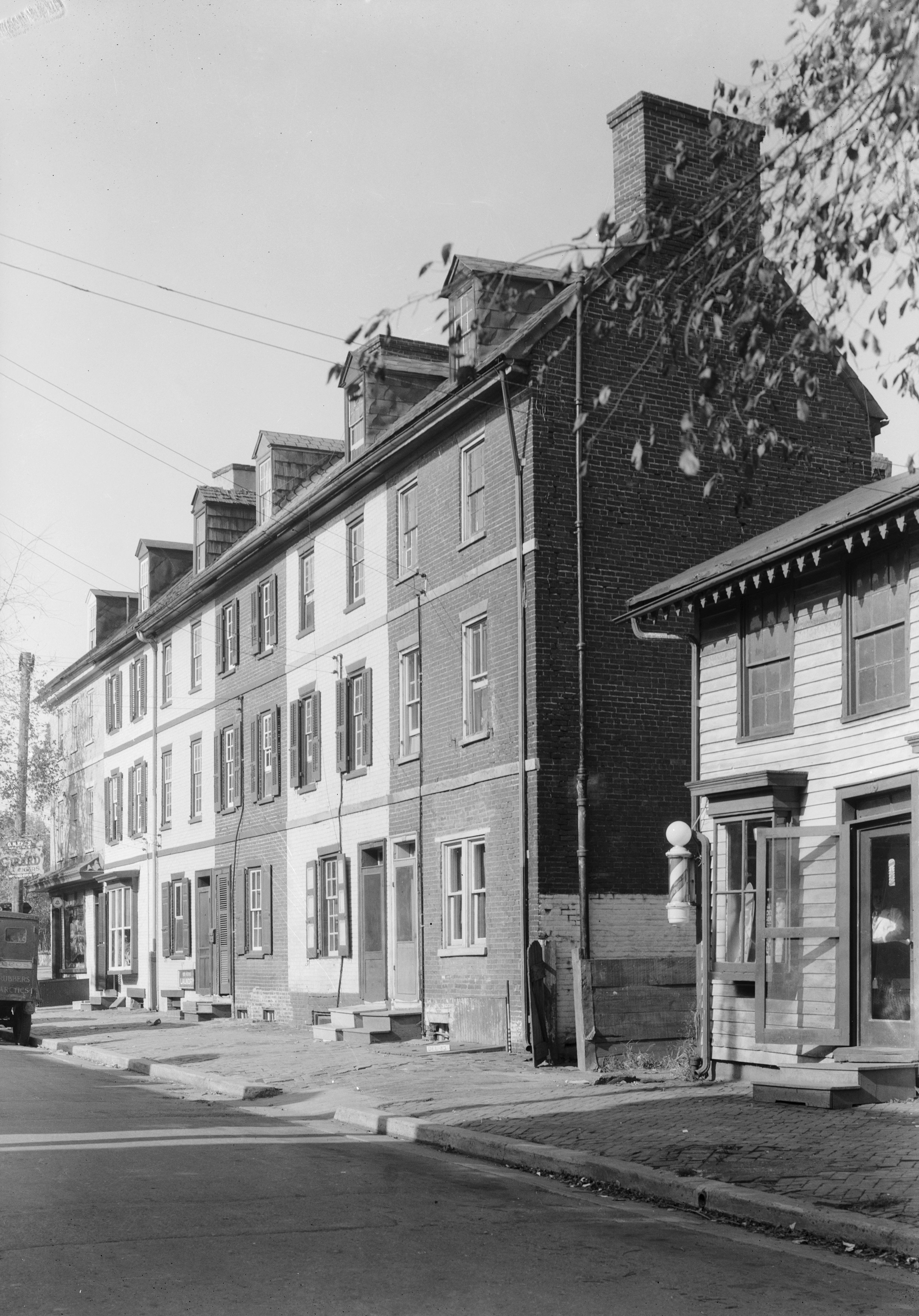
Newcastle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. The city is located six miles (10 km) south of Wilmington and is situated on the Delaware River. As of 2020, the city's population was 5,551. New Castle constitutes part of the Delaware Valley or Philadelphia metropolitan area. History 17th century New Castle was originally settled by the Dutch West India Company in 1651 under the leadership of Peter Stuyvesant on the site of a former indigenous village, "Tomakonck" ("Place of the Beaver"), to assert their claim to the area based on a prior agreement with the original inhabitants of the area. The Dutch originally named the settlement Fort Casimir, but this was changed to Fort Trinity following its seizure by the colony of New Sweden on Trinity Sunday in 1654. The Dutch conquered the entire colony of New Sweden the following year and rechristened the fort as Nieuw-Amstel, named after the Amstel. This marked the end of the Swedish colony in Delaware as an of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Incorporated Places In Delaware
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole". Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Casimir
Fort Casimir or Fort Trinity was a Dutch fort in the seventeenth-century colony of New Netherland. It was located on a no-longer existing barrier island at the end of Chestnut Street in what is now New Castle, Delaware. Background The Dutch called the Delaware River the ''Zuyd Rivier'', or South River, and considered the lands along it banks and those of its bay to be the southern flank of its colony of New Netherland. In 1638, the Delaware Valley began to be settled by Swedes, Finns, Dutch, and Walloons and became the colony of New Sweden, though this was not officially recognized by the Dutch Empire. Sovereignty The fort changed hands several times. Shortly after his arrival to take up his position as up as Director-General of New Netherland in 1647, Peter Stuyvesant, attempted to re-assert control of the region and its lucrative trade. In his initial attempt at control, he effected the construction of Fort Beversreede near the terminus of the Great Minquas Path, at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason–Dixon Line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon as part of the resolution of a border dispute involving Maryland, Pennsylvania, and Delaware in the colonial United States. The largest portion of the Mason–Dixon line, along the southern Pennsylvania border, later became informally known as the boundary between the Slave states and free states, Southern slave states and Northern free states. This usage came to prominence during the debate around the Missouri Compromise of 1820, when drawing boundaries between slave and free territory, and resurfaced during the American Civil War, with border states (American Civil War), border states also coming into play. The Confederate States of America claimed the Virginia (now West Virginia) portion of the line as part of its n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Calvert, 3rd Baron Baltimore
Charles Calvert, 3rd Baron Baltimore (August 27, 1637 – February 21, 1715) was an English colonial administrator. He inherited the province of Maryland in 1675 upon the death of his father, Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore. He had been his father's Deputy Governor since 1661 when he arrived in the colony at the age of 24. However, Charles left Maryland for England in 1684 and would never return. The events following the Glorious Revolution in Kingdom of England, England in 1688 would cost Calvert his title to Maryland; in 1689 the royal charter to the colony was withdrawn, leading to direct rule by the British Crown. Calvert's political problems were largely caused by his Roman Catholic faith which was at odds with the established Church of England. Calvert married four times, outliving three wives, and had at least two children. He died in England in 1715 at the age of 78, his family fortunes much diminished. With his death he passed his title, and his claim to Maryland, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livery Of Seisin
Livery of seisin () is an archaic legal conveyancing ceremony, formerly practised in feudal England and in other countries following English common law, used to convey holdings in property. The term ''livery'' is closely related to if not synonymous with ''delivery'' used in some jurisdictions in contract law or the related law of deeds. The oldest forms of common law provided that a valid conveyance of a feudal tenure in land required physical transfer by the transferor to the transferee in the presence of witnesses of a piece of the ground itself, in the literal sense of a hand-to-hand passing of an amount of soil, a twig, key to a building on that land, or other token. Varieties Livery of seisin could refer to either: * ''Livery in deed'', whereby the parties met together on the land and the transferor symbolically delivered possession of the land by handing over a twig or a clump of earth to the recipient. * ''Livery in law'', whereby the parties went within sight of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James II Of England
James II and VII (14 October 1633 – 16 September 1701) was King of England and Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1685, until he was deposed in the 1688 Glorious Revolution. The last Catholic monarch of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, his reign is now remembered primarily for conflicts over religion. However, it also involved struggles over the principles of Absolute monarchy, absolutism and divine right of kings, with his deposition ending a century of political and civil strife by confirming the primacy of the English Parliament over the Crown. James was the second surviving son of Charles I of England and Henrietta Maria of France, and was created Duke of York at birth. He succeeded to the throne aged 51 with widespread support. The general public were reluctant to undermine the principle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religious freedom, Penn was known for his amicable relations and successful treaties with the Lenape Native Americans who had resided in present-day Pennsylvania prior to European settlements in the state. Penn also owned at least twelve enslaved people at his Pennbury estate. In 1681, Charles II of England, King Charles II granted an area of land corresponding to the present-day U.S. states of Pennsylvania and Delaware to Penn to offset debts he owed Penn's father, the admiral and politician William Penn (Royal Navy officer), Sir William Penn. The following year, Penn left England and sailed up Delaware Bay and the Delaware River, where he founded Philadelphia on the river's western bank. Penn's Quaker government was not viewed favourably by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Westminster (1674)
The Treaty of Westminster of 1674 was the peace treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War. Signed by the Dutch Republic and the Kingdom of England, the treaty provided for the return of the colony of New Netherland (now New York) to England and renewed the Treaty of Breda of 1667. The treaty also provided for a mixed commission for the regulation of commerce, particularly in the East Indies. It was signed on 9 February 1674 Old Style (19 February 1674 New Style) by Charles II of England and ratified by the States General of the Netherlands on 5 March 1674. England was forced to sign the treaty since Parliament would not allow more money to be spent on the war and had become aware of the secret Treaty of Dover in which Charles had promised Louis XIV of France to convert to Catholicism at an opportune moment. The English were dismayed by the unexpected fact that Dutch raiders had managed to capture more English ships than vice versa and that New Amsterdam had been retaken by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
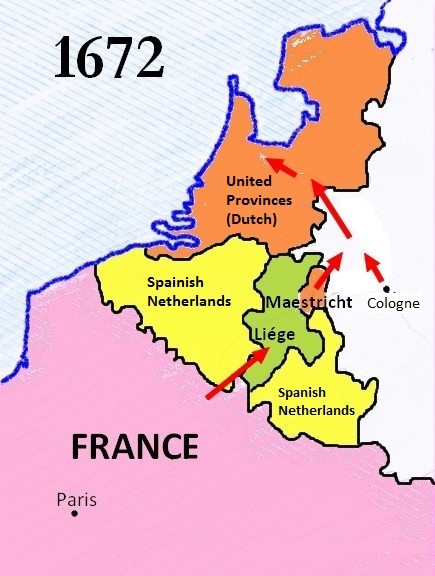
Third Anglo-Dutch War
The Third Anglo-Dutch War, began on 27 March 1672, and concluded on 19 February 1674. A naval conflict between the Dutch Republic and England, in alliance with France, it is considered a related conflict of the wider 1672 to 1678 Franco-Dutch War. In the 1670 Secret Treaty of Dover, Charles II of England agreed to support an attack by Louis XIV of France on the Dutch Republic. By doing so, Louis hoped to gain control of the Spanish Netherlands, while Charles sought to restore the damage to his prestige caused by the 1667 Raid on the Medway. Under the treaty, Charles also received secret payments which he hoped would make him financially independent of Parliament. The French offensive in May and June 1672 quickly overran most of the Republic, with the exception of the core province of Holland, where they were halted by water defences. In early June, the Anglo-French fleet was badly damaged by the Dutch under Michiel de Ruyter at the Battle of Solebay. Shortly thereafter, Joha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware Colony
The Delaware Colony, officially known as the three Lower Counties on the Delaware, was a semiautonomous region of the proprietary Province of Pennsylvania and a '' de facto'' British colony in North America. Although not royally sanctioned, Delaware consisted of the three counties on the west bank of the Delaware River Bay. In the early 17th century, the area was inhabited by Lenape and possibly Assateague Native American Indian tribes. The first European settlers were Swedes, who established the colony of New Sweden at Fort Christina in present-day Wilmington, Delaware, in 1638. The Dutch captured the colony in 1655 and annexed it to New Netherland to the north. England subsequently took control of it from the Dutch in 1664. In 1682, William Penn, the Quaker proprietor of the Province of Pennsylvania to the north leased the three lower counties on the Delaware River from James, the Duke of York, who went on to become King James II. The three lower counties on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Anglo-Dutch War
The Second Anglo-Dutch War, began on 4 March 1665, and concluded with the signing of the Treaty of Breda (1667), Treaty of Breda on 31 July 1667. It was one in a series of Anglo-Dutch Wars, naval wars between Kingdom of England, England and the Dutch Republic, driven largely by commercial disputes. Despite several major battles, neither side was able to score a decisive victory, and by the end of 1666 the war had reached stalemate. Peace talks made little progress until the Dutch Raid on the Medway in June 1667 forced Charles II of England, Charles II to agree to the Treaty of Breda. By eliminating a number of long-standing issues, the terms eventually made it possible for England and the Dutch Republic to unite against the expansionist policies pursued by Louis XIV of France. In the short-term however, Charles' desire to avenge this setback led to the Third Anglo-Dutch War in 1672. Background Despite similar ideologies, commercial disputes and political differences between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of New Netherland
The conquest of New Netherland occurred in 1664 as an English expedition led by Richard Nicolls that arrived in New York Harbor effected a peaceful capture of New Amsterdam and Fort Amsterdam, and the Articles of Surrender of New Netherland were agreed. The conquest was mostly peaceful in the rest of the colony as well, except for some fighting in New Amstel. Background The commercial rivalry between the Dutch and the English, which provoked the First Anglo-Dutch War, was not resolved by the Treaty of Westminster (1654). Hostilities continued between the countries' trading companies. Religious and political differences between the Anglican royalists in England and the Calvinist republicans that ruled the Netherlands also hampered peace. During the Anglo-Spanish War of 1654–1660, Dutch traders supplanted the English in trade with Spain and its possessions in Italy and America. Conflict developed between the States of Holland and Charles II of England's sister Mary, the wido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |