|
New York Edition
The ''New York Edition'' of Henry James' fiction was a 24-volume collection of the Anglo-American writer's novels, novellas and short stories, originally published in the U.S. and the UK between 1907 and 1909, with a photogravure frontispiece for each volume by Alvin Langdon Coburn. Two more volumes containing James' unfinished novels, ''The Ivory Tower'' and ''The Sense of the Past'', were issued in 1917 in a format consistent with the original set. The entire collection was republished during the 1960s by Charles Scribner's Sons. The official title of the set was ''The Novels and Tales of Henry James'', though the more informal title was suggested by James himself and appears as a subtitle on the series title page in each volume. It has been used almost exclusively by subsequent commentators. Prefaces James wrote a series of prefaces for the set which have become the focus of intense critical attention. Written in the ornate style of his final years, the prefaces discuss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information; and to retain it as knowledge to be applied to adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. The term rose to prominence during the early 1900s. Most psychologists believe that intelligence can be divided into various domains or competencies. Intelligence has been long-studied in humans, and across numerous disciplines. It has also been observed in the Animal cognition, cognition of non-human animals. Some researchers have suggested that Plant, plants exhibit forms of intelligence, though this remains controversial. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''wikt:intelligence#English, intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roderick Hudson
''Roderick Hudson'' is a novel by Henry James. Originally published between January and December 1875 as a serial in ''The Atlantic Monthly'', it is a bildungsroman that traces the development of the title character, a sculptor. Plot summary Rowland Mallet, a wealthy Bostonian bachelor and art connoisseur, visits his cousin Cecilia in Northampton, Massachusetts, before leaving for Europe. There he sees a Grecian figure he thinks is a remarkable work of art. Cecilia introduces him to the local sculptor, Roderick Hudson, a young law student who sculpts in his spare time. Mallet—who loves art but is without artistic talent himself—sees an opportunity to contribute: he offers to advance Roderick a sum of money against future works which will allow Roderick to join him in moving to Italy for two years. Mallet believes that in Rome, Roderick will be exposed to the kind of artistic influences which will allow his natural talent to fully mature. Roderick is galvanized by the offer, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Gosse
Sir Edmund William Gosse (; 21 September 184916 May 1928) was an English poet, author and critic. He was strictly brought up in a small Protestant sect, the Plymouth Brethren, but broke away sharply from that faith. His account of his childhood in the book ''Father and Son'' has been described as the first psychological biography. His friendship with the sculptor Hamo Thornycroft inspired a successful career as a historian of late-Victorian sculpture. His translations of Henrik Ibsen helped to promote that playwright in England, and he encouraged the careers of W. B. Yeats and James Joyce. He also lectured in English literature at Cambridge University. Early life Gosse was the son of Philip Henry Gosse and Emily Bowes. His father was a naturalist and his mother an illustrator who published a number of books of poetry. Both were deeply committed to a small Protestant sect, the Plymouth Brethren. His childhood was initially happy as they spent their summers in Devon where hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Europeans
''The Europeans: A sketch'' is a short novel by Henry James, published in 1878. It is essentially a comedy contrasting the behaviour and attitudes of two visitors from Europe with those of their relatives living in the "new" world of New England. The novel first appeared as a serial in ''The Atlantic Monthly'' for July–October 1878. James made numerous minor revisions for the first book publication. Plot introduction The tale opens in Boston and New England in the middle of the 19th century, and describes the experiences of two European siblings shifting from the old to the new world. The two protagonists are Eugenia Münster and Felix Young, who since their early childhood have lived in Europe, moving from France to Italy and from Spain to Germany. In this last place, Eugenia entered into a Morganatic marriage with Prince Adolf of Silberstadt-Schreckenstein, the younger brother of the reigning prince who is now being urged by his family to dissolve the marriage for political r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Square (novel)
''Washington Square'' is a novel written in 1880 by Henry James about a father's attempts to thwart a romance between his naive daughter and the man he believes wishes to marry her for her money. The novel was famously adapted into a play, '' The Heiress'', which in turn became an Academy Award-winning film starring Olivia de Havilland in the title role. Background The plot of the novel is based upon a story told to James by his close friend, British actress Fanny Kemble. An 1879 entry in James' notebooks details an incident where Kemble told James about her brother, who romantically pursued "a dull, commonplace girl...who had a very handsome private fortune." Plot In 1840s New York City, naive, introverted Catherine Sloper lives with her tyrannical father, Dr. Austin Sloper, in Washington Square, a fashionable neighborhood near Greenwich Village. Embittered by the deaths of his wife and son, Dr. Sloper makes Catherine a constant target for verbal and mental abuse. Catherine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Portrait Of A Lady
''The Portrait of a Lady'' is a novel by Henry James, first published as a serial in ''The Atlantic Monthly'' and '' Macmillan's Magazine'' in 1880–81 and then as a book in 1881. It is one of James's most popular novels and is regarded by critics as one of his finest. ''The Portrait of a Lady'' is the story of a spirited young American woman, Isabel Archer, who, "affronting her destiny," finds it overwhelming. She inherits a large amount of money and subsequently becomes the victim of Machiavellian scheming by two American expatriates. Like many of James's novels, it is set in Europe, mostly England and Italy. Generally regarded as the masterpiece of James's early period, this novel reflects James's continuing interest in the differences between the New World and the Old, often to the detriment of the former. It also treats in a profound way the themes of personal freedom, responsibility, and betrayal. Plot summary Isabel Archer, from Albany, New York, is invited by her ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta and the Sile). In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the ''Comune di Venezia'', of whom around 55,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua and Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Veneti people who inhabited the region by the 10th century BC. The city was historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realism (arts)
Realism in the arts is generally the attempt to represent subject matter truthfully, without artificiality and avoiding speculative fiction, speculative and fantasy literature, supernatural elements. The term is often used interchangeably with naturalism, although these terms are not synonymous. Naturalism, as an idea relating to visual representation in Western art, seeks to depict objects with the least possible amount of distortion and is tied to the development of linear perspective and illusionism in Renaissance Europe. Realism, while predicated upon naturalistic representation and a departure from the idealization of earlier academic art, often refers to a Realism (art movement), specific art historical movement that originated in France in the aftermath of the French Revolution of 1848. With artists like Gustave Courbet capitalizing on the mundane, ugly or sordid, realism was motivated by the renewed interest in the common man and the rise of leftist politics. The Realist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether nonfictional ( memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller Thriller may refer to: * Thriller (genre), a broad genre of literature, film and television ** Thriller film, a film genre under the general thriller genre Comics * ''Thriller'' (DC Comics), a comic book series published 1983–84 by DC Comics i ..., novel, etc.). Narratives can be presented through a sequence of written or spoken words, through still or moving images, or through any combination of these. The word derives from the Latin verb ''narrare'' (to tell), which is derived from the adjective ''gnarus'' (knowing or skilled). Narration (i.e., the process of presenting a narrative) is a rhetorical modes, rhetorical mode of discourse, broadly defined (and paralleling argumentation, description, and exposition (narrative), exposition), is one of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reader-response Criticism
Reader-response criticism is a school of literary theory that focuses on the reader (or "audience") and their experience of a literary work, in contrast to other schools and theories that focus attention primarily on the author or the content and form of the work. Development Although literary theory has long paid some attention to the reader's role in creating the meaning and experience of a literary work, modern reader-response criticism began in the 1960s and '70s, particularly in the US and Germany. This movement shifted the focus from the text to the reader and argues that affective response is a legitimate point for departure in criticism. Its conceptualization of critical practice is distinguished from theories that favor textual autonomy (for example, formalism) as well as recent critical movements (for example, structuralism, semiotics, and deconstruction) due to its focus on the reader's interpretive activities. Classic reader-response critics include Norman Holland, St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

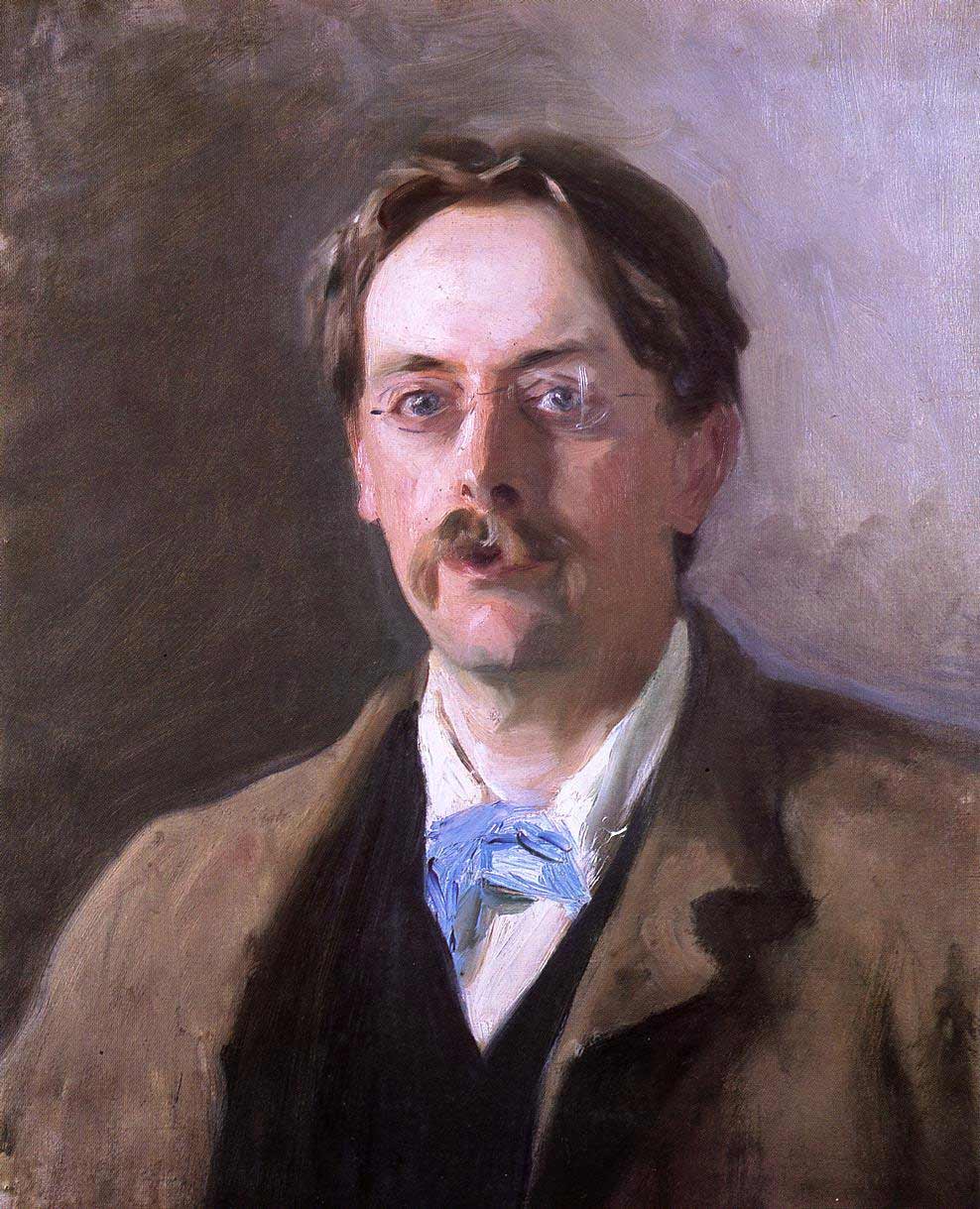
.jpg)


