|
New York Call
The ''New York Call'' was a socialist daily newspaper published in New York City from 1908 through 1923. The ''Call'' was the second of three English-language dailies affiliated with the Socialist Party of America, following the ''Chicago Daily Socialist'' (1906–1912) and preceding the '' Milwaukee Leader'' (1911–1938). History Political background In 1899 a bitter factional fight swept the Socialist Labor Party of America (SLP), pitting loyalists to the party's English-language newspaper, ''The People,'' and its intense and autocratic editor, Daniel DeLeon, against a dissident faction organized around the party's German-language paper, the '' New Yorker Volkszeitung.'' In addition to personal antipathy, the two sides differed on the fundamental question of trade union policy, with the DeLeon faction favoring a continuation of the party's policy of establishing an explicitly socialist union organization and the dissidents seeking to abandon the course of dual unionis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
080620-nycall-frontpage
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. Etymology English ''eight'', from Old English '', æhta'', Proto-Germanic ''*ahto'' is a direct continuation of Proto-Indo-European numerals, Proto-Indo-European '':wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/oḱtṓw, *oḱtṓ(w)-'', and as such cognate with Greek and Latin , both of which stems are reflected by the English prefix :wikt:oct-, oct(o)-, as in the ordinal adjective ''octaval'' or ''octavary'', the distributive adjective is ''octonary''. The adjective ''octuple'' (Latin ) may also be used as a noun, meaning "a set of eight items"; the diminutive ''octuplet'' is mostly used to refer to eight siblings delivered in one birth. The Semitic numerals, Semitic numeral is based on a root ''*θmn-'', whence Akkadian ''smn-'', Arabic ''ṯmn-'', Hebrew ''šmn-'' etc. The Chinese numeral, written (Standard Mandarin, Mandarin: ''bā''; Cantonese language, Cantonese: ''baat''), is from Old Chinese ''*priāt-'', ultim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algernon Lee
Algernon H. Lee (September 15, 1873 – January 5, 1954) was an American socialist politician and educator. In addition to serving as a member of the New York City Council (then the New York City Board of Aldermen) during World War I, Lee was one of three co-authors of the controversial anti-war resolution at the 1917 St. Louis emergency convention of the Socialist Party of America. He is best remembered as the Director of Education at the Rand School of Social Science for 35 years. Biography Early years Algernon Lee was born September 15, 1873, in Dubuque, Iowa, the son of a millwright and carpenter.Solon DeLeon with Irma C. Hayssen and Grace Poole (eds.), ''The American Labor Who's Who.'' New York: Hanford Press, 1925; pg. 133. He was educated in public schools in Fishkill, New York, and Minneapolis, Minnesota.Bernard K. Johnpoll, "Algernon Lee (1873-1954)," in Bernard K. Johnpoll and Harvey Klehr (eds.), ''Biographical Dictionary of the American Left.'' Westport, CT: Greenwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Krantz
Jacob Rombro (October 10, 1858 – November 28, 1922), better known by his pen name Philip Krantz, was a Belarusian-born Jewish-American socialist, newspaper editor, and Yiddish writer. Life Krantz was born on October 10, 1858, in Zhuprany, Vilna Governorate, Russian Empire, the son of Baruch Rombro and Bella Rosa Uger. Some biographers claimed he was born in Khodaki, Podolian Governorate. Krantz moved with his parents to Ashmyany, where he studied in a Russian school and had private tutors. In 1872, he began attending the Zhitomir rabbinical school. In 1873, he switched to the Kremenchug senior high school, graduating from there in 1879. In school, he became involved with the revolutionary movement. He was arrested in 1877 for political propaganda and imprisoned for a year in Kharkov. He studied at the St. Petersburg Technological Institute from 1879 to 1881. He began working as a journalist in 1880 and initially wrote for the Russian Jewish weekly ''Razsviet''. He then studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial Day
Memorial Day (originally known as Decoration Day) is a federal holiday in the United States for mourning the U.S. military personnel who died while serving in the United States Armed Forces. It is observed on the last Monday of May. It is the unofficial beginning of summer in the United States. Memorial Day is a time for visiting cemeteries and memorials to mourn the military personnel who died in the line of duty. Volunteers will place American flags on the graves of those military personnel in national cemeteries. The first national observance of Memorial Day occurred on May 30, 1868. Then known as ''Decoration Day'' and observed on May 30, the holiday was proclaimed by Commander in Chief John A. Logan of the Grand Army of the Republic to honor the Union soldiers who had died in the American Civil War. This national observance followed many local observances which were inaugurated between the end of the Civil War and Logan's declaration. Many cities and people ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May Day
May Day is a European festival of ancient origins marking the beginning of summer, usually celebrated on 1 May, around halfway between the Northern Hemisphere's March equinox, spring equinox and midsummer June solstice, solstice. Festivities may also be held the night before, known as May Eve. Traditions include gathering green branches and wildflowers ("bringing in the May"), which are used to decorate buildings and made into wreaths; crowning a May Queen, sometimes with a Jack in the Green, male companion decked in greenery; setting up a Maypole, May Tree, or May Bush, around which people dance and sing; as well as parades and processions involving these. Bonfires are also a major part of the festival in some regions. Regional varieties and related traditions include Walpurgis Night in central and northern Europe, the Gaels, Gaelic festival Beltane, the Wales, Welsh festival Calan Mai, and May devotions to the Blessed Virgin Mary. It has also been associated with the Religion i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Socialist Fellowship
Christian Socialist Fellowship was an international religious society of Protestant ministers and other believers in Christian socialist principles. It was formed at Louisville, Kentucky, U.S. in 1906, for the purpose of "permeating the churches, denominations, and other religious institutions with the social message of Jesus; to show that Socialism is the necessary economic expression of the Christian life; to end the class struggle by establishing industrial democracy, and to hasten the reign of justice and brotherhood upon earth." The Christian Socialist Fellowship was one of the many organizations in England and the U.S. devoted to the propagation of the social religious teachings. Charles Kingsley, Archbishop Whately, Bishop van Ketteler, and Bishop Fripple were clergymen both Protestant and Catholic, who lead the movement In Europe. Drs, Lyman Abbott, Washington Gladden, and Professor Ely were leaders in the movement in the U.S. Out of the broad term "Christian Socialism" som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercollegiate Socialist Society
The Intercollegiate Socialist Society (ISS) was a socialist student organization active from 1905 to 1921. It attracted many prominent intellectuals and writers and acted as an unofficial student wing of the Socialist Party of America. The Society sponsored lecture tours, magazines, seminars and discussion circles all over the US to propagate socialist ideas among America's college population. The group expanded into a philosophy in the 1920s that did not focus exclusively or even primarily on college students. To symbolize the shift in emphasis, the group changed its name to the League for Industrial Democracy in 1921. History Establishment Supporters of the Socialist Party of America (SPA) were heartened by the results of the 1904 United States presidential election, Presidential election of 1904, which saw the party's candidate, Eugene V. Debs, win approximately 400,000 votes.Harry W. Laidler, "Ten Years of ISS Progress," ''The Intercollegiate Socialist,'' vol. 4, no. 1 (Oct. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rand School Of Social Science
The Rand School of Social Science was formed in 1906 in New York City by adherents of the Socialist Party of America. The school aimed to provide a broad education to workers, imparting a politicizing class-consciousness, and additionally served as a research bureau, a publisher, and the operator of a summer camp for socialist and trade union activists. The school changed its name to the "Tamiment Institute and Library" in 1935 and it was closely linked to the Social Democratic Federation (U.S.), Social Democratic Federation after the 1936 split of the Socialist Party. Its collection became a key component of today's Tamiment Library and Robert F. Wagner Archives at New York University in 1963. Institutional history Forerunners The idea of establishing new schools for the promotion of socialism, socialist ideas in the United States emerged at the end of the 19th century, when a group of Christian socialists, organized as the Social Reform Union, established the correspondence sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Hanford
Benjamin Hanford (1861 – January 24, 1910) was an American socialist politician during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. A printer by trade, Hanford is best remembered for his 1904 and 1908 runs for Vice President of the United States on the ticket of the Socialist Party of America, running next to Presidential nominee Eugene V. Debs. Hanford was also the creator of the fictional character "Jimmie Higgins," a prototypical Socialist rank-and-filer whose silent work on the unglamorous tasks needed by any political organization made the group's achievements possible — a character later reprised in a novel by Upton Sinclair. Biography Early life Benjamin Hanford was born in Cleveland, Ohio in 1861, the son of George Byington Hanford and Susan Elizabeth Martin Hanford. Ben's mother died when he was in infancy.Joshua Wanhope, "Biographical Sketch of Ben Hanford," in Ben Hanford, ''Fight For Your Life! Recording Some Activities of a Labor Agitator.'' New York: Wilshire Book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene V
Eugene may refer to: People and fictional characters * Eugene (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Gene Eugene, stage name of Canadian born actor, record producer, engineer, composer and musician Gene Andrusco (1961–2000) * Eugene (wrestler), professional wrestler Nick Dinsmore * Eugene (actress) (born 1981), Kim Yoo-jin, South Korean actress and former member of the singing group S.E.S. Places Canada * Mount Eugene, in Nunavut; the highest mountain of the United States Range on Ellesmere Island United States * Eugene, Oregon Eugene ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Lane County, Oregon, United States. It is located at the southern end of the Willamette Valley, near the confluence of the McKenzie River (Oregon), McKenzie and Willamette River, Willamette rivers, ..., a city ** Eugene, OR Metropolitan Statistical Area ** Eugene (Amtrak station) * Eugene Apartments, NRHP-listed apartment complex in Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
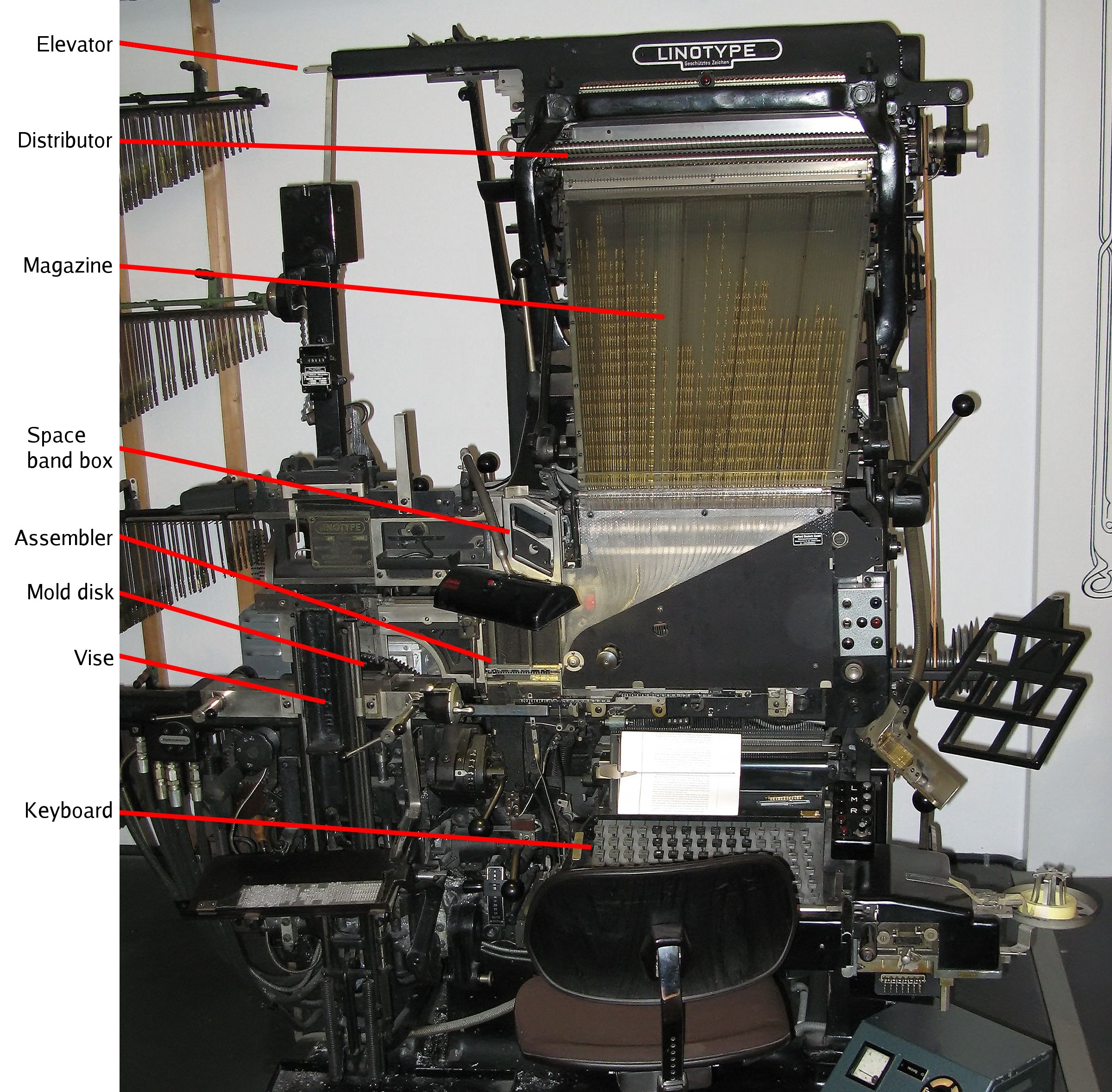
Linotype Machine
The Linotype machine ( ) is a "line casting" machine used in printing which is manufactured and sold by the former Mergenthaler Linotype Company and related It was a hot metal typesetting system that cast lines of metal type for one-time use. Linotype became one of the mainstays for typesetting, especially small-size body text, for newspapers, magazines, and posters from the late 19th century to the 1970s and 1980s, when it was largely replaced by phototypesetting and digital typesetting. The name of the machine comes from producing an entire line of metal Sort (typesetting), type at once, hence a ''line-o'-type''. It was a significant improvement over the previous industry standard of letter-by-letter manual typesetting using a composing stick and shallow subdivided trays, called "cases". The Linotype machine operator enters text on a 90-character keyboard. The machine assembles ''matrices'', or molds for the letter forms, in a line. The assembled line is then cast as a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |