|
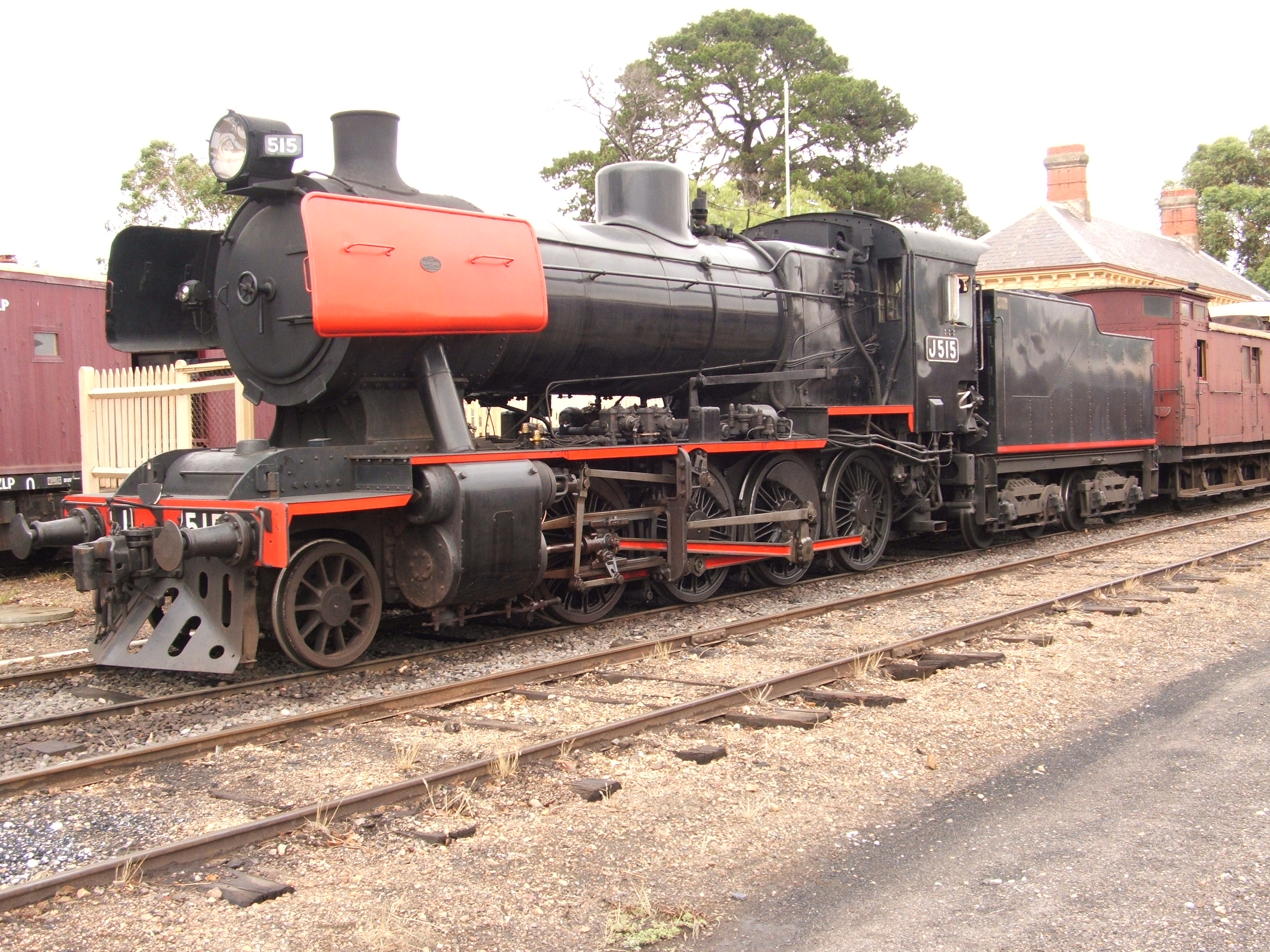
New York, Susquehanna And Western 142
New York, Susquehanna and Western 142 is a China Railway, China Railways SY class 2-8-2 "Mikado" type steam locomotive. It was built as SY-1647M in May 1989 by the Tangshan Locomotive and Rolling Stock Works for the Valley Railroad (Connecticut), Valley Railroad in the United States. Its design was altered to meet requirements for U.S. operation. It made its inaugural run for the VALE in early 1990. Inspired by VALE, the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway ordered a similar locomotive, but it sank with its cargo ship en route from China. So the NYS&W bought VALE's locomotive in late 1991, renumbered it as 142, and used it pull mainline Excursion train, excursion trains throughout New Jersey and New York (state), New York state. Since 2003, the locomotive has been owned by the NYS&W Technical and Historical Society, and since 2004, it has been operated by the Belvidere and Delaware River Railway. Background Design No. 142’s associated class, the SY locomotive, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortland, New York
Cortland is a city and the county seat of Cortland County, New York, United States. Known as the Crown City, Cortland is in New York's Southern Tier region. As of 2024, the estimated population of Cortland, New York, is 17,196, reflecting a decline of approximately 1.82% since the 2020 census, which recorded 17,515 residents. The city of Cortland, near the county's western border, is surrounded by the town of Cortlandville. History The city is within the former Central New York Military Tract. It is named after Pierre Van Cortlandt, the first lieutenant governor of New York. Cortland, settled in 1791, was made a village in 1853 (rechartered in 1864), and incorporated in 1900 as New York's 41st city. When the county was formed in 1808, Cortland vied with other villages to become the county seat. Known as the "Crown City" because of its location on a plain formed by the convergence of seven valleys, Cortland is above sea level. Forty stars representing the 40 cities incor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Industry In China
The impact of the petroleum industry has been increasing globally as the People's Republic of China ranks seventh for oil production and second in crude oil consumption in the world. China became the world's largest oil importer in 2013. History Early history The late Qing dynasty banned mining because of the traditional cosmological beliefs which regarded the land as a sacred legacy. This ban was lifted during the modernization effort of the Self-Strengthening Movement as the Qing dynasty sought to develop a modern navy and modern industry. In 1875, the court designated Cizhou (in what is now Hebei province) and Taiwan as testing grounds for oil extraction. Qing attempts at oil exploration were hampered by corruption, low efficiency, and lack of sufficient domestic investment capacity for oil extraction and transportation. The Qing court was also concerned about foreign investment and the perceived risk of selling the country to foreigners. Nationalist Era In the 1930s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Railroad 97
Valley Railroad 97 is a preserved 200 class 2-8-0 "Consolidation" type steam locomotive, built in November 1923 by the American Locomotive Company's Cooke Works for the Birmingham and Southeastern Railroad, it is now preserved and operated by the Valley Railroad. History Revenue service No. 97 was built by the American Locomotive Company's former Cooke Locomotive Works in November 1923 as No. 200. It was one of two locomotives that were intended to be exported to Cuba for use on the National Railway Company of Cuba. No. 200 however, never made it to Cuba as the order was cancelled, it was kept in storage at the Cooke Works factory until its closure in 1926. Instead, it was subsequently sold to the Birmingham and Southeastern Railroad in February 1926 and was moved to the company's shortline in Alabama on March 5, 1926. The locomotive pulled multiple passenger and freight trains on Birmingham and Southeastern trackage until it was retired from revenue service in 1958 and put i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. In the United States and elsewhere, this wheel arrangement is commonly known as a Consolidation, after the Lehigh and Mahanoy Railroad’s ''Consolidation'', the name of the first 2-8-0.White, John H. Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, p. 65. The notation 2-8-0T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in side-tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender (rail), tender. The Consolidation represented a notable advance in locomotive power. After 1875, it became "the most popular type of freight locomotive in the United States and was built in greater quantities tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essex, Connecticut
Essex is a town in Middlesex County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Lower Connecticut River Valley Planning Region. The population was 6,733 at the 2020 census. It is made up of three villages: Essex Village, Centerbrook, and Ivoryton. History The Great Attack Essex is one of the few American towns to have ever been attacked by a foreign power; this occurred on April 8, 1814, and the economic losses were among the largest sustained by the United States during the War of 1812. Twenty-eight vessels, with a total value estimated to be close to $200,000 (at a time when a very large two story home in Essex, then known as Potapoug Point, would have been worth no more than $1,000), were destroyed by the British. One historian has called it the "Pearl Harbor" of that war. On that date, approximately 136 British marines and sailors under the command of Richard Coote (or Coot"Essex", Mary Murphy, the Hartford Courant, April 25, 2007, Middlesex County adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRRC Tangshan
CRRC Tangshan Co., Ltd., is a manufacturer of rolling stock located in Tangshan, Hebei province, People's Republic of China. While Datong built mainline steam locomotives until 1988, Tangshan built steam for industrial use until 1999, becoming the last works in the world to build steam for non-tourist use. History The predecessor of the subsidiary, Tangshan Locomotive and Rolling Stock Works was founded before the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949. It was nationalized and remaining as an entity of the Ministry of Railways until 2002, when it was a manufacturing facility of (LORIC). In 2002, LORIC was split into CNR Group and CSR Group, which Tangshan works belonged to the former due to geographical location. CNR Group and CSR Group also belonged to newly established State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, another department of the State Council. Due to the initial public offering of China CNR, the assets of the works was injected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axle Load
The axle load of a wheeled vehicle is the total weight bearing on the roadway for all wheels connected to a given axle. Axle load is an important design consideration in the engineering of roadways and railways, as both are designed to tolerate a maximum weight-per-axle (axle load); exceeding the maximum rated axle load will cause damage to the roadway or railway tracks. Railway use On railways, a given section of tracks is designed to support a maximum axle load. The maximum axle load is determined by train speeds, weight of rails, density of sleepers and fixtures, amount and standard of ballast, and strength of bridges and earthworks. Higher operating speeds can be achieved by reducing axle loads and increased load-carrying capacity. Operating above the specified load can cause catastrophic failure of track components. The diameter of the wheels also affects the maximum axle load of a Talgo RD wagon. United Kingdom The standard rail weight for British railways is now . Befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
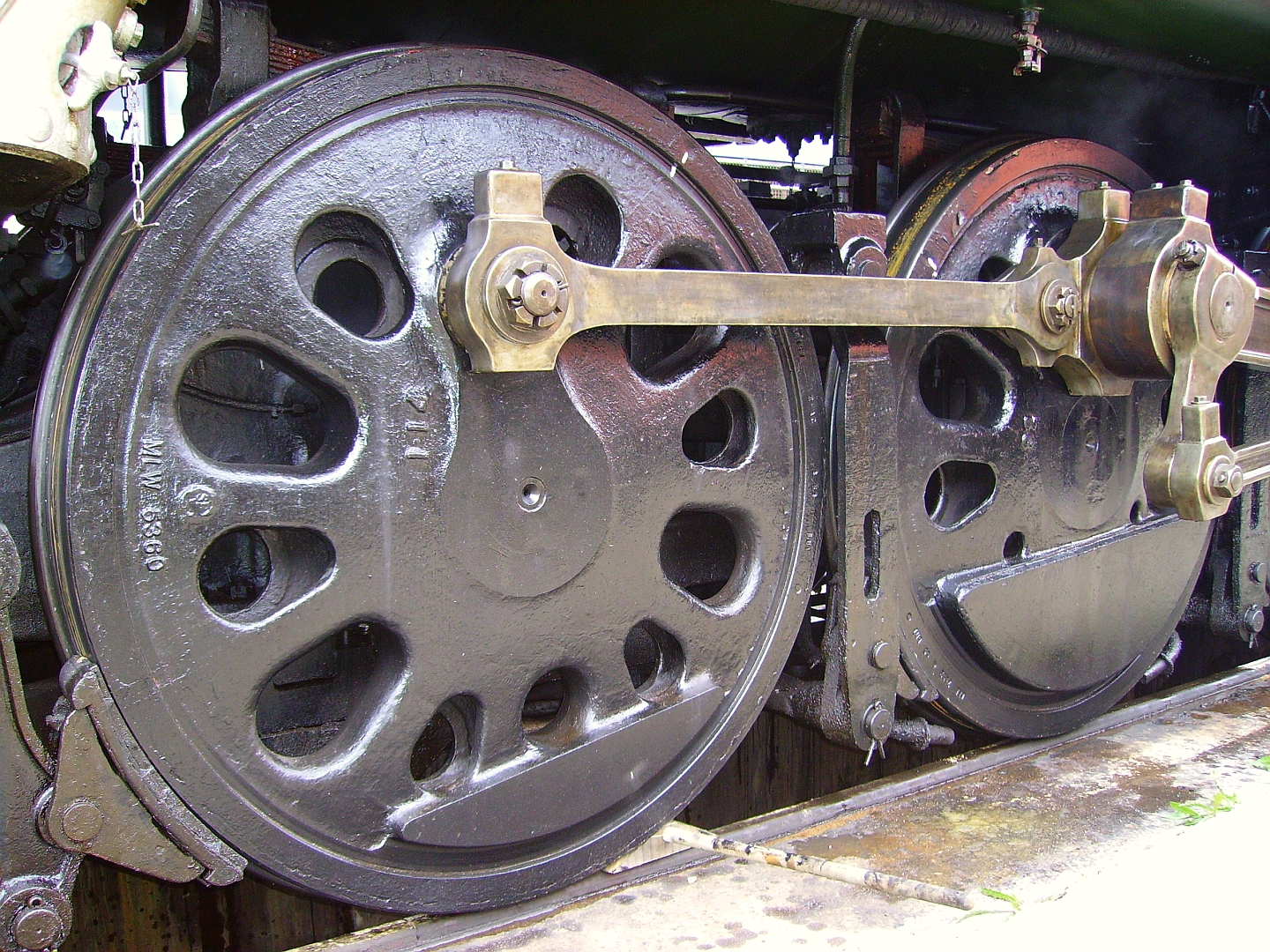
Boxpok
A Boxpok is a steam locomotive wheel that gains its strength through being made of a number of box sections rather than having traditional solid spokes (the name is a variation on "box-spoke"). Being hollow, they allow better counterbalancing and stability than conventional drivers, which is important for fast locomotives. The Boxpok wheel was patented by General Steel Castings Corporation of Granite City, Illinois Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its .... Other wheels The Boxpok was the most common of the four disk wheels in use by US steam locomotive designers, the others being the Baldwin and Scullin. A fourth design, the Universal, was used in locomotive rebuilds. All vary slightly in appearance but are essentially the same in structure. The term "Boxpok" is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimney (locomotive)
The chimney (smokestack or stack in American and Canadian English) is the part of a steam locomotive through which smoke leaves the boiler. As well, steam locomotive exhaust systems typically vent cylinder steam exhaust through the chimney, to enhance the draught through the boiler. Chimneys are designed to carry the exhaust steam and smoke clear of the driver's line of sight while remaining short enough to clear overhead structures. Some chimneys included apparatus to suppress the dispersal of sparks. Function The chimney was usually located at the leading end of the locomotive, above the smokebox, furthest away from the driver's cab and firebox. The earliest locomotive chimneys were typically tall enough to sustain temperature-induced density difference draught through a fire-tube boiler while the locomotive was stationary. However, following the example of Richard Trevithick's first locomotive in 1804, most designs diverted steam cylinder exhaust upward through the chimney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversing Gear
Reversing gear is a mechanism used to both control the direction of travel of a steam locomotive and adjust its engine's steam cutoff. Reversing lever The most common form of reversing gear uses a lever to engage (known as a ''Johnson bar'' in the United States) mounted parallel to the direction of travel on the driver’s side of the cab. It is controlled by a handle and sprung trigger at the top, and pivots at the bottom to pass between two notched sector plates. The reversing rod, which connects to the valve gear, is attached to the lever either above or below the pivot in an alignment that gives good leverage. A square pin is arranged to engage with notches cut in the plates and holds the lever (and valve gear) in the desired position when the trigger is released. The advantages of this design are that change between forward and reverse gear can be made very quickly (as is needed in, for example, a shunting engine). Limitations and drawbacks The reversing lever has a cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Railways JF1
The China Railways JF1 (解放1, ''Jiěfàng'', "liberation") class steam locomotive was a class of 2-8-2 steam locomotives for freight trains operated by the China Railway. They were originally built in the United States, Japan and Manchukuo between 1918 and 1945 for the South Manchuria Railway (''Mantetsu''), the Manchukuo National Railway, the North China Transportation Company, and the Central China Railway. After the end of the Pacific War, they were taken over by the China Railway, the Korean State Railway in North Korea and by the Korean National Railroad in South Korea, and more were built in China after 1949 for the China Railway, which ultimately operated over 2,000 of the type. As well, more were built in Japan for the US Army Transportation Corps during the Korean War; these were later taken over by the Korean National Railroad. Similarly, China supplied some to the Korean State Railway as war aid. History Mantetsu Mikai (ミカイ) and MNR "Big Mika" (國大ミカ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer that operated from 1901 to 1969, initially specializing in the production of locomotives but later diversifying and fabricating at various times diesel generators, automobiles, steel, tanks, munitions, oil-production equipment, as well as heat exchangers for nuclear power plants. The company was formed by the merger of seven locomotive manufacturers and Schenectady Locomotive Works, Schenectady Locomotive Engine Manufactory of Schenectady, New York. A subsidiary, American Locomotive Automobile Company, designed and manufactured automobiles under the Alco brand from 1905 to 1913. ALCO also produced nuclear reactors from 1954 to 1962. After World War II, Alco closed all of its manufacturing plants except those in Schenectady and Montreal. In 1955, the company changed its name to Alco Products, Incorporated. In 1964, the Worthington Corporation acquired the company. The company wen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |