|
New Impositions
The Crown of England traditionally exercised the right to impose import duties for the regulation of trade and the protection of domestic industry. New impositions of this kind were imposed by Elizabeth I on currants and tobacco (1601) and extended by King James I to most imports (1608) after a favourable ruling in Bates' Case (1606). John Bates was a merchant from the Levant Company who refused to pay the import duty on currants. In the face of Parliament's angry protests in 1610, the tax was amended to ensure that the greatest impact fell on foreign merchants.''The Stuart Age, 1603–1714'', by John Wroughton. Pages 151–152 Impositions were among the prerogative rights that King James I was to give up under the Great Contract of 1610, as drawn up by Lord Treasurer Robert Cecil, then Lord Salisbury, in return for an immediate sum to pay off Royal debt and an annual subsidy that would greatly increase income. However negotiations fell through, mainly because both sides kept cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive government specifically or only to the monarch and their Viceroy, direct representatives. The term can be used to refer to the rule of law; or to the functions of executive (government), executive (the Crown-King-in-Council, in-council), legislative (the Crown-in-parliament), and judicial (the Crown on the bench) governance and the civil service. The concept of the Crown as a corporation sole developed first in the Kingdom of England as a separation of the physical crown and property of the kingdom from the person and personal property of the monarch. It spread through English and later British colonisation and developed into an imperial crown, which rooted it in the legal lexicon of all 15 Commonwealth realms, their various dependencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Treasurer
The Lord High Treasurer was an English government position and has been a British government position since the Acts of Union of 1707. A holder of the post would be the third-highest-ranked Great Officer of State in England, below the Lord High Steward and the Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain. The Lord High Treasurer functions as the head of His Majesty's Treasury. The office has, since the resignation of Charles Talbot, 1st Duke of Shrewsbury in 1714, been vacant. Although the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was created in 1801, it was not until the Consolidated Fund Act 1816 that the separate offices of Lord High Treasurer of Great Britain and Lord High Treasurer of Ireland were united into one office as the "Lord High Treasurer of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland" on 5 January 1817. Section 2 of the Consolidated Fund Act 1816 also provides that "whenever there shall not be Lord High Treasurer of the United Kingdom of Great Britain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudal Duties
Feudal duties were the set of reciprocal financial, military and legal obligations among the warrior nobility in a feudal system. Translated into English by Philip Grierson as ''Feudalism'', 1st ed., London, 1952. These duties developed in both Europe and Japan with the decentralisation of empire and due to lack of monetary liquidity, as groups of warriors took over the social, political, judicial, and economic spheres of the territory they controlled. While many feudal duties were based upon control of a parcel of land and its productive resources, even landless knights owed feudal duties such as direct military service in their lord's behest. Feudal duties were not uniform over time or across political boundaries, and in their later development also included duties from and to the peasant population, such as abergement. Feudal duties ran both ways, both up and down the feudal hierarchy; however, aside from distribution of land and maintenance of landless retainers, the main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
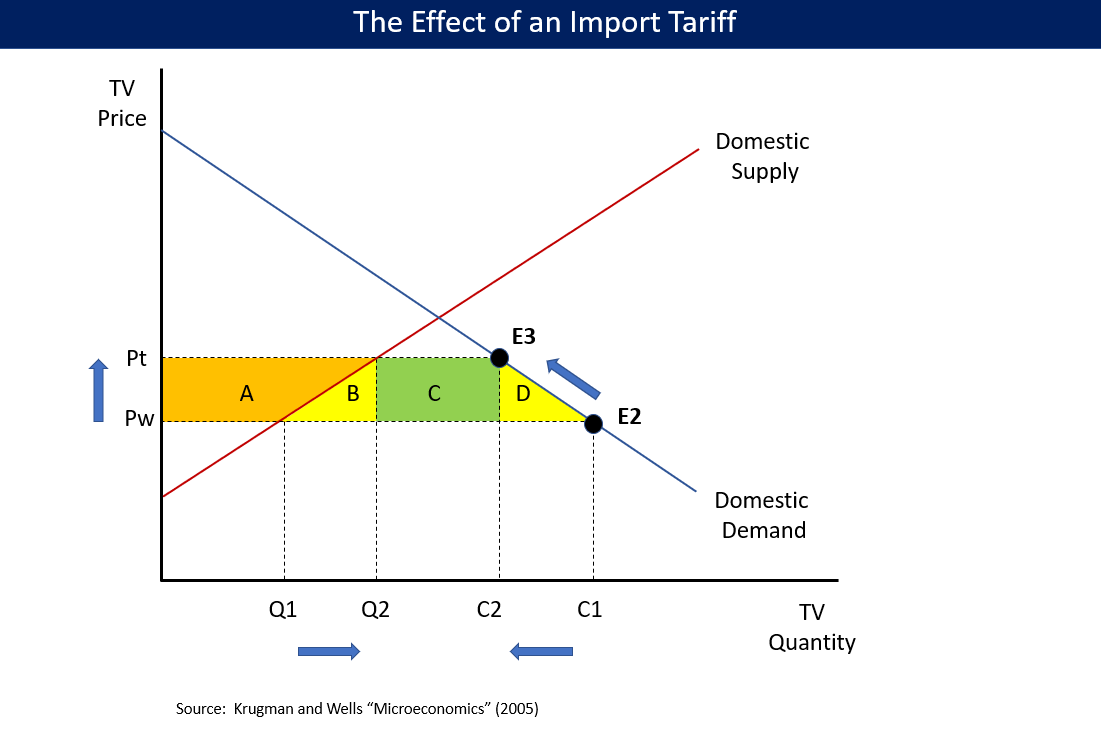
Customs Duties
A tariff or import tax is a duty (tax), duty imposed by a national Government, government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is paid by the exporter. Besides being a source of revenue, import duties can also be a form of regulation of International trade, foreign trade and policy that burden foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Protective tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Tariffs on imports are designed to raise the price of imported goods to discourage consumption. The intention is for citizens to buy local products instead, which, according to support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Taxation In The United Kingdom
300px, ''The Friend of the People; & his Petty New Tax Gatherer paying John Bull a visit'' (1806), James Gillray , alt=A satirical cartoon by James Gilroy. John Bull, speaking from a first floor window, says "TAXES? TAXES? TAXES? why how an I to get money to pay them all? I shall very soon have neither a House nor Hole to put my head in! The history of taxation in the United Kingdom includes the history of all collections by governments under law, in money or in kind, including collections by monarchs and lesser feudal lords, levied on persons or property subject to the government, with the primary purpose of raising revenue. Background Prior to the formation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707 and the United Kingdom in 1801, taxation had been levied in the countries that joined to become the UK. For example, in England, King John introduced an export tax on wool in 1203 and King Edward I introduced taxes on wine in 1275. Also in England, a Poor Law tax was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Of Rights 1689
The Bill of Rights 1689 (sometimes known as the Bill of Rights 1688) is an Act of Parliament (United Kingdom), act of the Parliament of England that set out certain basic civil rights and changed the succession to the Monarchy of England, English Crown. It remains a crucial statute in UK constitutional law, English constitutional law. Largely based on the ideas of political theorist John Locke, the Bill sets out a constitutional requirement for the Crown to seek the consent of the people as represented in Parliament of England, Parliament. As well as setting limits on the powers of the monarch, it established the rights of Parliament, including regular parliaments, free elections, and parliamentary privilege. It also listed individual rights, including the prohibition of cruel and unusual punishment and the right not to pay taxes levied without the approval of Parliament. Finally, it described and condemned several misdeeds of James II of England, James II of England. The Bill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange (William III and II), a nephew of James who thereby had an interest to the throne irrespective of his marriage to his cousin Mary. The two ruled as joint monarchs of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland until Mary's death in 1694, when William became ruler in his own right. Jacobitism, the political movement that aimed to restore the exiled James or his descendants of the House of Stuart to the throne, persisted into the late 18th century. William's invasion was the last successful invasion of England. Despite his own Catholicism, usually an impediment to Protestant support, James became king in February 1685 with widespread backing from the Protestant majorities in England and Scotla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Salisbury
Robert Arthur Talbot Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury (; 3 February 183022 August 1903), known as Lord Salisbury, was a British statesman and Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom three times for a total of over thirteen years. He was also Foreign Secretary (United Kingdom), Foreign Secretary before and during most of his tenure. He avoided international alignments or alliances, maintaining the policy of "splendid isolation". Lord Robert Cecil, later known as Lord Salisbury, was first elected to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons in 1854 and served as Secretary of State for India in Lord Derby's Conservative government 1866–1867. In 1874, under Disraeli, Salisbury returned as Secretary of State for India, and, in 1878, was appointed foreign secretary, and played a leading part in the Congress of Berlin. After Disraeli's death in 1881, Salisbury emerged as the Conservative leader i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Cecil, 1st Earl Of Salisbury
Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury, (1 June 156324 May 1612) was an English statesman noted for his direction of the government during the Union of the Crowns, as Tudor England gave way to Stuart period, Stuart rule (1603). Lord Salisbury served as the Secretary of State (England), Secretary of State of England (1596–1612) and Lord High Treasurer (1608–1612), succeeding his William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley, father as Queen Elizabeth I's Lord Privy Seal and remaining in power during the first nine years of King James VI and I, James I's reign until his own death. The principal discoverer of the Gunpowder Plot of 1605, Robert Cecil remains a controversial historic figure as it is still debated at what point he first learned of the plot and to what extent he acted as an ''agent provocateur''. Early life and family Cecil (created Earl of Salisbury in 1605) was the younger son of William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley by his second wife, Mildred Cooke, eldest daughter of Sir Anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Contract
The Great Contract was a plan submitted to James I and Parliament in 1610 by Robert Cecil. It was an attempt to increase Crown income and ultimately rid it of debt. Cecil suggested that, in return for an annual grant of £200,000, the Crown should give up its feudal rights of Wardship and Purveyance, as well as the power of creating new impositions. The Commons were allergic to the idea of permanent taxation, particularly for the benefit of the spendthrift James, but eventually accepted Cecil's proposal, though they offered far less than he had hoped for. The contract was duly formalized, but during the parliamentary recess members were made aware that their constituents were implacably opposed to it. The plan was eventually rejected by both James and Parliament: the failure of his cherished project was thought by some to have hastened Cecil's early death in 1612, although it is most likely that he died of cancer. The King withdrew from the contract because it meant that he wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Import Duties
A tariff or import tax is a duty imposed by a national government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is paid by the exporter. Besides being a source of revenue, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that burden foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Protective tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import quotas and export quotas and other non-tariff barriers to trade. Tariffs can be fixed (a constant sum per unit of imported goods or a percentage of the price) or variable (the amount varies according to the price). Tariffs on imports are designed to raise the price of imported goods to discourage consumption. The intention is for citizens to buy local products instead, which, according to supporters, would stimulate their country's economy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prerogative
In law, a prerogative is an exclusive right bestowed by a government or State (polity), state and invested in an individual or group, the content of which is separate from the body of rights enjoyed under the general law. It was a common facet of Feudalism, feudal law. The word is derived from Old French ''prerogative'' (14c.), M.L. ''prerogativa'' "special right", from Latin ''Prorogatio, praerogativa'' "prerogative, previous choice or election", originally (with Roman assemblies#Legislative Assemblies of the Roman Republic, tribus, Roman assemblies#Legislative Assemblies of the Roman Republic, centuria) "100 voters who by lot voted first in the Roman Roman assemblies#Legislative Assemblies of the Roman Republic, comitia", from ''praerogativus'' (adj.) "chosen to vote first". Topics * Extraterritoriality * Prerogative court * Prerogative writ * Royal prerogative See also * Individual rights * Sui juris * "My Prerogative" (song) References External links * Legal ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |