|
New Britain Thrush
The New Britain thrush (''Zoothera talaseae'') is a species of bird in the thrush family Turdidae. It is found in the montane forests on the Papua New Guinean islands of New Britain and Umboi. The Bougainville thrush was formerly considered to be conspecific Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organism ... with the New Britain thrush and together the complex was known as the black-backed thrush. References Birds described in 1926 category:Birds of New Britain Endemic fauna of Papua New Guinea Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Endemic birds of Papua New Guinea {{Turdidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild
Lionel Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild, Baron de Rothschild, (8 February 1868 – 27 August 1937) was a British banker, politician, zoology, zoologist, and soldier, who was a member of the Rothschild family. As a Zionist leader, he was presented with the Balfour Declaration, which pledged United Kingdom, British support for a Jewish national home in Palestine (region), Mandatory Palestine. Rothschild was the president of the Board of Deputies of British Jews from 1925 to 1926. Early life Walter Rothschild was born in London as the eldest son and heir of Emma Louise von Rothschild and Nathan Rothschild, 1st Baron Rothschild, an immensely wealthy financier of the international Rothschild financial dynasty and the first Jewish Peerage, peer in England. The eldest of three children, Walter was deemed to have delicate health and was educated at home. As a young man, he travelled in Europe, attending the University of Bonn for a year before entering Magdalene College, Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Hartert
Ernst Johann Otto Hartert (29 October 1859 – 11 November 1933) was a widely published German ornithologist. Life and career Hartert was born in the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg on 29 October 1859. In July 1891, he married the illustrator Claudia Bernadine Elisabeth Hartert in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, with whom he had a son named Joachim Karl (Charles) Hartert, (1893–1916), who was killed as an English soldier on the Somme. Together with his wife, he was the first to describe the blue-tailed Buffon hummingbird subspecies (''Chalybura buffonii intermedia'' Hartert, E & Hartert, C, 1894). The article ''On a collection of Humming Birds from Ecuador and Mexico'' appears to be their only joint publication. Hartert was employed by Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild as ornithological curator of Rothshild's private Natural History Museum at Tring, in England from 1892 to 1929. Hartert published the quarterly museum periodical ''Novitates Zoologicae'' (1894–39) wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turdidae
The thrushes are a passerine bird family, Turdidae, with a worldwide distribution. The family was once much larger before biologists reclassified the former subfamily Saxicolinae, which includes the chats and European robins, as Old World flycatchers. Thrushes are small to medium-sized ground living birds that feed on insects, other invertebrates, and fruit. Some unrelated species around the world have been named after thrushes due to their similarity to birds in this family. Characteristics Thrushes are plump, soft-plumaged, small to medium-sized birds that inhabit wooded areas and often feed on the ground. The smallest thrush may be the shortwings, which have ambiguous alliances with both thrushes and Old World flycatchers. The lesser shortwing averages . The largest thrush is the great thrush at and ; the larger, commonly recognized blue whistling thrush is an Old world flycatcher. The Amami thrush might, however, grow larger than the great thrush. Most species are gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. It has Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, a land border with Indonesia to the west and neighbours Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest list of island countries, island country, with an area of . The nation was split in the 1880s between German New Guinea in the North and the Territory of Papua, British Territory of Papua in the South, the latter of which was ceded to Australia in 1902. All of present-day Papua New Guinea came under Australian control following World War I, with the legally distinct Territory of New Guinea being established out of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
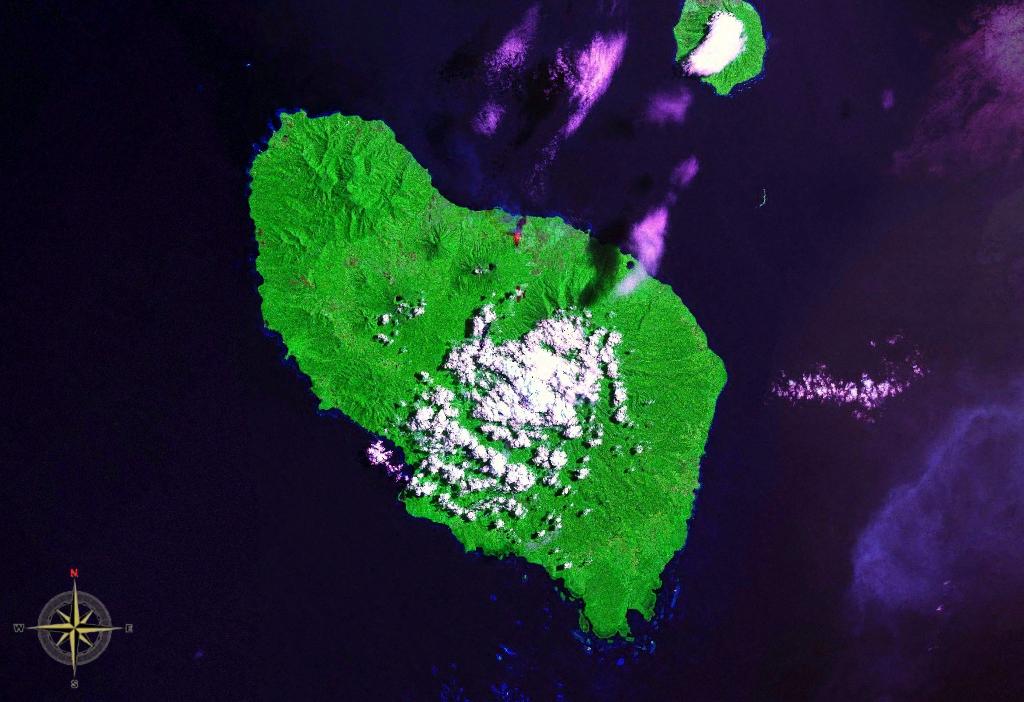
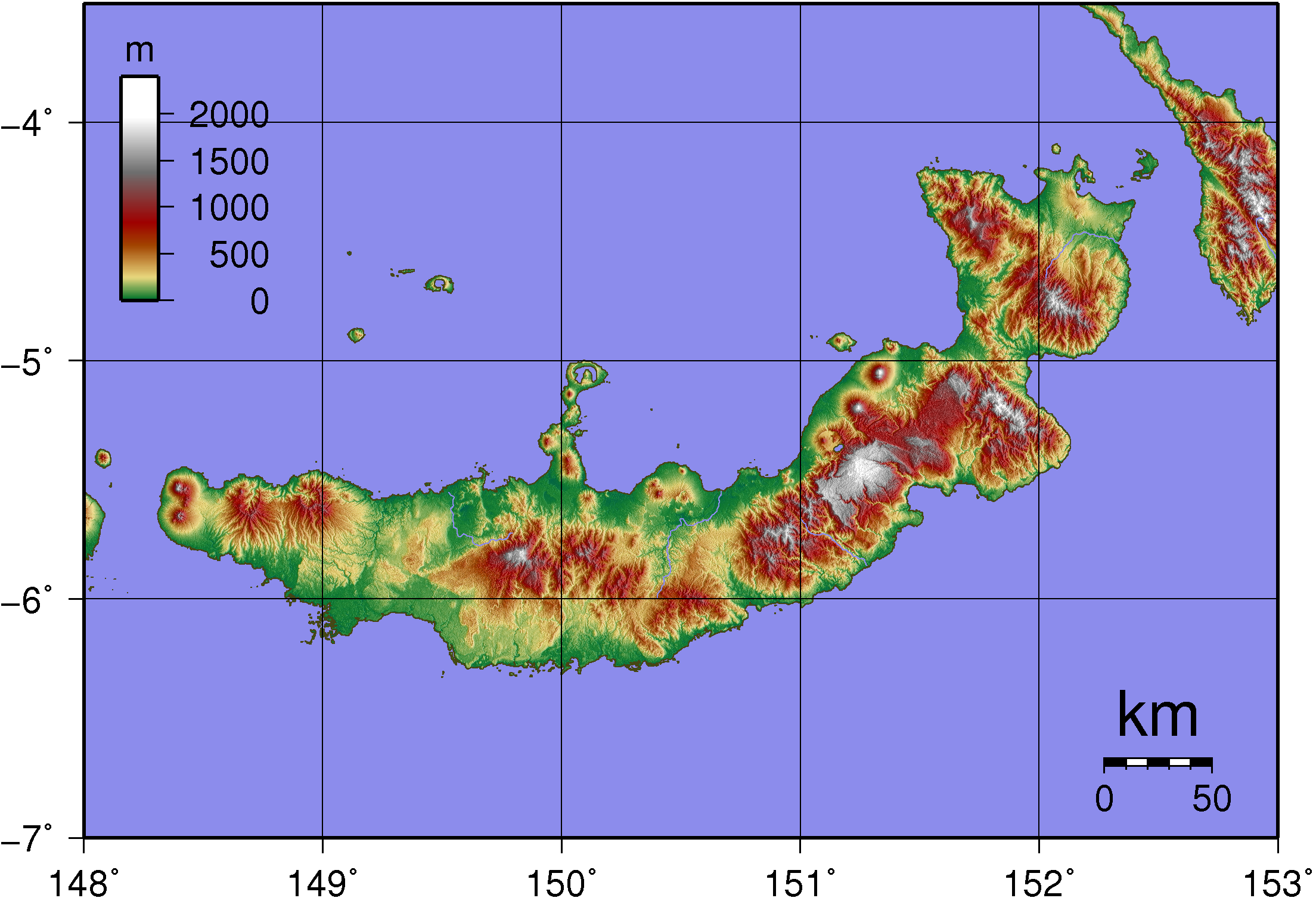
New Britain
New Britain () is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi Island, Umboi the Dampier Strait (Papua New Guinea), Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland (island), New Ireland by St. George's Channel (Papua New Guinea), St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. When the island was part of German New Guinea, its name was Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan (volcano), Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umboi
Umboi (also named Rooke or Siassi) is a volcanic island between the mainland of Papua New Guinea and the island of New Britain. It is separated from New Britain by the Dampier Strait, and Huon Peninsula and New Guinea by the Vitiaz Strait. It has an elevation of . The Siassi Archipelago lies off the southeast coast of Umboi Island (a total of 18 islands, only seven are inhabited). History During the mid-1920s, the population of the Siassi Islands was a little over 700 people. It had more than doubled (to almost 1700 people) by the early 1960s, and then decreased to a little more than 1600 people by the early 1980s. In 1936 a Lutheran mission was established on the island which was headed by Pastor P.H Freund. in 1940 Freund was recruited by Lt. Commander Eric Feldt of the Royal Australian Navy to act as a Coastwatcher. During 1943 the island was briefly occupied by 500 Japanese troops from the 51st Reconnaissance Regiment which was commanded by Col. Jiro Sato. By early Dece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bougainville Thrush
The Bougainville thrush (''Zoothera atrigena'') is a species of bird in the thrush family Turdidae. It is found in the montane forests of Bougainville Island in the Solomon Islands Archipelago. It was formerly considered to be conspecific with the New Britain thrush with the combined taxa known as the black-backed thrush. Taxonomy The Bougainville thrush was formally described in 1982 by Dillon Ripley and Don Hadden from a specimen collected at an altitude of on Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea. They considered it to be a subspecies of the black-backed thrush (now renamed the New Britain thrush) and coined the trinomial name ''Zoothera talaseae atrigena''. The epithet ''atrigena'' combines Latin Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ... ''ater'' meaning "black" wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organisms or constituents of living organisms of being special or doing something special. Each animal or plant species is special. It differs in some way from all other species...biological specificity is the major problem about understanding life." Biological specificity within ''Homo sapiens'' ''Homo sapiens'' has many characteristics that show the biological specificity in the form of behavior and morphological traits. Morphologically, humans have an enlarged cranial capacity and more gracile features in comparison to other hominins. The reduction of dentition is a feature that allows for the advantage of adaptability in diet and survival. As a species, humans are culture dependent and much of human survival relies on the culture and soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Described In 1926
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of Papua New Guinea
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are Indigenous (ecology), indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy Articles Created By Polbot
280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation of things to the classes (classification). Originally, taxonomy referred only to the classification of organisms on the basis of shared characteristics. Today it also has a more general sense. It may refer to the classification of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such work. Thus a taxonomy can be used to organize species, documents, videos or anything else. A taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon"). Many are hierarchies. One function of a taxonomy is to help users more easily find what they are searching for. This may be effected in ways that include a library classification system and a search engine taxonomy. Etymology The word was coined in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |