|
Neuroreflexotherapy
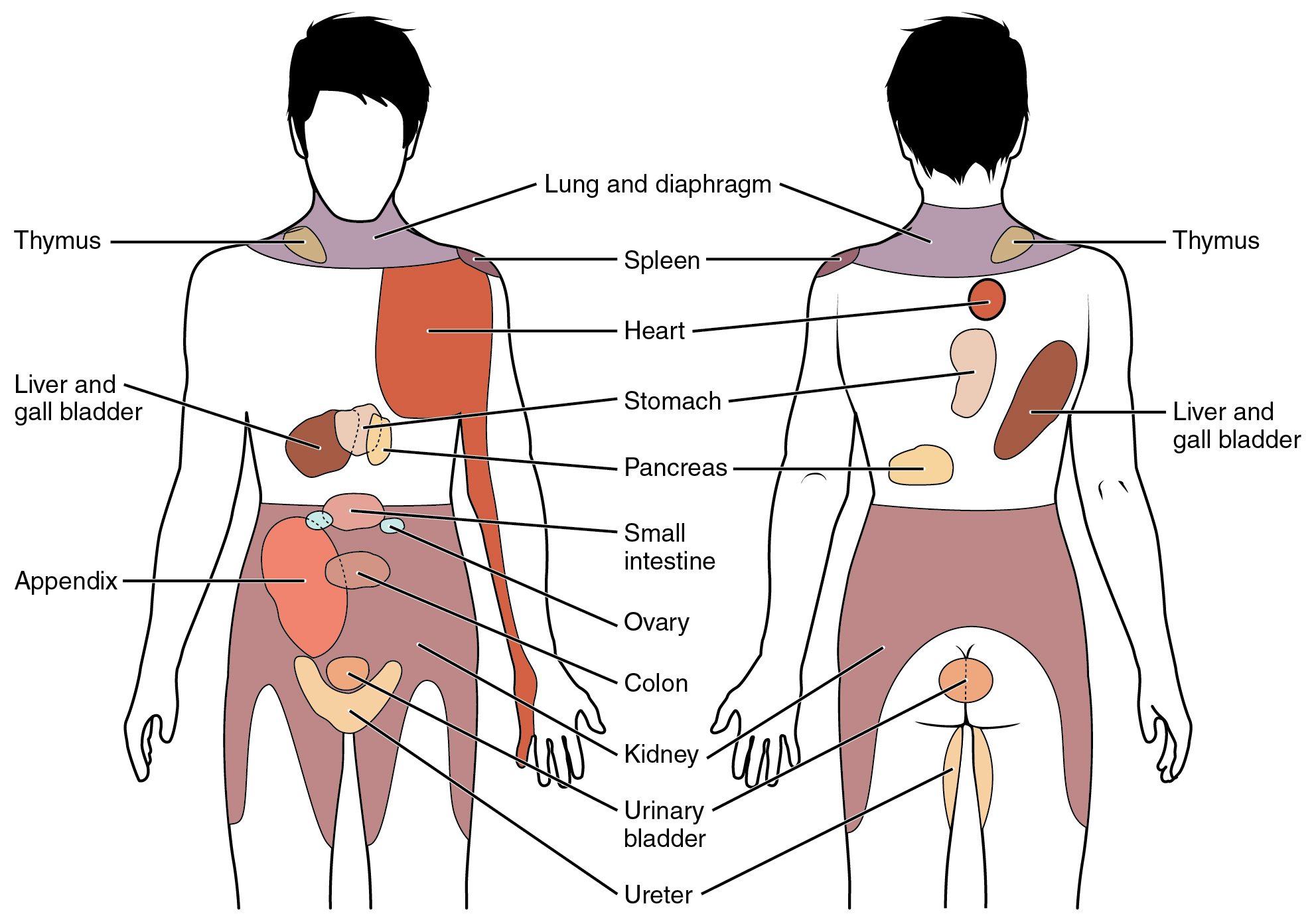
Neuroreflexotherapy (NRT) is a type of alternative medicine treatment used for some cases of low back pain (LBP). Small pieces of metal are placed just under the surface of the skin in the ear and back, and are intended to interrupt the neural pain processes. Totally, there are three publications devoted to this method in the world medical science ovacs FM, 1993, 1997, 2002 They are published by the same first author and claim almost absolute efficacy of the therapy and lack of effect of other treatments. Also, three reviews repeat the definition of the method and the claimed results. Efficacy A 2005 Cochrane review said that while some limited research reported "surprising" results for the efficacy of this therapy in treating nonspecific LBP, a lack of confirming research made it impossible to reach general conclusions about its overall efficacy. A note from the Co‐Editors of the review says that the conclusions would be more sound "if similar evidence was available from RCTs c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Back Pain
Low back pain or wiktionary:lumbago#Etymology, lumbago is a common musculoskeletal disorders, disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling. Low back pain may be classified by Pain#Chronic versus acute, duration as acute (pain lasting less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks). The condition may be further classified by the underlying cause as either mechanical, non-mechanical, or referred pain. The symptoms of low back pain usually improve within a few weeks from the time they start, with 40–90% of people recovered by six weeks. In most episodes of low back pain a specific underlying cause is not identified or even looked for, with the pain believed to be due to mechanical problems such as muscle strain, muscle or joint strain. If the pain does not go away with conservative treatmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Medicine
Alternative medicine refers to practices that aim to achieve the healing effects of conventional medicine, but that typically lack biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or supporting evidence of effectiveness. Such practices are generally not part of evidence-based medicine. Unlike modern medicine, which employs the scientific method to test plausible therapies by way of Guidelines for human subject research, responsible and ethical clinical trials, producing repeatable evidence of either effect or of no effect, alternative therapies reside outside of mainstream medicine and do not originate from using the scientific method, but instead rely on testimonials, anecdotes, religion, tradition, superstition, belief in supernatural "Energy (esotericism), energies", pseudoscience, fallacy, errors in reasoning, propaganda, fraud, or other unscientific sources. Frequently used terms for relevant practices are New Age medicine, wikt:pseudo-medicine, pseudo-medicine, unortho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is also called eczema but the same term is often used for the most common type of skin inflammation, atopic dermatitis. The exact cause of the condition is often unclear. Cases may involve a combination of allergy and poor venous return. The type of dermatitis is generally determined by the person's history and the location of the rash. For example, irritant dermatitis often occurs on the hands of those who frequently get them wet. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs upon exposure to an allergen, causing a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin. Prevention of atopic dermatitis is typically with essential fatty acids, and may be treated with moistu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatome (anatomy)
A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibres from the dorsal root of any given spinal nerve. There are 8 cervical nerves (C1 being an exception with no dermatome), 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and 5 sacral nerves. Each of these nerves relays sensation (including pain) from a particular region of skin to the brain. The term is also used to refer to a part of an embryonic somite. Along the thorax and abdomen, the dermatomes are like a stack of discs forming a human, each supplied by a different spinal nerve. Along the arms and the legs, the pattern is different: the dermatomes run longitudinally along the limbs. Although the general pattern is similar in all people, the precise areas of innervation are as unique to an individual as fingerprints. An area of skin innervated by a single nerve is called a peripheral nerve field. The word ''dermatome'' is formed from Ancient Greek 'skin, hide' and 'cut'. Clinical significance A derma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenic Inflammation
Neurogenic inflammation is inflammation arising from the local release by afferent neurons of inflammatory mediators such as substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), neurokinin A (NKA), and endothelin-3 (ET-3). In such neurons, the release of these pro-inflammatory mediators is thought to be triggered by the activation of ion channels that are the principal detectors of noxious environmental stimuli. In particular, the heat/capsaicin receptor TRPV1 and the wasabi receptor TRPA1. TRPA1 channels stimulated by lipopolysaccharides may also cause acute neurogenic inflammation. Once released, these neuropeptides induce the release of histamine from nearby mast cells. In turn, histamine evokes the release of substance P and CGRP; thus, a bidirectional link between histamine and neuropeptides in neurogenic inflammation is established. Neurogenic inflammation appears to play a role in the pathogenesis of numerous disorders, including migraine, psoriasis, asthma, vasomotor rh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience concerned with the functions of the nervous system and their mechanisms. The term ''neurophysiology'' originates from the Greek word ''νεῦρον'' ("nerve") and ''physiology'' (which is, in turn, derived from the Greek ''φύσις'', meaning "nature", and ''-λογία'', meaning "knowledge"). Neurophysiology has applications in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of many neurological and psychiatric diseases. Neurophysiological techniques are also used by clinical neurophysiologists to diagnose and monitor patients with neurological diseases. The field involves all levels of nervous system function, from molecules and cells to systems and whole organisms. Areas of study include: * The electrochemical properties of neurons * Function and regulation of proteins in neurons and glia * Metabolic reactions relevant to neural function * Cell signalling in the nervous system * Neurotransmission and synaptic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." Pain motivates organisms to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Congenital insensitivity to pain may result in reduced life expectancy. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |