|
Neural Decoding
Neural decoding is a neuroscience field concerned with the hypothetical reconstruction of sensory and other stimuli from information that has already been encoded and represented in the brain by biological neural network, networks of neurons. Reconstruction refers to the ability of the researcher to predict what sensory stimuli the subject is receiving based purely on neuron action potentials. Therefore, the main goal of neural decoding is to characterize how the Electrophysiology, electrical activity of neurons elicit activity and responses in the brain. This article specifically refers to neural decoding as it pertains to the mammalian neocortex. Overview When looking at a picture, people's brains are constantly making decisions about what object they are looking at, where they need to move their eyes next, and what they find to be the most salient aspects of the input stimulus. As these images hit the back of the retina, these stimuli are converted from varying wavelengths to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Cell
A simple cell in the visual cortex, primary visual cortex is a cell that responds primarily to oriented edges and gratings (bars of particular orientations). Torsten Wiesel and David Hubel discovered these cells in the late 1950s. Such cells are tuned to different frequencies and orientations, even with different phase relationships, possibly to extract disparity (depth) information and to attribute depth to detected lines and edges. This may result in a 3D 'wire-frame' representation as used in computer graphics. The fact that input from the left and right eyes is very close in the so-called cortical hypercolumns indicates that depth processing occurs very early, aiding the recognition of 3D objects. Later, many other cells with specific functions have been discovered: (a) end-stopped cells, which are thought to detect singularities like line and edge crossings, vertices, and line endings; (b) bar and grating cells. The latter are not linear operators because a bar cell does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spike-timing-dependent Plasticity
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is a biological process that adjusts the strength of synaptic connections between neurons based on the relative timing of their action potentials (or spikes). It is a temporally sensitive form of synaptic plasticity, meaning that the efficiency of synaptic transmission is modified by the timing of neural activity. When a presynaptic neuron consistently fires just before a postsynaptic neuron, the connection is typically strengthened—a process known as long-term potentiation (LTP). If the timing is reversed and the presynaptic neuron fires after the postsynaptic neuron, the connection is weakened through long-term depression (LTD). STDP is considered a key mechanism in learning and memory formation and helps explain activity-dependent development of neural circuits. It has been observed in multiple brain regions, including the hippocampus, neocortex, and visual system, and has been widely implemented in computational models of biologically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal_and_ventral, ventral projection of the thalamus where the thalamus connects with the optic nerve. There are two LGNs, one on the left and another on the right side of the thalamus. In humans, both LGNs have six layers of neurons (grey matter) alternating with optic fibers (white matter). The LGN receives information directly from the ascending retinal ganglion cells via the optic tract and from the reticular activating system. Neurons of the LGN send their axons through the optic radiation, a direct pathway to the primary visual cortex. In addition, the LGN receives many strong feedback connections from the primary visual cortex. In humans as well as other mammals, the two strongest pathways linking the eye to the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the photographic film, film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by Chemical synapse, synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rod cell, rods and cone cell, cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-gated Potassium Channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels (VGKCs) are potassium channel, transmembrane channels specific for potassium and Voltage-gated ion channel, sensitive to voltage changes in the cell's membrane potential. During action potentials, they play a crucial role in returning the depolarized cell to a resting state. Classification Alpha subunits Alpha subunits form the actual conductance pore. Based on sequence homology of the hydrophobic transmembrane cores, the alpha subunits of voltage-gated potassium channels are grouped into 12 classes. These are labeled Kvα1-12. The following is a list of the 40 known human voltage-gated potassium channel alpha subunits grouped first according to function and then subgrouped according to the Kv sequence homology classification scheme: Delayed rectifier slowly inactivating or non-inactivating *Kvα1.x - shaker superfamily of potassium channels, Shaker-related: Kv1.1 (KCNA1), Kv1.2 (KCNA2), Kv1.3 (KCNA3), Kv1.5 (KCNA5), Kv1.6 (KCNA6), Kv1.7 (KCN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-gated Sodium Channel
Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs), also known as voltage-dependent sodium channels (VDSCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeability to the sodium ion Na+. They are the main channels involved in action potential of excitable cells. Structure Sodium channels consist of large alpha subunits that associate with accessory proteins, such as beta subunits. An alpha subunit forms the core of the channel and is functional on its own. When the alpha subunit protein is expressed by a cell, it is able to form a pore in the cell membrane that conducts Na+ in a voltage-dependent way, even if beta subunits or other known modulating proteins are not expressed. When accessory proteins assemble with α subunits, the resulting complex can display altered voltage dependence and cellular localization. The alpha subunit consists of four repeat domains, labelled I through IV, each cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
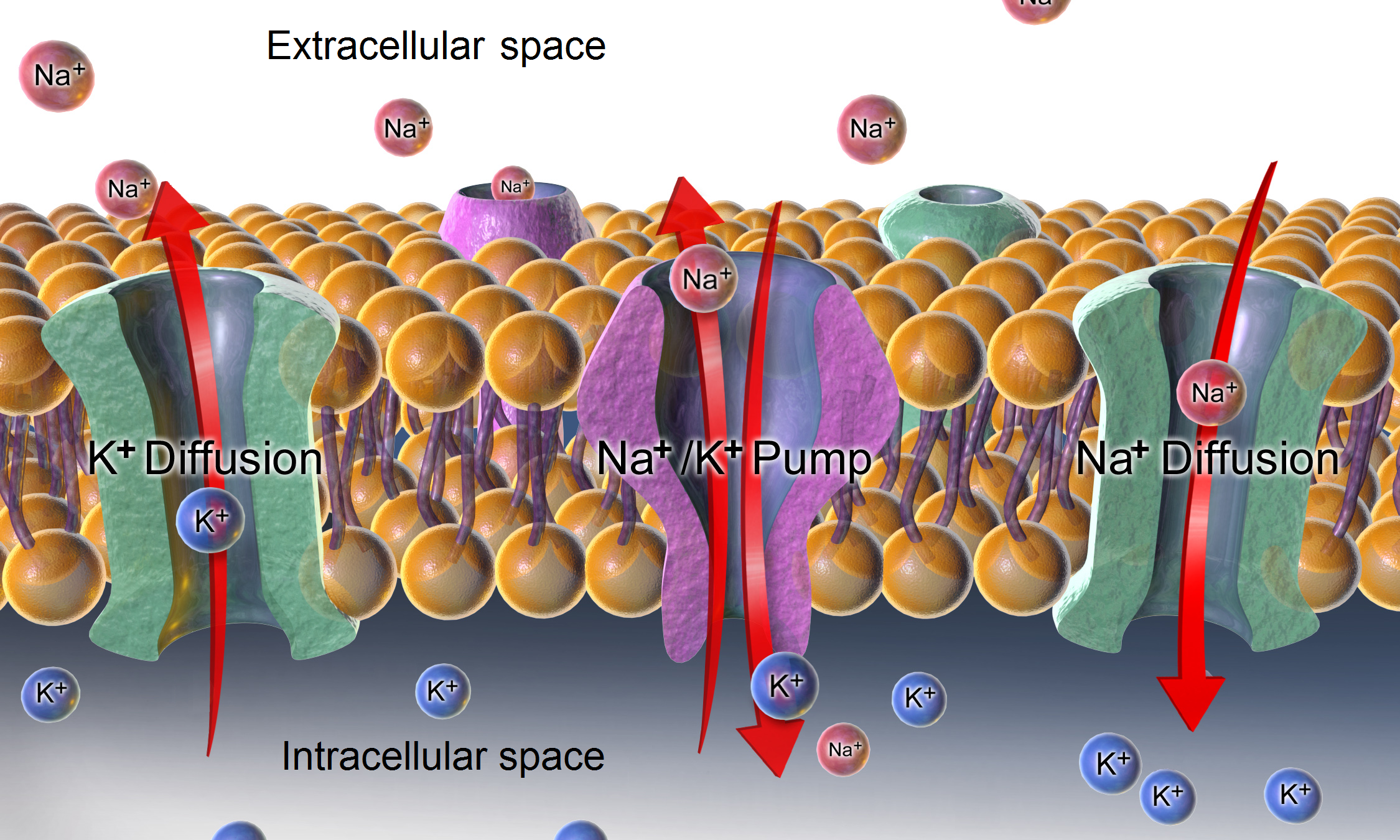
Resting Potential
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The resting membrane potential has a value of approximately −70 mV or −0.07 V. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Because the membrane pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Potential
Electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as electric potential energy per unit of electric charge. More precisely, electric potential is the amount of work (physics), work needed to move a test charge from a reference point to a specific point in a static electric field. The test charge used is small enough that disturbance to the field is unnoticeable, and its motion across the field is supposed to proceed with negligible acceleration, so as to avoid the test charge acquiring kinetic energy or producing radiation. By definition, the electric potential at the reference point is zero units. Typically, the reference point is Earth (electricity), earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. In classical electrostatics, the electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar (physics), scalar quantity denoted by or occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinotopy
Retinotopy () is the mapping of visual input from the retina to neurons, particularly those neurons within the visual stream. For clarity, 'retinotopy' can be replaced with 'retinal mapping', and 'retinotopic' with 'retinally mapped'. Visual field maps (retinotopic maps) are found in many amphibian and mammalian species, though the specific size, number, and spatial arrangement of these maps can differ considerably. Sensory topographies can be found throughout the brain and are critical to the understanding of one's external environment. Moreover, the study of sensory topographies and retinotopy in particular has furthered our understanding of how neurons encode and organize sensory signals. Retinal mapping of the visual field is maintained through various points of the visual pathway including but not limited to the retina, the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus, the optic tectum, the primary visual cortex (V1), and higher visual areas (V2-V4). Retinotopic maps in cortical ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedforward Neural Network
Feedforward refers to recognition-inference architecture of neural networks. Artificial neural network architectures are based on inputs multiplied by weights to obtain outputs (inputs-to-output): feedforward. Recurrent neural networks, or neural networks with loops allow information from later processing stages to feed back to earlier stages for sequence processing. However, at every stage of inference a feedforward multiplication remains the core, essential for backpropagationRumelhart, David E., Geoffrey E. Hinton, and R. J. Williams.Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. David E. Rumelhart, James L. McClelland, and the PDP research group. (editors), Parallel distributed processing: Explorations in the microstructure of cognition, Volume 1: Foundation. MIT Press, 1986. or backpropagation through time. Thus neural networks cannot contain feedback like negative feedback or positive feedback where the outputs feed back to the ''very same'' inputs and modify them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Ganglion Cell
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptor cell, photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Bipolar cell of the retina, bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that extends into the brain. These axons form the optic ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |