|
Netherton, Wakefield
Netherton is a village in the City of Wakefield metropolitan borough of West Yorkshire, England. It lies about 4 miles south-west of Wakefield, 3 miles south of Ossett and 1 mile south of Horbury. The village is in the Wakefield Rural ward of Wakefield Metropolitan District Council. The village name is shown on map "Dvcatvs Eboracensis pars occidentalis" from 1646. The ''h'' was dropped from nearby Shitlington and Sitlington was adopted in 1929 with the approval of the county council. History Netherton, originally Nether Shitlington was, with Over Shitlington ( Overton) and Middle Shitlington (Middlestown), part of the township of Shitlington in the ancient ecclesiastical parish of Thornhill in the wapentake of Agbrigg and Morley in the West Riding of Yorkshire. A Mesolithic axe was found near the Star Inn in 1963. Shitlington was probably settled in Anglo-Saxon times and was recorded in the ''Domesday Book'' as ''Schellingtone''. Netherton Hall, a Grade II* listed manor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire is a Metropolitan counties of England, metropolitan and Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and east, South Yorkshire and Derbyshire to the south, Greater Manchester to the south-west, and Lancashire to the west. The city of Leeds is the largest settlement. The county has an area of and a population of 2.3 million, making it the fourth-largest ceremonial county by population. The centre of the county is urbanised, and contains the city of Leeds in the north-east, the city of Bradford in the north-west, Huddersfield in the south-west, and Wakefield in the south-east. The outer areas of the county are rural. For local government purposes the county comprises five metropolitan boroughs: City of Bradford, Bradford, Calderdale, Kirklees, City of Leeds, Leeds, and City of Wakefield, Wakefield, which collaborate through West Yorkshire Combined Authority. The cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in Epipaleolithic Near East, the Levant and Epipaleolithic Caucasus, Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 Before Present, BP; in the Middle East (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 Before Present, BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Buildings In Sitlington
Sitlington is a civil parish in the metropolitan borough of the City of Wakefield, West Yorkshire, England. The parish contains ten Listed building#England and Wales, listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. Of these, two are listed at Grade II*, the middle of the three grades, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade. The parish contains the villages of Middlestown, Netherton, Wakefield, Netherton, and Overton, Wakefield, Overton, and the surrounding countryside. In the parish is the large house, Netherton Hall, which is listed together with associated structures. Also in the parish is the former Caphouse Colliery, later the National Coal Mining Museum for England, which contains two listed buildings. The other listed buildings consist of farm buildings, a wagonway tunnel and its portal (architecture), portal, a row of cottages, a milepost, and a church. __NOTOC__ Key Buildings References Citations Sources [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cribs
The Cribs are a British indie rock band originally from Wakefield, West Yorkshire, that formed in 2001. The band consists of twins Gary Jarman, Gary and Ryan Jarman and their younger brother Ross Jarman. They were subsequently joined by ex-The Smiths, Smiths guitarist Johnny Marr, who was an official member of the group from 2008 until 2011. The band, who first became active on the concert circuit in 2002, were initially tied to other like-minded UK bands of that time, most notably the Libertines, by a British music press that were looking for a 'British rearguard' to the wave of popular US alternative rock bands of the time. They had outgrown this tag by the time of the commercial success of their third LP. In 2008, ''Q (magazine), Q'' magazine described the band as "the biggest cult band in the UK". In 2012, the band's 10th anniversary year, they were honoured with the Spirit of Independence award at the annual Q Awards. Several months later, they received the Outstanding Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
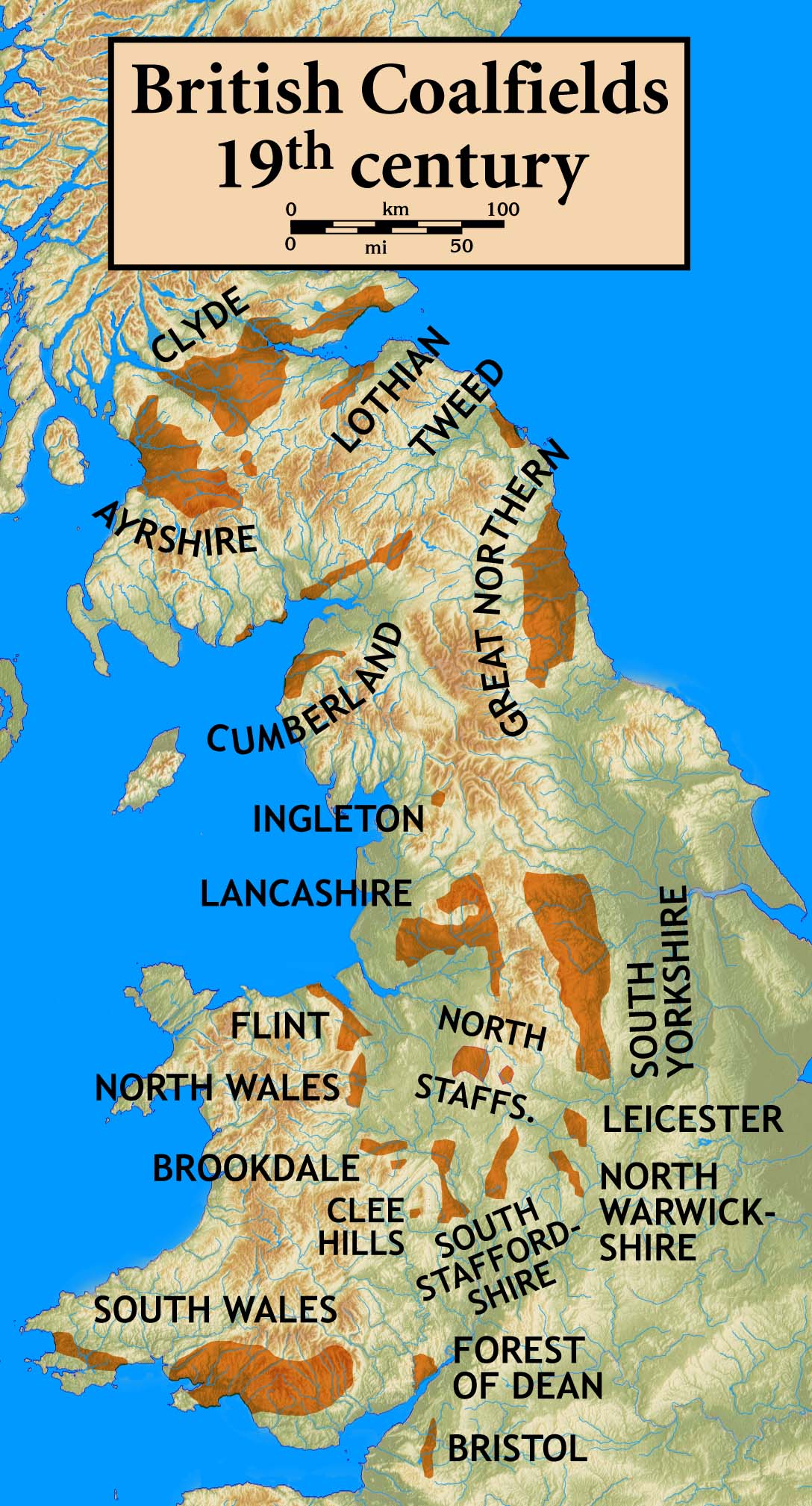
South Yorkshire Coalfield
The South Yorkshire Coalfield is so named from its position within Yorkshire. It covers most of South Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and a small part of North Yorkshire. The exposed coalfield outcrops in the Pennine foothills and dips under Permian rocks in the east. Its most famous coal seam is the Barnsley Bed. Coal has been mined from shallow seams and outcrops since medieval times and possibly earlier. Geography and geology The coalfield stretches from Halifax in the north west, to the north of Bradford and Leeds in the north east, Huddersfield and Sheffield in the west, and Doncaster in the east. The major towns of Wakefield, Barnsley and Rotherham are within its boundaries. It is part of the larger Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire Coalfield. Its western boundary is defined by the outcropping of coal seams in the foothills of the Pennines and in the east by the descent of the coal-bearing strata under overlying rocks as they approach the North Sea. Since the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Calder, West Yorkshire
The River Calder () is a river in West Yorkshire, in Northern England. The Calder rises on Heald Moor in Lancashire close to the source of another river with the same name, and then flows east into West Yorkshire through green countryside, former woollen-mill villages and towns before joining the River Aire near Castleford. The river's valley is generally known as the Calder Valley. The name Calderdale usually refers to the large urban and rural borough (centred on Halifax) through which the upper river flows. The lower reaches flow through the boroughs of Kirklees (based on Huddersfield) and Wakefield. However, the river does not flow through the centres of Halifax and Huddersfield, which are on the Calder's main tributaries, Hebble Brook and the River Colne respectively. The only large town centres through which the Calder flows are Brighouse, Mirfield, Dewsbury and the city of Wakefield. The river itself is only navigable in short sections, but these sections are conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firedamp
Firedamp is any flammable gas found in coal mines, typically coalbed methane. It is particularly found in areas where the coal is bituminous. The gas accumulates in pockets in the coal and adjacent strata and, when they are penetrated, the release of the gas can cause explosions. Historically, if such a pocket was highly pressurized, it was termed a "bag of foulness". Name Damp is the collective name given to all gases (other than air) found in coal mines in Great Britain and North America. As well as firedamp, other damps include '' blackdamp'' (nonbreathable mixture of carbon dioxide, water vapour and other gases); whitedamp (carbon monoxide and other gases produced by combustion); poisonous, explosive '' stinkdamp'' (hydrogen sulfide), with its characteristic rotten-egg odour; and the insidiously lethal '' afterdamp'' (carbon monoxide and other gases) which are produced following explosions of firedamp or coal dust. Etymology Often hyphenated as fire-damp, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adit
An adit (from Latin ''aditus'', entrance) or stulm is a horizontal or nearly horizontal passage to an underground mine. Miners can use adits for access, drainage, ventilation, and extracting minerals at the lowest convenient level. Adits are also used to explore for mineral veins. Although most strongly associated with mining, the term ''adit'' is sometimes also used in the context of underground excavation for non-mining purposes; for example, to refer to smaller underground passageways excavated for underground metro systems, to provide pedestrian access to stations (pedestrian adits), and for access required during construction (construction adits). Construction Adits are driven into the side of a hill or mountain, and are often used when an ore body is located inside the mountain but above the adjacent valley floor or coastal plain. In cases where the mineral vein outcrops at the surface, the adit may follow the lode or vein until it is worked out, in which case the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calder And Hebble Navigation
The Calder and Hebble Navigation is a broad inland waterway, with locks and bridge holes that are suitable for boats, in West Yorkshire, England. Construction to improve the River Calder and the River Hebble began in 1759, and the initial scheme, which included of new cuts, was completed in 1770 and has remained navigable since it was opened. Significant improvements were made, including the Salterhebble branch to Halifax, opened in 1828, and ever-longer cuts to bypass river sections. Trade was assisted by the opening of the Rochdale Canal in 1804, which provided a through route from Sowerby Bridge to Manchester. There were plans to abandon the river sections completely in the 1830s, but these were modified as the needs of mill owners and other riparian landowners were recognised. With the coming of the railways, the canal was leased to the Manchester and Leeds Railway in 1843, but this was subsequently deemed to be illegal, and the Aire and Calder Navigation with which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire And Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company before the Railways Act 1921, 1923 Grouping. It was Incorporation (business)#Incorporation in the United Kingdom, incorporated in 1847 from an amalgamation of several existing railways. It was the third-largest railway system based in northern England (after the Midland Railway, Midland and North Eastern Railway (United Kingdom), North Eastern Railways). The intensity of its service was reflected in the 1,650 steam locomotive, locomotives it owned – it was by far the most densely-trafficked system in the British Isles with more locomotives per mile than any other company – and that one third of its 738 signal boxes controlled junctions averaging one every . No two adjacent stations were more than apart and its 1,904 passenger services occupied 57 pages in ''George Bradshaw#Bradshaw.27s railway timetables, Bradshaw'', a number exceed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
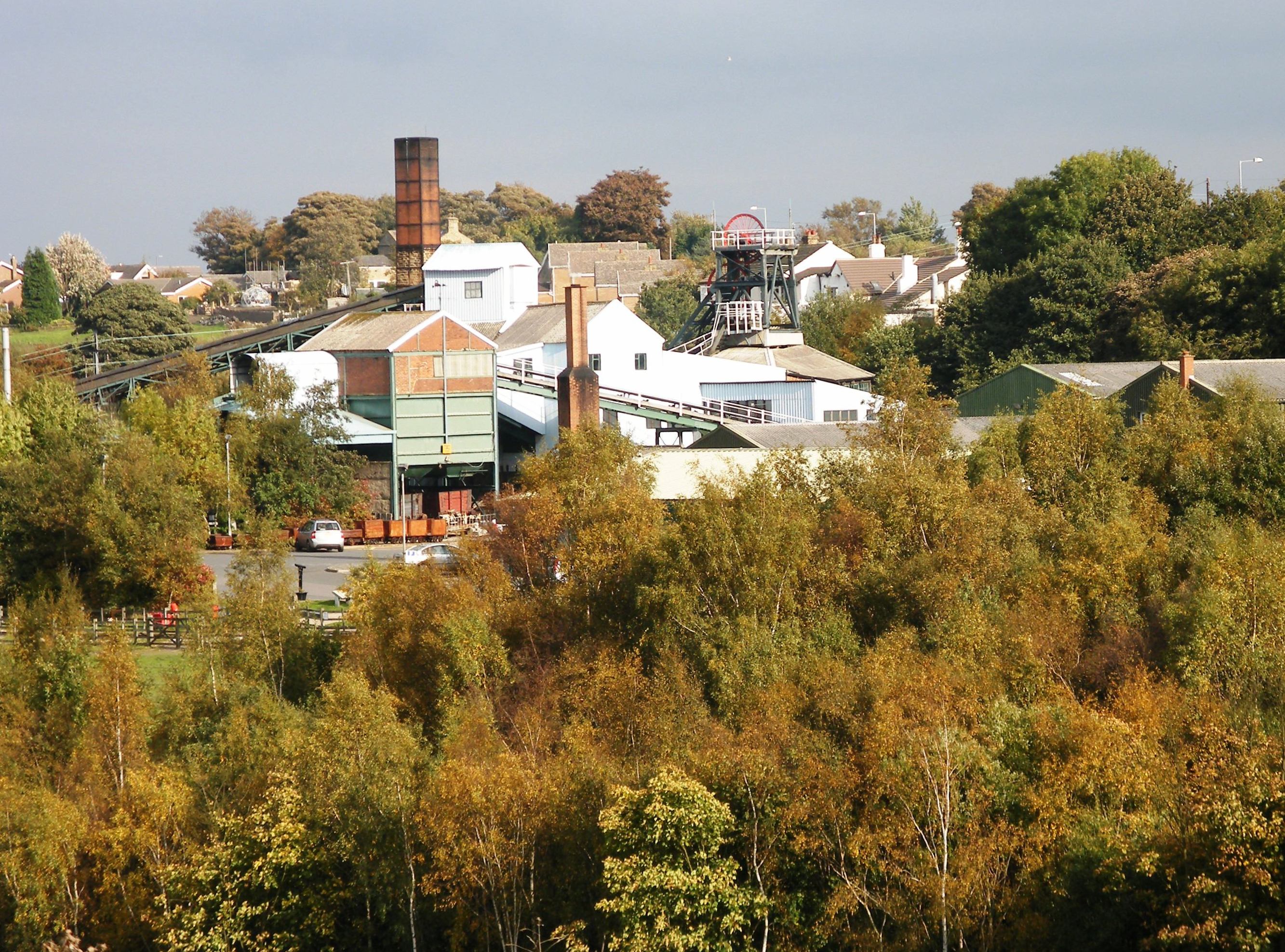
Caphouse Colliery
Caphouse Colliery, originally known as Overton Colliery, was a coal mine in Overton, Wakefield, Overton, near Wakefield, West Yorkshire, England. It was situated on the Denby Grange estate owned by the Lister Kaye family, and was worked from the 18th century until 1985. It reopened as the Yorkshire Mining Museum in 1988, and is now the National Coal Mining Museum for England. History The colliery was on the Denby Grange Estate, home of the Lister Kayes, in an area where coal had been mined for many years. Coal was close to the surface and the Flockton Seam, Flockton Thick Seam was mined in 1793. Leases for mining coal were held by Timothy Smith who leased the original Denby Grange Colliery north of Flockton and James Milnes who mined coal at Emroyd and Old Flockton. Some coal was supplied locally, but much more was sent to distant markets to the east of Pontefract via the Calder and Hebble Navigation. Smith's coal pits were under the control of Sir John Lister Kaye, 1st Baronet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |