|
Nervous System Tumor
A nervous system tumor is a tumor that arises within the nervous system, either the central nervous system (CNS) or the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Nervous system primary tumors include various types of brain tumor and spinal tumors, such as gliomas, and meningiomas (of the CNS), and schwannomas (of the PNS) and can be either benign or malignant. There are over 120 types of brain and spinal cord tumors. In the CNS a tumor may be a malignant secondary tumor having metastasised (spread from a primary site in the body). Secondary tumors are more common in adults. Treatment and prognosis depend on factors such as the type of tumor, location, and molecular characteristics. Types Primary tumors can affect either the peripheral nervous system (PNS) or the central nervous system (CNS). They may be either benign or malignant. A nerve sheath tumor may be found in both the CNS and PNS. There are over 120 types of brain and spinal cord tumor. A secondary tumor may be found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRI Scan
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although "ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasised
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymphatic or blood vessels, and circulate through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a common type of primary brain cancer in children. It originates in the part of the brain that is towards the back and the bottom, on the floor of the skull, in the cerebellum, or posterior fossa. The brain is divided into two main parts, the larger cerebrum on top and the smaller cerebellum below towards the back. They are separated by a membrane called the tentorium. Tumors that originate in the cerebellum or the surrounding region below the tentorium are, therefore, called infratentorial. Historically, medulloblastomas have been classified as a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), but it is now known that medulloblastoma is distinct from supratentorial PNETs and they are no longer considered similar entities. Medulloblastomas are invasive, rapidly growing tumors that, unlike most brain tumors, spread through the cerebrospinal fluid and frequently metastasize to different locations along the surface of the brain and spinal cord. Metastasis all the way d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges is to protect the central nervous system. Structure Dura mater The dura mater (), is a thick, durable membrane, closest to the Human skull, skull and vertebrae. The dura mater, the outermost part, is a loosely arranged, fibroelastic layer of cells, characterized by multiple interdigitating cell processes, no extracellular collagen, and significant extracellular spaces. The middle region is a mostly fibrous portion. It consists of two layers: the endosteal layer, which lies closest to the skull, and the inner meningeal layer, which lies closer to the brain. It contains larger blood vessels that split into the capillaries in the pia mater. It is composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningioma
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur. Risk factors include exposure to ionizing radiation such as during radiation therapy, a family history of the condition, and neurofibromatosis type 2. They appear to be able to form from a number of different types of cells including arachnoid cells. Diagnosis is typically by medical imaging. If there are no symptoms, periodic observation may be all that is required. Most cases that result in symptoms can be cured by surgery. Following complete removal fewer than 20% recur. If surgery is not possible or all the tumor cannot be removed, radiosurgery may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), also known as oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main function is to provide the myelin sheath to neuronal axons in the central nervous system (CNS). Myelination gives metabolic support to, and insulates the axons of most vertebrates. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its Cellular extensions, processes to cover up to 40 axons, that can include multiple adjacent axons. The myelin sheath is segmented along the axon's length at gaps known as the nodes of Ranvier. In the peripheral nervous system the myelination of axons is carried out by Schwann cells. Oligodendrocytes are found exclusively in the CNS, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. They are the most widespread cell lineage, including oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, pre-myelinating cells, and mature myelinating oligodendrocytes in the CNS white matter. Non-myelinating oligodendrocytes are found in the grey matter surrounding and lying next to neuronal cell bodies. They are known as neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a oligodendrocyte progenitor cell, glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults (9.4% of all primary brain and central nervous system tumors) but are also found in children (4% of all primary brain tumors). With a 0.2 incidence (epidemiology), incidence rate out of 100,000 adults, oligodendrogliomas comprise approximately 5% of all central nervous system tumors. Signs and symptoms Oligodendroglioma arise mainly in the frontal lobe and in 50–80% of cases, the first symptom is the onset of seizure activity without any prior symptoms . Headaches combined with increased intracranial pressure are also a common symptom of oligodendroglioma. Depending on the location of the tumor, many different neurological and neuropsychological deficits can be induced, including, but not limited to, visual loss, muscle weakness, motor weakness, cognitive decline, and anxiety. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to around 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor. Astrocytomas (also astrocytomata) originate from a specific kind of star-shaped glial cell in the cerebrum called an astrocyte. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord, and it does not usually affect other organs. After glioblastomas, astrocytomas are the second most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord. Within the astrocytomas, two broad classes are recognized in literature, those with: * Narrow zones of infiltration (mostly noninvasive tumors; e.g., pilocytic astrocytoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma), that often are clearly outlined on diagnostic images * Diffuse zones of infiltration (e.g., high-grade astrocytoma), that share various features, including the ability to arise at any location in the central nervous system, but with a preference for the cerebral hemispheres; they occur usually in adults, and have an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
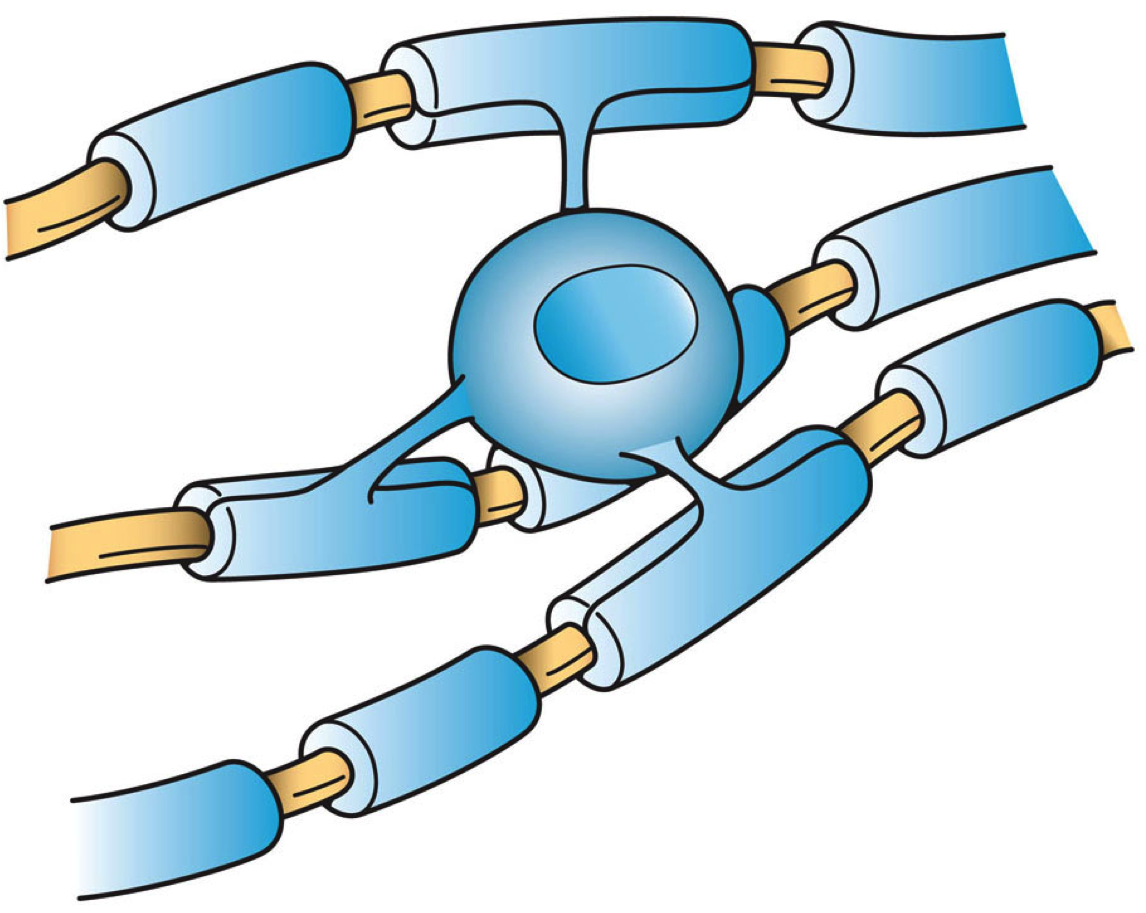
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial Cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in the human body. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes (that produce myelin), astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells (that produce myelin), and satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: * to surround neurons and hold them in place * to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons * to insulate one neuron from another * to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and synaptic connections, and in physiological processes such as breathing. While glia wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioma
A glioma is a type of primary tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or spinal cord. They are malignant but some are extremely slow to develop. Gliomas comprise about 30% of all brain and central nervous system tumors and 80% of all malignant brain tumors. They are a few common types that include astrocytoma (cancer of astrocytes), glioblastoma (an aggressive form of astrocytoma), oligodendroglioma (cancer of oligodendrocytes), and ependymoma (cancer of ependymal cells). Signs and symptoms Symptoms of gliomas depend on the part of the central nervous system (CNS) that is affected. A brain glioma can cause headaches, vomiting, memory loss, seizures, vision problems, speech difficulties, and cranial nerve disorders as a result of increased intracranial pressure. Cognitive impairments such as vision loss arise in glioma patients when a tumor arises in or around their optic nerve. Spinal cord gliomas can cause pain, weakness, or numbness in the extremities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |