|
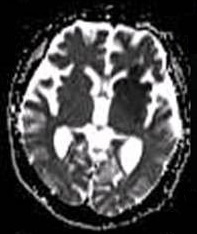
Neonatal Encephalopathy
Neonatal encephalopathy (NE), previously known as neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (neonatal HIE or NHIE), is defined as a encephalopathy syndrome with signs and symptoms of abnormal neurological function, in the first few days of life in an infant born after 35 weeks of gestation. In this condition there is difficulty initiating and maintaining respirations, a subnormal level of consciousness, and associated depression of tone, reflexes, and possibly seizures. Hypoxia refers to deficiency of oxygen, Ischemia refers to restriction in blood flow to the brain. The result is “encephalopathy” which refers to damaged brain cells. Encephalopathy is a nonspecific response of the brain to injury which may occur via multiple methods, but is commonly caused by birth asphyxia, leading to cerebral hypoxia. Signs and symptoms In neonates born at or beyond 35 weeks, neonatal encephalopathy may present itself as the following symptoms: * Reduced level of consciousness * Seiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; ) means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome has many possible organic and inorganic causes. Types There are many types of encephalopathy. Some examples include: * Mitochondrial encephalopathy: Metabolic disorder caused by dysfunction of mitochondrial DNA. Can affect many body systems, particularly the brain and nervous system. * Acute necrotizing encephalopathy, rare disease that occurs following a viral infection. * Glycine encephalopathy: A genetic metabolic disorder involving excess production of glycine. * Hepatic encephalopathy: Arising from advanced cirrhosis of the liver. * Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Permanent or transitory encephalopathy arising from severely reduced oxygen delivery to the brain. * Static encephalopathy: Unchanging, or permanent, brain damage, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Asphyxia
Perinatal asphyxia (also known as neonatal asphyxia or birth asphyxia) is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm, usually to the brain. It remains a serious condition which causes significant mortality and morbidity. It is also the inability to establish and sustain adequate or spontaneous respiration upon delivery of the newborn, an emergency condition that requires adequate and quick resuscitation measures. Perinatal asphyxia is also an oxygen deficit from the 28th week of gestation to the first seven days following delivery. It is also an insult to the fetus or newborn due to lack of oxygen or lack of perfusion to various organs and may be associated with a lack of ventilation. In accordance with WHO, perinatal asphyxia is characterised by: profound metabolic acidosis, with a pH less than 7.20 on umbilical cord arterial blood sample, persistence of an Apgar score of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia is a form of Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia (reduced supply of oxygen), specifically involving the human brain, brain; when the brain is completely deprived of oxygen, it is called ''cerebral anoxia''. There are four categories of cerebral hypoxia; they are, in order of increasing severity: diffuse cerebral hypoxia (DCH), focal cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and global cerebral ischemia. Prolonged hypoxia induces neuronal cell death via apoptosis, resulting in a hypoxic brain injury. Cases of total Oxygen saturation in medicine, oxygen deprivation are termed "anoxia", which can be hypoxic in origin (reduced oxygen availability) or ischemic in origin (oxygen deprivation due to a disruption in blood flow). Brain injury as a result of oxygen deprivation either due to hypoxic or anoxic mechanisms is generally termed hypoxic/anoxic injury (HAI). Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a condition that occurs when the entire brain is deprived of an adequate oxyge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging
Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) is a noninvasive imaging method that provides spectroscopic information in addition to the image that is generated by MRI alone. Whereas traditional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) generates a black-and-white image in which brightness is determined primarily by the T1 or T2 relaxation times of the tissue being imaged, the spectroscopic information obtained in an MRSI study can be used to infer further information about cellular activity (metabolic information). For example, in the context of oncology, an MRI scan may reveal the shape and size of a tumor, while an MRSI study provides additional information about the metabolic activity occurring in the tumor. MRSI can be performed on a standard MRI scanner, and the patient experience is the same for MRSI as for MRI. MRSI has broad applications in medicine, including oncology and general physiological studies. When hydrogen is the target element, MRSI is also called 1H-nuclear magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarnat Staging
Sarnat staging, Sarnat Classification or the Sarnat Grading Scale is a classification scale for hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy of the newborn (HIE), a syndrome caused by a lack of adequate oxygenation around the time of birth which manifests as altered consciousness, altered muscle tone, and seizures.Sarnat H, Sarnat M. Neonatal encaphalopathy following fetal distress. Arch Neurol. 33:695 - 705. 1976. HIE is graded based on the infant's clinical presentation, examination findings, the presence of seizures and the duration of illness. Sarnat staging is used alongside electroencephalogram findings to provide information about the prognosis for the infant. Mild HIE, according to the scale, usually has a normal outcome, whereas in severe HIE the mortality rate is 75%, and 80% of survivors have neurological sequelae.Gardiner M, Eisen S, Murphy C. Training in paediatrics: the essential curriculum. Oxford University Press, Oxford 2009. UK Resuscitation Council guidelines on newborn lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periventricular Leukomalacia
Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a form of white-matter brain injury, characterized by the necrosis (more often coagulation) of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It can affect newborns and (less commonly) fetuses; premature infants are at the greatest risk of neonatal encephalopathy which may lead to this condition. Affected individuals generally exhibit motor control problems or other developmental delays, and they often develop cerebral palsy or epilepsy later in life. The white matter in preterm born children is particularly vulnerable during the third trimester of pregnancy when white matter developing takes place and the myelination process starts around 30 weeks of gestational age. This pathology of the brain was described under various names ("encephalodystrophy", "ischemic necrosis", "periventricular infarction", "coagulation necrosis", "leukomalacia", "softening of the brain", "infarct periventricular white matter", "necrosis of white matter", "diffuse symm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor control, motor movements, procedural memory, procedural learning, habituation, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main functional components of the basal ganglia include the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum, the substa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub (network science), hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory neuron, sensory and motor neuron, motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, the thalami are paramedian symmetrical structures (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalami ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion MRI
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast (vision), contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not random, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and Biological membrane, membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain. Introduction In diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), the intensity of each image element (voxel) reflects the best estimate of the rate of water diffusion at that location. Because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothermia Therapy For Neonatal Encephalopathy
Mild total body hypothermia, induced by cooling a baby to 33-34°C for three days after birth, is nowadays a standardized treatment after moderate to severe hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in full-term and near to fullterm neonates. It has recently been proven to be the only medical intervention which reduces brain damage, and improves an infant's chance of survival and reduced disability. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy has many causes and is defined essentially as the reduction in the supply of blood or oxygen to a baby's brain before, during, or even after birth. It is a major cause of death and disability, occurring in approximately 2–3 per 1000 births and causing around 20% of all cases of cerebral palsy. A 2013 Cochrane review found that therapeutic hypothermia is useful in full term babies with encephalopathy. Medical uses Extended follow-up of trial participants Studies have been undertaken to determine the effects of hypothermia beyond early childhood. Participants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |