|
Neodymium Tribromide
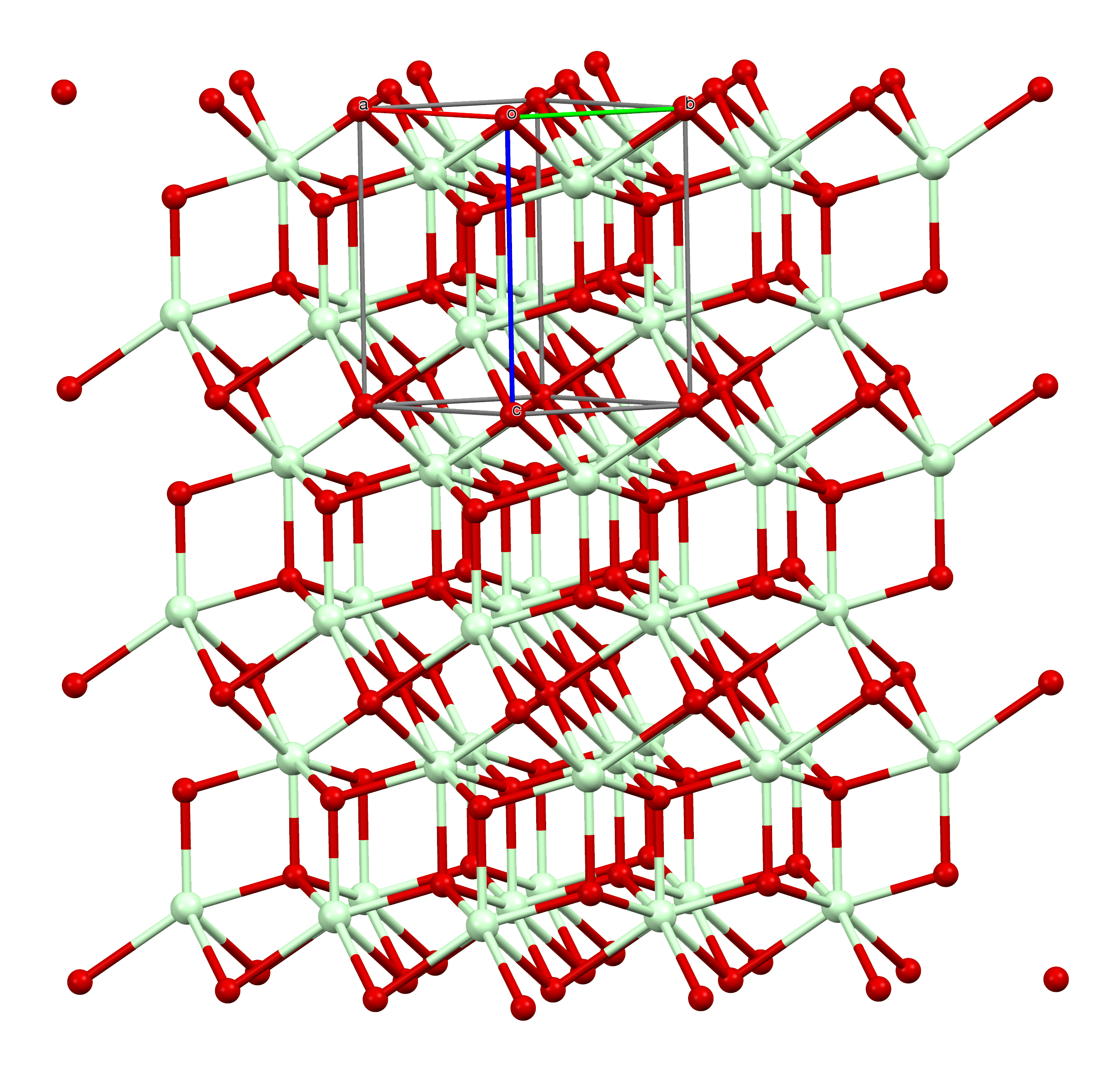
Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopicDavid R. Lide (Hrsg.): ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics.'' 90. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2010), CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, ''Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds,'' S. 4-77. and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride. Preparation The direct reaction of neodymium with bromine can create neodymium(III) bromide: :2Nd + 3Br2 → 2NdBr3 In the presence of carbon, neodymium(III) oxide reacts with carbon tetrabromide to produce neodymium(III) bromide. Structure Neodymium(III) bromide adopts the plutonium(III) bromide crystal structure. The neodymium ions are 8-coordinate and adopt a bicapped trigonal prismatic geometry. The neodymium–bromine b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodymium(III) Compounds
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly producing pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. It is generally regarded as having one of the most complex spectra of the elements. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach, who also discovered praseodymium. Neodymium is present in significant quantities in the minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Neodymium is fairly common—about as common as cobalt, nickel, or copper—and is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Most of the world's commercial neodymium is mined in China, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Crystallographica
''Acta Crystallographica'' is a series of peer-reviewed scientific journals, with articles centred on crystallography, published by the International Union of Crystallography (IUCr). Originally established in 1948 as a single journal called ''Acta Crystallographica'', there are now six independent ''Acta Crystallographica'' titles: *'' Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations and Advances'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section C: Structural Chemistry'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section E: Crystallographic Communications'' *'' Acta Crystallographica Section F: Structural Biology Communications'' ''Acta Crystallographica'' has been noted for the high quality of the papers that it produces, as well as the large impact that its papers have had on the field of crystallography. The current six journals form part of the journal po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicapped Trigonal Prismatic Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, the bicapped trigonal prismatic molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds where eight atoms or groups of atoms or ligands are arranged around a central atom defining the vertices of a biaugmented triangular prism. This shape has C2v symmetry and is one of the three common shapes for octacoordinate transition metal complexes, along with the square antiprism and the dodecahedron. It is very similar to the square antiprismatic molecular geometry, and there is some dispute over the specific geometry exhibited by certain molecules. One example of the bicapped trigonal prismatic molecular geometry is the ion. The bicapped trigonal prismatic coordination geometry is found in the plutonium(III) bromide crystal structure type, which is adopted by many of the bromides and iodides of the lanthanides and actinide The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium(III) Bromide
Plutonium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and plutonium with the formula PuBr3. This radioactive green solid has few uses, however its crystal structure is often used as a structural archetype in crystallography. Crystal structure The PuBr3 crystal structure was first published in 1948 by William Houlder Zachariasen. The compound forms orthorhombic crystals, a type of square antiprism, within which the Pu atoms adopt an 8-coordinate bicapped trigonal prismatic arrangement. Its Pearson symbol is oS16 with the corresponding space group No. 63 (in International Union of Crystallography classification) or Cmcm (in Hermann–Mauguin notation). The majority of trivalent chloride and bromide salts of lanthanide and actinides crystallise in the PuBr3 structure. References Plutonium(III) compounds Actinide halides Crystal structure types {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Tetrabromide
Carbon tetrabromide, CBr4, also known as tetrabromomethane, is a bromide of carbon Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 .... Both names are acceptable under IUPAC nomenclature. Production CBr4 can be obtained by the bromination of methane. The byproducts include other brominated methanes ( methyl bromide, dibromomethane and bromoform) and hydrogen bromide. This process is analogous to the chlorination of methane: :Br2 + ''hν'' → 2 Br·; : Br· + CH4 → ·CH3 + HBr. : ·CH3 + Br2 → CH3Br + Br·. : CH3Br + Br· → ·CH2Br + HBr, : ·CH2Br + Br2 → CH2Br2 + Br·, : CH2Br2 + Br· → ·CHBr2 + HBr, : ·CHBr2 + Br2 → CHBr3 + Br·, :CHBr3 + Br· → ·CBr3 + HBr, : ·CBr3 + Br2 → CBr4 + Br· Halogen exchange of carbon tetrachloride with aluminium bromid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodymium(III) Oxide
Neodymium(III) oxide or neodymium sesquioxide is the chemical compound composed of neodymium and oxygen with the formula Nd2O3. It forms very light grayish-blue hexagonal crystals. The rare-earth mixture didymium, previously believed to be an element, partially consists of neodymium(III) oxide. Uses Neodymium(III) oxide is used to dope glass, including sunglasses, to make solid-state lasers, and to color glasses and enamels. Neodymium-doped glass turns purple due to the absorbance of yellow and green light, and is used in welding goggles. Some neodymium-doped glass is dichroic; that is, it changes color depending on the lighting. One kind of glass named for the mineral alexandrite appears blue in sunlight and red in artificial light. About 7000 tonnes of neodymium(III) oxide are produced worldwide each year. Neodymium(III) oxide is also used as a polymerization In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodymium(III) Chloride
Neodymium(III) chloride or neodymium trichloride is a chemical compound of neodymium and chlorine with the formula NdCl3. This anhydrous compound is a mauve-colored solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to air to form a purple-colored hexahydrate, NdCl3·6H2O. Neodymium(III) chloride is produced from minerals monazite and bastnäsite using a complex multistage extraction process. The chloride has several important applications as an intermediate chemical for production of neodymium metal and neodymium-based lasers and optical fibers. Other applications include a catalyst in organic synthesis and in decomposition of waste water contamination, corrosion protection of aluminium and its alloys, and fluorescent labeling of organic molecules (DNA). Appearance NdCl3 is a mauve colored hygroscopic solid whose color changes to purple upon absorption of atmospheric water. The resulting hydrate, like many other neodymium salts, has the interesting property that it appears differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived , referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a free element in nature. Instead, it can be isolated from colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide Ionic salt, salts analogous to table salt, a property it shares with the other halogens. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its Bromine cycle, accumulation in the oceans. Commercially the element is easily extracted from brine evaporation ponds, mostly in the United States and Israel. The mass of bromine in the oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Handbook Of Chemistry And Physics
The ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' is a comprehensive one-volume reference resource for science research. First published in 1914, it is currently () in its 105th edition, published in 2024. It is known colloquially among chemists as the "Rubber Bible", as CRC originally stood for "Chemical Rubber Company". As late as the 1962–1963 edition (3604 pages), the ''Handbook'' contained myriad information for every branch of science and engineering. Sections in that edition include: Mathematics, Properties and Physical Constants, Chemical Tables, Properties of Matter, Heat, Hygrometric and Barometric Tables, Sound, Quantities and Units, and Miscellaneous. ''Mathematical Tables from Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' was originally published as a supplement to the handbook up to the 9th edition (1952); afterwards, the 10th edition (1956) was published separately as '' CRC Standard Mathematical Tables''. Earlier editions included sections such as "Antidotes of Poisons", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |