|
Neo-Communist Party Of The Soviet Union
The Neo-Communist Party of the Soviet Union (NCPSU; ; ''Neokommunisticheskaya partiya Sovetskogo Soyuza'', ''NKPSS'') was a Secrecy, clandestine Far-left politics, far-left group, which existed in the Soviet Union between September 1974 and January 1985. NCPSU is seen by modern researchers as one of the first organizations of the New Left in the USSR. However, Austrian researcher Hans Azenbaum, who studied the ideology of NCPSU, tends to view this party as the one focusing on the "third way", i.e. neither capitalism, nor real socialism. History The party was the result of a merger of two clandestine radical left groups: Party of New Communists (PNC) (Russian: Партия новых коммунистов (ПНК)) and "Left School" (Russian: Левая школа), which were formed simultaneously, but independently from each other in December 1972 - January 1973. Members of the two groups established contact in September 1973 and the possibility of a merger was broached in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natalia Magnat
Natalia Yakovlevna Magnat (; November 5, 1954 – October 18, 1997) was a Soviet and Russian translator of English, author of works on literary criticism and aesthetics, leader of underground leftist organizations "Left School" (Russian: Левая школа) and "Neo-Communist Party of the Soviet Union" (NCPSU) (Russian: Неокоммунистическая партия Советского Союза (НКПСС)). Biography Natalia Magnat was born in a family of a violinist and a pediatrician. She graduated from the Moscow State Pedagogical University as a teacher of English and German languages. In the late 1970s - early 1980s she worked in SIC Informkultura (Scientific Information Center for Culture and Arts). After the beginning of perestroika she became professionally engaged in translation of fiction. She has translated, among others, works of: Aldous Huxley, Henry Kuttner, Roger Zelazny, Douglas Adams, Glen Cook, George R. R. Martin, Jack Vance, Gordon R. Dickson, A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Left
The New Left was a broad political movement that emerged from the counterculture of the 1960s and continued through the 1970s. It consisted of activists in the Western world who, in reaction to the era's liberal establishment, campaigned for freer lifestyles on a broad range of social issues such as feminism, LGBT movements, gay rights, Drug liberalization, drug policy reforms, and gender relations. The New Left differs from the traditional left in that it tended to acknowledge the struggle for various forms of social justice, whereas previous movements prioritized explicitly economic goals. However, many have used the term "New Left" to describe an evolution, continuation, and revitalization of traditional Left-wing politics, leftist goals. Some who self-identified as "New Left" rejected involvement with the Labour movement, labor movement and Marxism's historical theory of Class conflict, class struggle; however, others gravitated to their own takes on established forms of Marxis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Camus
Albert Camus ( ; ; 7 November 1913 – 4 January 1960) was a French philosopher, author, dramatist, journalist, world federalist, and political activist. He was the recipient of the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the second-youngest recipient in history. His works include ''The Stranger (Camus novel), The Stranger'', ''The Plague (novel), The Plague'', ''The Myth of Sisyphus'', ''The Fall (Camus novel), The Fall'' and ''The Rebel (book), The Rebel''. Camus was born in French Algeria to ''pied-noir'' parents. He spent his childhood in a poor neighbourhood and later studied philosophy at the University of Algiers. He was in Paris when the Battle of France, Germans invaded France during World War II in 1940. Camus tried to flee but finally joined the French Resistance where he served as editor-in-chief at ''Combat (newspaper), Combat'', an outlawed newspaper. After the war, he was a celebrity figure and gave many lectures around the world. He married twice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Paul Sartre
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre (, ; ; 21 June 1905 – 15 April 1980) was a French philosopher, playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary criticism, literary critic, considered a leading figure in 20th-century French philosophy and Marxism. Sartre was one of the key figures in the philosophy of existentialism (and Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology). His work has influenced sociology, critical theory, post-colonial theory, and literary studies. He was awarded the 1964 Nobel Prize in Literature despite attempting to refuse it, saying that he always declined official honors and that "a writer should not allow himself to be turned into an institution." Sartre held an open relationship with prominent feminist and fellow existentialist philosopher Simone de Beauvoir. Together, Sartre and de Beauvoir challenged the culture, cultural and society, social assumptions and expectations of their upbringings, which they considered bourgeois, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atheist Existentialism
Atheistic existentialism is a kind of existentialism which strongly diverged from the Christian existential works of Søren Kierkegaard and developed within the context of an atheistic world view. The philosophies of Søren Kierkegaard and Friedrich Nietzsche provided existentialism's theoretical foundation in the 19th century, although their differing views on religion proved essential to the development of alternate types of existentialism. Atheistic existentialism was formally recognized after the 1943 publication of ''Being and Nothingness'' by Jean-Paul Sartre and Sartre later explicitly alluded to it in '' Existentialism is a Humanism'' in 1946. Thought Atheistic existentialism is the exclusion of any transcendental, metaphysical, or religious beliefs from philosophical existentialist thought (e.g. anguish or rebellion in light of human finitude and limitations). Nevertheless, it shares elements with religious existentialism (e.g. the philosophy of Søren Kierkegaard) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
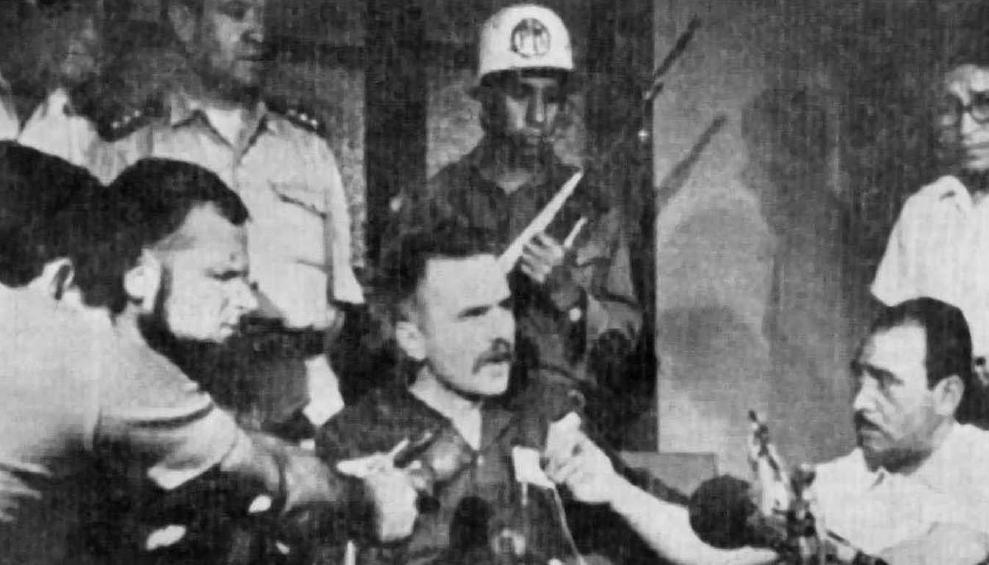
Régis Debray
Jules Régis Debray (; born 2 September 1940) is a French philosopher, journalist, former government official and academic. He is known for his theorization of mediology, a critical theory of the long-term transmission of cultural meaning in human society, and for associating with Marxist revolutionary Che Guevara in Bolivia in 1967 and advancing Salvador Allende's presidency in Chile in the early 1970s. He returned to France in 1973 and later held various official posts in the French government. Life 1960 to 1973 Born in Paris, Régis Debray studied at the École Normale Supérieure where he was taught by Louis Althusser. He appeared as himself in the cinema verité movie ''Chronique d'un été'' by Jean Rouch and Edgar Morin in 1960. He became an " agrégé de philosophie" in 1965. During the late 1960s, he was a professor of philosophy at the University of Havana in Cuba and became an associate of Che Guevara in Bolivia. He wrote the book ''Revolution in the Revol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Che Guevara
Ernesto "Che" Guevara (14th May 1928 – 9 October 1967) was an Argentines, Argentine Communist revolution, Marxist revolutionary, physician, author, Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla leader, diplomat, and Military theory, military theorist. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous Counterculture of the 1960s, countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia Che Guevara in popular culture, in popular culture. As a young medical student, Guevara travelled throughout South America and was appalled by the poverty, hunger, and disease he witnessed.On Revolutionary Medicine Speech by Che Guevara to the Cuban Militia on 19 August 1960. "Because of the circumstances in which I traveled, first as a student and later as a doctor, I came into close contact with poverty, hunger a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
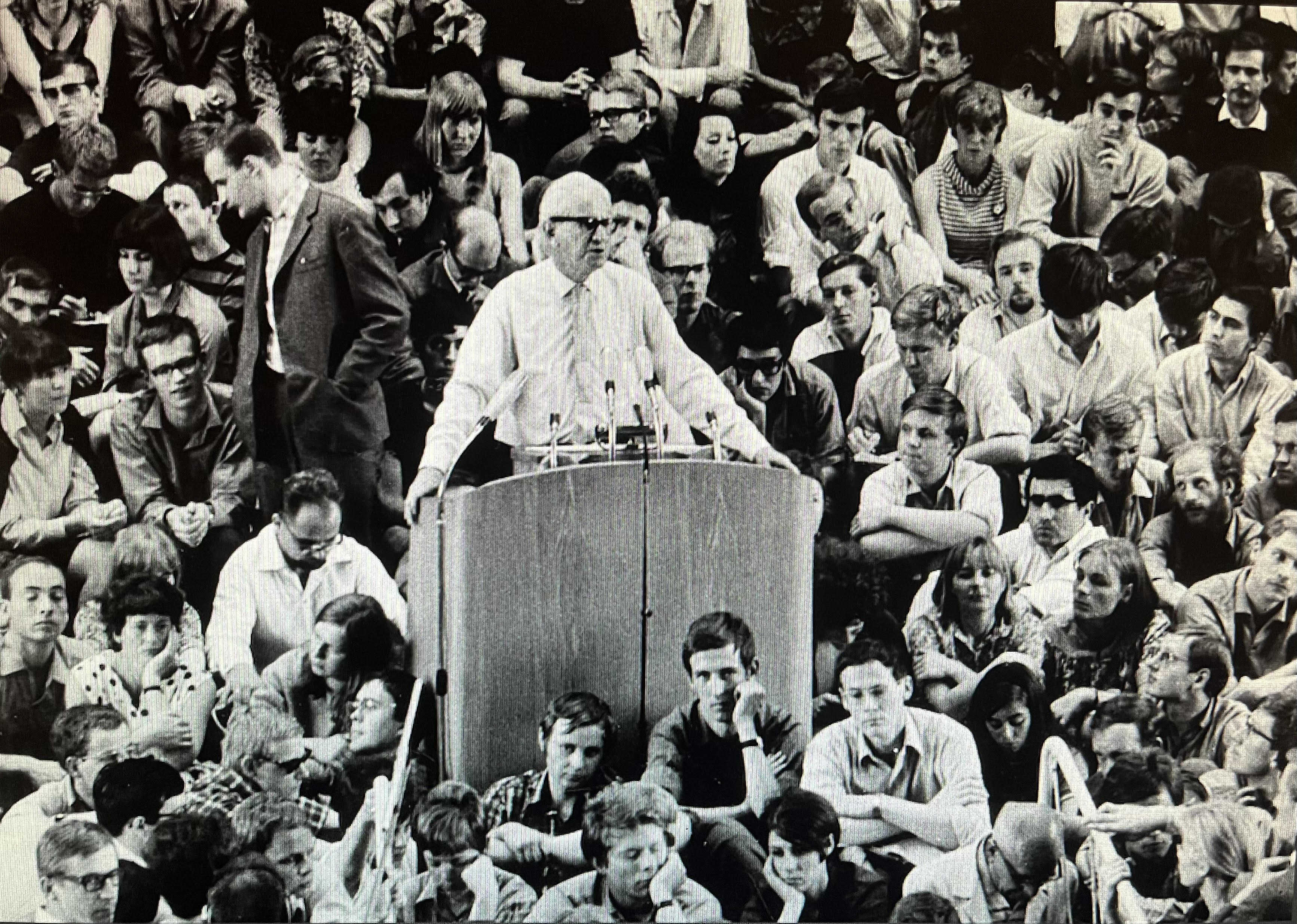
Herbert Marcuse
Herbert Marcuse ( ; ; July 19, 1898 – July 29, 1979) was a German–American philosopher, social critic, and Political philosophy, political theorist, associated with the Frankfurt School of critical theory. Born in Berlin, Marcuse studied at Berlin's Friedrich Wilhelm University of Berlin and then at the University of Freiburg, where he received his PhD.Lemert, Charles. ''Social Theory: The Multicultural and Classic Readings''. Westview Press, Boulder, CO. 2010. He was a prominent figure in the Frankfurt-based University of Frankfurt Institute for Social Research, Institute for Social Research, which later became known as the Frankfurt School. In his written works, he criticized capitalism, modern technology, Soviet Communism, and popular culture, arguing that they represent new forms of social control. Between 1943 and 1950, Marcuse worked in U.S. government service for the Office of Strategic Services (predecessor of the Central Intelligence Agency) where he criticized the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Socialism
Real socialism, better known as actually existing socialism was an ideological catchphrase popularized during the Brezhnev era in the Eastern Bloc countries and the Soviet Union. The term referred to the Soviet-type economic planning implemented by the Eastern Bloc at that particular time. From the 1960s onward, Communist states such as Poland, East Germany, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia began to argue that their policies represented what was realistically feasible given their level of productivity. The concept of real socialism alluded to a highly developed socialist system in the future. The actual party claims of nomenclatory socialism began to acquire not only negative, but also sarcastic meanings. In later years and especially after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the term began to be remembered as only one thing, i.e. as a reference for Soviet-style socialism. Definition After World War II, the terms "real socialism" or "really existing socialism" gradu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by a number of basic constituent elements: private property, profit motive, capital accumulation, competitive markets, commodification, wage labor, and an emphasis on innovation and economic growth. Capitalist economies tend to experience a business cycle of economic growth followed by recessions. Economists, historians, political economists, and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include '' laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, state capitalism, and welfare capitalism. Different forms of capitalism feature varying degrees of free markets, public ownership, obstacles to free competition, and state-sanctioned social poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Way
The Third Way is a predominantly centrist political position that attempts to reconcile centre-right and centre-left politics by advocating a varying synthesis of Right-wing economics, right-wing economic and Left-wing politics, left-wing social policies. The Third Way is a reconceptualization of social democracy. It supports workfare instead of welfare spending, welfare, work training programs, educational opportunities, and other government programs that give citizens a 'hand-up' instead of a 'hand-out'. The Third Way seeks a compromise between a less interventionist economic system as supported by Neoliberalism, neoliberals and Keynesian economics, Keynesian Social democracy, social democratic spending policy supported by social democrats and progressivism, progressives. The Third Way was born from a reevaluation of political policies within various centre to centre-left progressive movements in the 1980s in response to doubt regarding the economic viability of the state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |