|
Neferthenut
Neferthenut was an ancient Egyptian queen of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. She was most likely the wife of Senusret III. Neferthenut was ''king’s wife'', ''member of the elite'' (iryt-pat) and ''she who sees Horus and Seth''. She is so far only known from her sarcophagus and from fragments from the chapel found next to her pyramid, which was part of the pyramid complex of Senusret III at Dahshur. The position of her tomb, next to the pyramid of king Senusret III makes it highly likely that she was his wife. Dieter Arnold, who re-excavated the pyramid complex and the tomb of the queen noted the low quality of the inscription on her sarcophagus, which is in stark contrast to the sarcophagi of other royal women buried next to the pyramid. Her tomb was found robbed, only two mace heads were discovered by Jacques de Morgan Jean-Jacques de Morgan (3 June 1857 – 14 June 1924) was a French mining engineer, geologist, and archaeologist. He was the director of antiquities in Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesostris III
Khakaure Senusret III (also written as Senwosret III or the hellenised form, Sesostris III) was a pharaoh of Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to rule at the height of the Middle Kingdom. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development."''The Pyramids: Their Archeology and History''", Miroslav Verner, Translated by Steven Rendall, p386–387 & p416–421, Atlantic, Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a cult during their own lifetime. Family Senusret III was the son of Senusret II and Khenemetneferhedjet I, also called Khenemetneferhed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senusret III
Khakaure Senusret III (also written as Senwosret III or the hellenised form, Sesostris III) was a pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth dynasty of Egypt, Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to rule at the height of the Middle Kingdom. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of nomarch, regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development."''The Pyramids: Their Archeology and History''", Miroslav Verner, Translated by Steven Rendall, p386–387 & p416–421, Atlantic, Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a List of pharaohs deified during lifetime, cult during their own lifet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelfth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is a series of rulers reigning from 1991–1802 BC (190 years), at what is often considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom (Dynasties XI–XIV). The dynasty periodically expanded its territory from the Nile delta and valley South beyond the Cataracts of the Nile, second cataract and East into Canaan. The Twelfth Dynasty was marked by relative stability and development. It has a notably well recorded history for the period. Its first pharaoh was Amenemhat I and its final was Sobekneferu. History The chronology of the Twelfth Dynasty is the most stable of any period before the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The Turin King List, Turin Royal Canon gives 213 years (1991–1778 BC). Manetho stated that it was based in Thebes, Egypt, Thebes, but from contemporary records it is clear that the first king of this dynasty, Amenemhat I, moved its capital to a new city named "Amenemhat-itj-tawy" ("Amenemha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
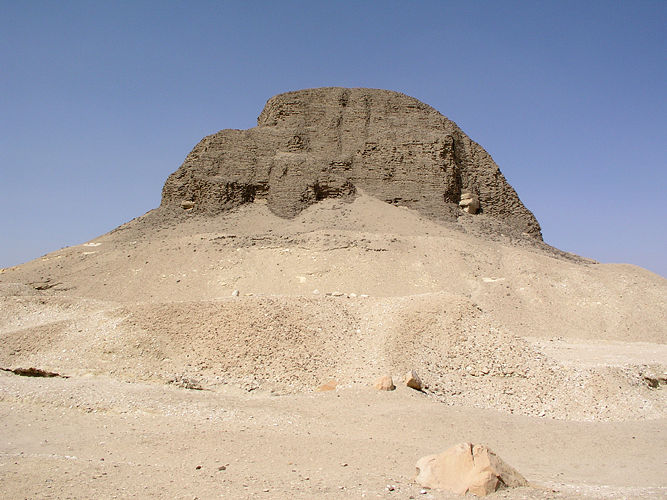
Pyramid Of Senusret III
The pyramid of Senusret III (''Lepsius list of pyramids, Lepsius XLVII'') is an ancient Egyptian Egyptian pyramids, pyramid located at Dahshur and built for pharaoh Senusret III of the 12th Dynasty (19th century BCE). The pyramid is the northernmost among those of Dahshur, and stands around 1.5 km northeast of Sneferu's Red Pyramid. It was erected on leveled ground and composed of a mudbricks core covered with a casing of white Tura, Egypt, Tura limestone blocks resting on foundations. It was first excavated in 1894 by the French Egyptologist Jacques de Morgan, who managed to reach the burial chamber after discovering a tunnel dug by ancient tomb robbers.Lehner 1997, p. 177 A more recent campaign was led by Dieter Arnold during the 1990s. Pyramid complex The original project included the main pyramid along with a northern chapel and a small eastern mortuary temple, all surrounded by an enclosure wall. Outside this enclosure were seven tombs belonging to Senusret's queens an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Royal Wife
Great Royal Wife, or alternatively, Chief King's Wife () is the title that was used to refer to the Queen consort, principal wife of the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, who served many official functions. Description While most ancient Egyptians were monogamy, monogamous, a male pharaoh would have had other, lesser wives and concubines in addition to the Great Royal Wife. This arrangement would allow the pharaoh to enter into diplomatic marriages with the daughters of allies, as was the custom of ancient kings. In the past the order of succession in Ancient Egypt was thought to pass through the royal women. This theory, referred to as the Heiress Theory, has been rejected regarding the Eighteenth Dynasty ever since a 1980s study of its royalty.O'Connor and Cline (Editors), Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign, pg 6 The throne likely passed to the eldest living son of those pharaohs. The mother of the heir to the throne was not always the Great Royal Wife, but once a pharaoh was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th Century BC
The 19th century BC was the century that lasted from 1900 BC to 1801 BC. Events * 1900 BC: Transition from Early Helladic III to Middle Helladic culture in Greece. * c. 1900 BC: Minoan Old Palace (Protopalatial) period starts in Crete. * c. 1900 BC: Fall of last Sumerian dynasty. * c. 1900 BC: Late Harappan phase of the Indus Valley civilization begins * c. 1900 BC: The Mokaya along the Pacific coast of present-day Chiapas, Mexico were preparing cacao beverages. * c. 1900 BC: Port of Lothal is abandoned. * c. 1897 BC: Senwosret II (Twelfth Dynasty) started to rule. He built Kahun near his pyramide tomb complex at el-Lahun. * c. 1895 BC–1878 BC: "Pectoral of Senwosret II", from the tomb of princess Sithathoryunet at el-Lahun was made. Twelfth Dynasty. It is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. * c. 1880 BC: Pharaoh Senwosret II starts to rule (other date is 1897 BC). * 1878 BC: Senwosret II (Twelfth Dynasty) died. * c. 1878 BC: Senwosret III (Twelfth Dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Language
The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian (; ), is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest known written languages, first recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4,000 years. Its classical form, known as " Middle Egyptian," served as the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity, the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era, diversified into various Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of Polytheism, polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with Ancient Egyptian deities, many deities believed to be present and in control of the world. About 1,500 deities are known. Rituals such as prayer and offerings were provided to the gods to gain their favor. Formal religious practice centered on the pharaohs, the rulers of Egypt, believed to possess divine powers by virtue of their positions. They acted as intermediaries between their people and the gods, and were obligated to sustain the gods through rituals and offerings so that they could maintain Ma'at, the order of the cosmos, and repel Isfet (Egyptian mythology), Isfet, which was chaos. The state dedicated enormous resources to religious rituals and to the construction of Egyptian temple, temples. Individuals could interact with the gods for their own purposes, appealing for hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social status, status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahshur
DahshurAlso transliterated ''Dahshour'' (in English often called ''Dashur''; ' ) is an ancient Egyptian pyramid complex and necropolis and shares the name of the nearby village of Manshiyyat Dahshur () in markaz Badrashin, Giza Governorate, Giza. Dahshur is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and is located on the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert plateau at the edge of the cultivated plain, and along with the pyramid complexes at Saqqara, Abusir, and Giza pyramid complex, Giza, to its north, forms the Memphite Necropolis, pyramid fields of the ancient capital city of Memphis, Egypt, Memphis. It is known chiefly for several pyramids, mainly Sneferu, Sneferu's Bent Pyramid and the Red Pyramid, which are among the oldest, largest and best preserved in Egypt, built from 2613 to 2589 BC. Pyramids The Dahshur pyramids were an extremely important learning experience for the Egyptians. It provided them with the knowledge and know-how to transition from step-sided pyramids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieter Arnold
Dieter Arnold (born 1936 in Heidelberg) is a German archaeology, archaeologist. Biography He received his doctorate on 31 January 1961 from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, University of Munich with the thesis "Wall relief and spatial function in Egyptian temples of the New Kingdom". Arnold worked for the German Archaeological Institute in Cairo during excavations in Dahshur, Deir el-Bahari and El-Tarif. From 1979 to 1984 he was a professor at the University of Vienna and then a curator at the Egyptian Department of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, New York. Arnold's specialty is the architecture of Ancient Egypt. As an employee of the Metropolitan Museum, he leads the museum's annual expeditions to el-Lisht and Dahshur. In 1981 he published a proposal for the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, Great Pyramid. The ramp runs first outside and then in a corridor inside the pyramid. Arnold was aware that the construction method could not be explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |