|
Naziba Bashar
Naziba, was a small 'city', or 'city-state' south of Dimašqu-( Damascus), in the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. The town of Naziba was located near Amarna letters ''Qanu'', now named Qanawat, and biblical '' Kenath''. Naziba, is part of a 6-letter series of letters, written by the same scribe, all entitled: "Ready for marching orders (1-6)". The letters are ''mostly'' identical, with only the city's ''Ruler'' and the ''location'' changing; they are letters EA 201-EA 206, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). EA 206, for the "ruler of Naziba" : Say to the king, my lord: Message of the ruler of Naziba, your servant. I fall at the feet of the king, my lord, 7 times plus 7 times. You hav wrt ento make preparations before the arrival of the archers, and I am herewith, along with my troops and my chariots, at the disposition of the archers. —EA 206, lines 1-17 (complete) List of the 6-letter series :#EA 201-marching orders (1)—for Artamanya of Siribašani :#EA 202-march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of Aram
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a garden, mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 BCE. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two- wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by light and heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and transport, in processions, for games, and in races. Etymology The word "chariot" comes from the Latin term ''carrus'', a loanword from Gaulish. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
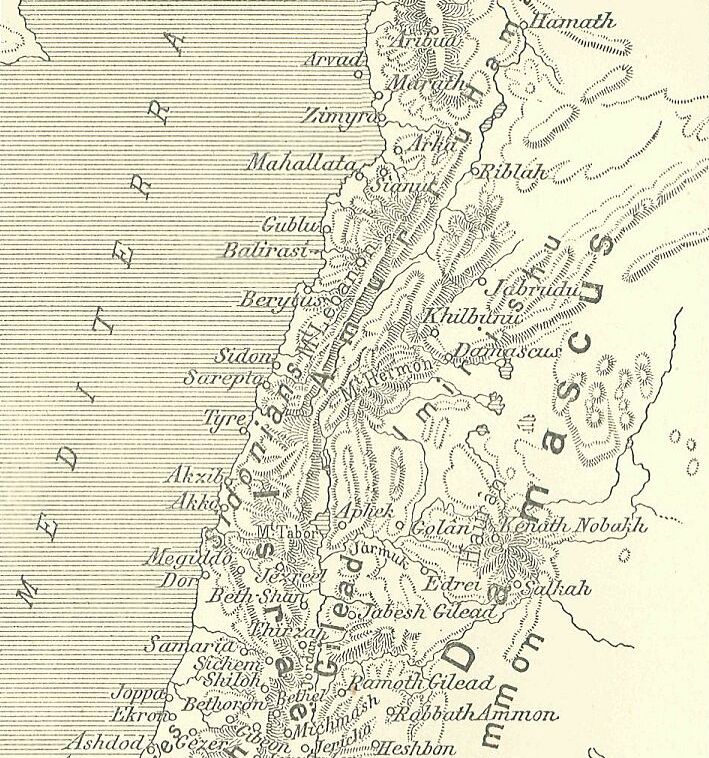
Amarna Letters–localities And Their Rulers
This is a list of Amarna letters –Text corpus, categorized by: Amarna letters–localities and their rulers. It includes countries, regions, and the cities or city-states. The regions are included in Canaan and the Levant. EA: '' 'el Amarna' ''–(Akhenaten's capitol of Akhetaten). The Amarna letters text corpus contains 382 numbered letters; there are "sub-Text corpora" in the letters, most notably the 68–letter ''corpus'' of Rib-Hadda of Gubla–(Byblos). Localities / Rulers Sub-corpus lists No. 201–206: ''"Ready for marching orders (1–6)"'' List of letters: EA 201–206.Actually authored by the same scribe. Also scribed EA 195, See: Prostration formula. Leaders only in reference Leaders that are only referred to in the letter corpus. See also *Foreign relations of Egypt during the Amarna period References *Moran, William L. William Lambert Moran (August 11, 1921 – December 19, 2000) was an American Assyriologist. He was born in Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biryawaza
Biryawaza was a powerful ruler in the area of Egyptian controlled Syria in the middle fourteenth century BC. He is often mentioned in the Amarna letters, although his title is never given clearly. Some scholars describe him as the king of Damascus, and others think he was a high Egyptian official. In the Amarna letters, Biryawaza was ordered by his Egyptian overlords to take armed action against Labaya's sons (EA 250). In another Amarna letter, King Burna-Buriash II of Babylonia said Biryazawa attacked a Babylonian caravan sending gifts to Pharaoh Akhenaten.Eric H. Cline, '' 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed'', p. 58 The name ''Biryawaza'' is Indo-European in origin. Biryawaza may have been of an Indo-European maryannu caste similar to that which ruled the Mitanni and later, the Hittites The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubu (town)
Tubu is the town east of the Sea of Galilee referred to in the (body) of the Amarna letters. Tubu is the probable biblical town of Tob. In the entire group of El Amarna letters, EA 205 is the only usage of the name Tubu, and only the "Man" (or Mayor/prince) is referenced. The scribe who wrote EA 205, visited and /or wrote from 6 towns, 5 south of or neighboring, Damascus. Three were named, as only from the "Man" of the town. Three were designated by the "Leader" of the town, and one of the 6 towns, was not mentioned by name. These Amarna letters are all written from the time centering about 1350 BCE and written in Akkadian cuneiform on clay tablets. See also *Umm el-Marra Umm el-Marra, ( ar, أم المرى), east of modern Aleppo in the Jabbul Plain of northern Syria, was one of the ancient Near East's oldest cities, located on a crossroads of two trade routes northwest of Ebla, in a landscape that was much more f ... Sources * Index, Introduction, Maps, etc. in ...''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

