|
Naval Surgeon
A naval surgeon, or less commonly ship's doctor, is the person responsible for the health of the ship's company aboard a warship. The term appears often in reference to Royal Navy's medical personnel during the Age of Sail. Ancient uses Specialised crew members capable of providing medical care have been a feature of military vessels for at least two thousand years. The second-century Roman Navy under Emperor Hadrian included a surgeon aboard each of its triremes, with the position earning twice a regular officer's pay. Royal Navy From the early days of the Royal Navy, surgeons had been carried on board ships (albeit intermittently, depending on the length of voyage and likelihood of hostilities). In the Tudor period, surgeons were regulated by the Company of Barber-Surgeons. William Clowes, sometime Warden of the Company, and his colleague John Banister (both of whom had served at sea early in their careers) did much to ensure that naval surgeons were properly qualified and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship's Company
A ship's company or complement comprises all officers, non-commissioned officers and enlisted personnel aboard a naval vessel, excluding civilians and guests. United States Aircraft-capable ships An exception to this rule is the definition of ship's company as it applies to the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps personnel assigned to aircraft-capable ships of the U.S. Navy, primarily aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships. In the case of aircraft carriers in the U.S. Navy, the total ship's complement is divided into three categories: # the ship's company physically assigned to the ship, and # the carrier air wing, with its associated strike fighter, U.S. Marine fighter/attack, electronic attack, airborne early warning and helicopter squadrons, and a detachment of a fleet logistics squadron, which is considered a separate "embarked" command, and # the carrier strike group commander and staff, which is also considered an "embarked" command The number of personnel assigned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
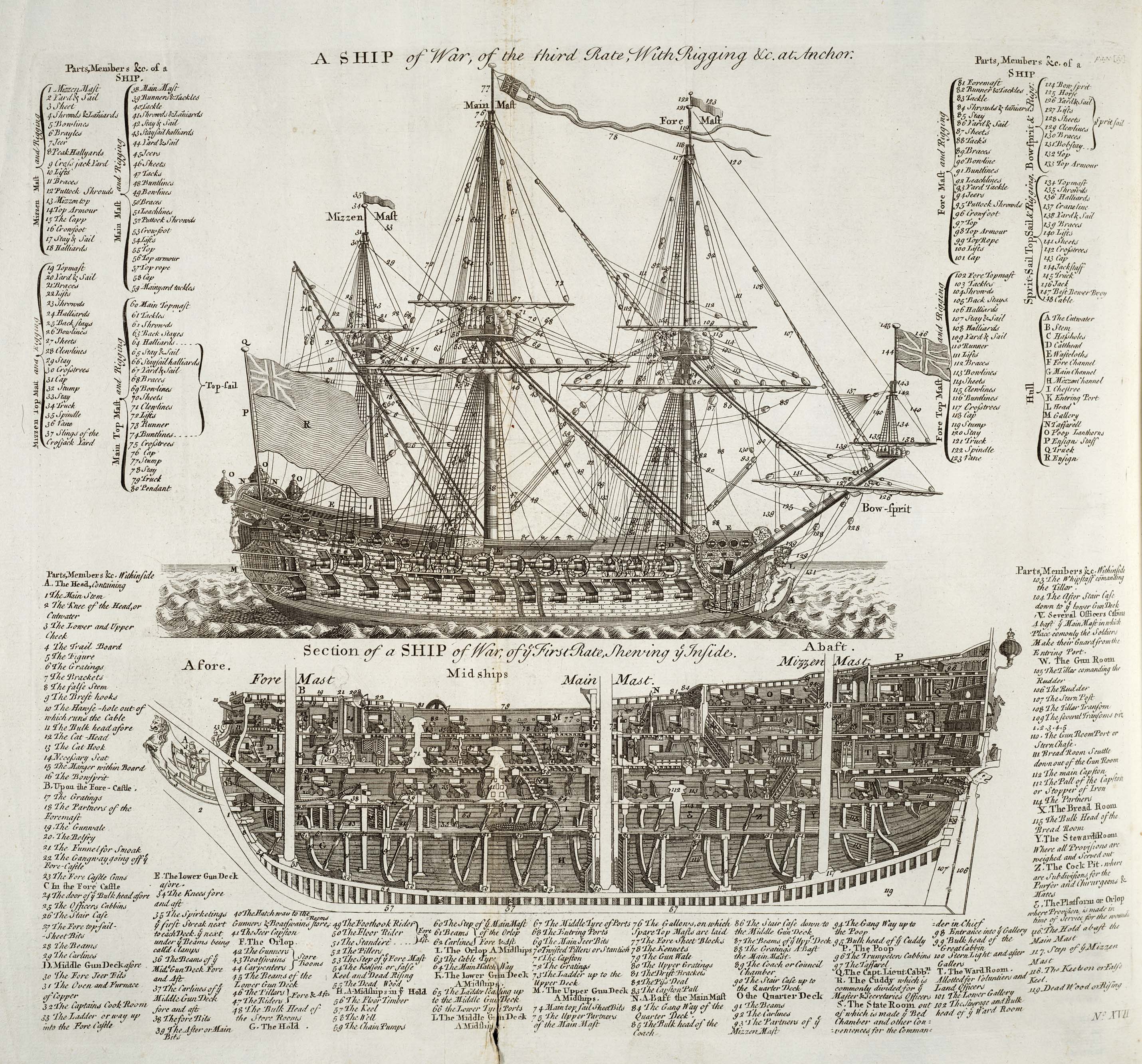
Rating System Of The Royal Navy
The rating system of the Royal Navy and its predecessors was used by the Royal Navy between the beginning of the 17th century and the middle of the 19th century to categorise sailing warships, initially classing them according to their assigned complement of men, and later according to the number of their carriage-mounted guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy formally came to an end in the late 19th century by declaration of the Admiralty; rating ships by the number of guns had become obsolete with new types of gun, the introduction of steam propulsion and the use of iron and steel armour. Origins and description The first movement towards a English naval rating system began in the early 16th century, when the largest carracks in the Tudor navy, such as ''Mary Rose'', ''Peter Pomegranate'' and '' Henry Grace à Dieu'', were denoted as "great ships". This was due only to their size, not to their weight, crew or number of guns. When these carracks were superseded by ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sick Bay
A sick bay is a compartment in a ship, or a section of another organisation, such as a school or college, used for medical purposes. The sick bay contains the ship's medicine chest, which may be divided into separate cabinets, such as a refrigerator for medicines requiring cold storage and a locked cabinet for controlled substances such as morphine. The sick bay and the medicine chest should be kept locked, with the keys only being available to the medical officer and the ship's master. The term is also applied ashore by the United States Navy and Marine Corps to treatment clinics on naval stations and Marine bases. Sick bays (sometimes referred to as med bays) appear in popular science fiction franchises, such as '' Battlestar Galactica'' and ''Star Trek'', as the medical facility on board a starship A starship, starcraft, or interstellar spacecraft is a theoretical spacecraft designed for interstellar travel, traveling between planetary systems. The term is mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumigation
Fumigation is a method of pest control or the removal of harmful microorganisms by completely filling an area with gaseous pesticides, or fumigants, to suffocate or poison the pests within. It is used to control pests in buildings (structural fumigation), soil, grain, and produce. Fumigation is also used during the processing of goods for import or export to prevent the transfer of exotic organisms. Structural fumigation targets pests inside buildings (usually residences), including pests that inhabit the physical structure itself, such as woodborers and drywood termites. Commodity fumigation, on the other hand, is also to be conducted inside a physical structure, such as a storage unit, but it aims to eliminate pests from infesting physical goods, usually food products, by killing pests within the container which will house them. Each fumigation lasts for a certain duration. This is because after spraying the pesticides, or fumigants, only the pests around are eradicated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatchway
120px, View of the hold of a container ship A ship's hold or cargo hold is a space for carrying cargo in a ship or airplane compartment. Description Cargo in holds may be either packaged in crates, bales, etc., or unpackaged (bulk cargo). Access to holds is by a large hatch at the top. Ships have had holds for centuries; an alternative way to carry cargo is in standardized shipping containers, which may be loaded into appropriate holds or carried on deck. Holds in older ships were below the orlop deck, the lower part of the interior of a ship's hull, especially when considered as storage space, as for cargo. In later merchant vessels it extended up through the decks to the underside of the weather deck. Some ships have built in cranes and can load and unload their own cargo. Other ships must have dock side cranes or gantry cranes to load and unload. Cargo hatch A cargo hatch or deck hatch or hatchway is type of door used on ships and boats to cover the opening to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainmast
The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the median line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, giving necessary height to a navigation light, look-out position, signal yard, control position, radio aerial, or signal lamp. Large ships have several masts, with the size and configuration depending on the style of ship. Nearly all sailing masts are guyed. Until the mid-19th century, all vessels' masts were made of wood formed from a single or several pieces of timber which typically consisted of the trunk of a conifer tree. From the 16th century, vessels were often built of a size requiring masts taller and thicker than from single tree trunks. On these larger vessels, to achieve the required height, the masts were built from up to four sections (also called masts). From lowest to highest, these were called: lower, top, topgallant, and royal masts. Giving the lower sections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loblolly Boy
Loblolly boy is the informal name given to the assistants to a ship's surgeon aboard British and American warships during the Age of Sail. The name derives from a porridge traditionally served to sick or injured crew members. The term is no longer used; in the modern era surgeon's assistants are medical assistants in the Royal Navy, and hospital corpsmen in the U.S. Navy. Etymology The name comes from the serving of loblolly — a thick porridge, sometimes enhanced with chunks of meat or vegetables—to sick or injured crewmembers to hasten their recovery. Loblolly, in turn, probably comes from the fusion of lob, a Yorkshire word meaning to boil or bubble, and lolly, an archaic English word for a stew or soup. Loblolly itself eventually came to mean anything viscous, such as a swamp or bog, and terms such as the Loblolly pine were coined from the muddy habitat of the tree rather than from any culinary use. The name was first used to describe Royal Navy surgeon's assistants i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing Master
The master, or sailing master, is a historical rank for a naval Officer (armed forces), officer trained in and responsible for the navigation of a sailing ship, sailing vessel. In the Royal Navy, the master was originally a warrant officer who ranked with, but after, the lieutenant (Royal Navy), lieutenants. The rank became a commissioned officer rank and was renamed navigating lieutenant in 1867; the rank gradually fell out of use from around 1890 since all lieutenants were required to pass the same examinations. When the United States Navy was formed in 1794, master was listed as one of the warrant officer ranks and ranked between midshipmen and lieutenants. The rank was also a commissioned officer rank from 1837 until it was replaced with the current rank of lieutenant, junior grade in 1883. France Within the French Navy, there exists a number of "master" ranks. Russia Until 1733 the sailing masters in the Imperial Russian Navy were rated as petty officers, but in that y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval Hospital
A Royal Naval Hospital (RNH) was a hospital operated by the British Royal Navy for the care and treatment of sick and injured naval personnel. A network of these establishments were situated across the globe to suit British interests. They were part of the Royal Naval Medical Service. The British Army equivalent was a Military Hospital, and in the 20th century a number of RAF Hospitals were also established. The list below includes significant Royal Naval Hospitals established in the 18th-20th centuries; in addition numerous smaller facilities (often classed as Sick Quarters) were set up, where and when needed (especially in times of war). In 1996 the UK's last remaining Royal Naval Hospital was redesignated as a Joint Services establishment; it finally closed just over a decade later. No Royal Naval Hospitals survive in operation, although some have become civilian hospitals. Historical overview Individual surgeons had been appointed to naval vessels since Tudor times; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inspector-General Of Naval Hospitals And Fleets
The Royal Navy Medical Service (RNMS), also termed the Royal Naval Medical Service is the branch of the Royal Navy responsible for providing 'comprehensive healthcare to ships, submarines and Royal Marine personnel at sea and on land'. It includes within its remit of responsibility Queen Alexandra's Royal Naval Nursing Service. The Head of the Royal Navy Medical Service, also holds the position of 'Head of Navy Healthcare' in Navy Command Headquarters and the present incumbent is Commodore Alison Hofman. History The history of the service can be traced back to 1692 when treatment for sick and wounded naval personnel was administered by the Commissioners of the Sick and Hurt Board (a subsidiary body of the Navy Board) until 1806, when medical officers of the Royal Navy had been under the direction of the Transport Board. In 1817 the Transport Board was merged with the Navy Board, and responsibility for medical officers passed to the Victualling Board. In 1832 the Navy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |