|
Nauportus
Nauportus ''(Navport, Navportus)'' (), was an ancient Roman town in Pannonia Superior (later 10th Italian region) on the road from Aquileia to Emona with a port at the Nauportus river, now the Ljubljanica River, Slovenia. Strabo wrote that near the Nauportus was a river, called Corcoras (), which received the cargoes. According to historian Pliny the Elder, the name was derived from the legendary landing of the Argonauts at the river, where they are said to have founded the town. Tacitus reports that in year 14, the town was plundered by mutinous Roman forces that has been sent to build roads and bridges.Tacitus ''Annales'', 1.20: Interea manipuli ante coeptam seditionem Nauportum missi ob itinera et pontes et alios usus, postquam turbatum in castris accepere, vexilla convellunt direptisque proximis vicis ipsoque Nauporto, quod municipii instar erat, ... Remains of Nauportus were found in present-day Vrhnika in central Slovenia. A Late Roman emporium with warehouses and a cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vrhnika
Vrhnika (; ;''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 6: ''Kranjsko''. 1906. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, p. 120. ) is a town in Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Vrhnika. It is located on the Ljubljanica River, 21 km from Ljubljana along the A1 motorway. Geography Vrhnika lies at the southwest end of the Ljubljana Marsh near the sources of the Ljubljanica River, where the Ljubljana Basin opens up between the foot of Ljubljana Peak (, ) and Ulovka Hill (). Močilnik Springs is located south of the settlement; together with nearby Retovje Springs, water flows mainly from the subterranean streams of the Unica to produce the Little Ljubljanica River () and Big Ljubljanica River (), which in turn join to create the Ljubljanica River. The territory of the town extends south onto the Logatec Plateau (), where the Big and Little Drnovica Collapse Sinkholes () are found. Name The settlement at the location of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emona
Emona (early ) or Aemona (short for ) was a Roman castrum, located in the area where the navigable Nauportus River came closest to Castle Hill,Exhibition catalogue Emona: myth and reality ; Museum and Galleries of Ljubljana 2010 serving the trade between the city's settlers – colonists from the northern part of – and the rest of the empire. Emona was the region's easternmost city,Šašel Kos, M. (2002 "The boundary stone between Aquileia and Emona" Arheološki Vestnik 53, pp. 373–382. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
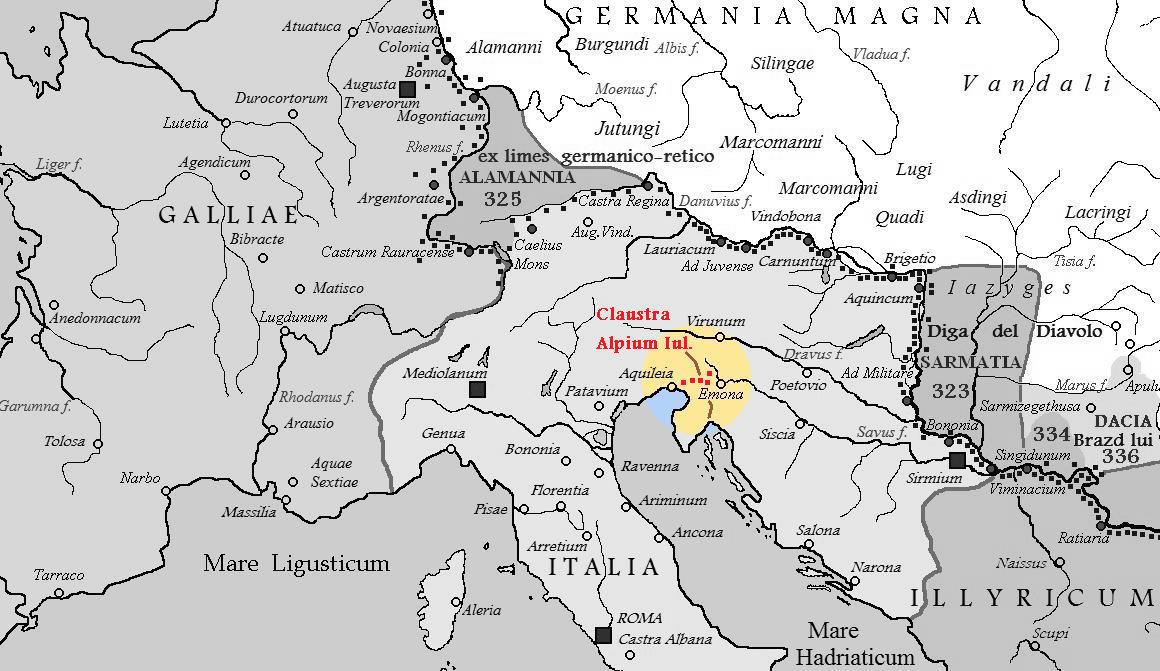
Claustra Alpium Iuliarum
(Latin for 'Barrier of the Julian Alps'; hereby, the term Julian Alps refers to the wider mountainous and hilly region from the Julian Alps to the Kvarner Gulf) was a defense system within the Roman Empire between Italia and Pannonia that protected Italy from possible invasions from the East. It secured the Postojna Gate, the land link between the eastern and western part of the empire, and thus the Claustra represented an inner border defense of the empire. Unlike a linear rampart, the Claustra consisted of a series of interconnected fortifications with its center at Castra ad Fluvium Frigidum (in the area of today's town of Ajdovščina, the Vipava Valley); other important fortresses were '' Ad Pirum'' on today's Hrušica Plateau and '' Tarsatica'', now a part of the city of Rijeka. They had been governed from the town of Aquileia. Development In the year 6 AD the Great Illyrian Revolt took place threatening the Roman heartland. Subsequently, in order to protect Italy, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argonauts
The Argonauts ( ; ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, ''Argo'', named after its builder, Argus (Argonaut), Argus. They were sometimes called Minyans, after a prehistoric tribe in the area. Mythology The Golden Fleece After the death of King Cretheus, the Aeolian Pelias usurped the throne from his half-brother Aeson and became king of Iolcus in ancient Thessaly, Thessaly (near the modern city of Volos). Because of this unlawful act, an oracle warned him that a descendant of Aeolus would seek revenge. Pelias put to death every prominent descendant of Aeolus he could, but spared Aeson because of the pleas of their mother Tyro. Instead, Pelias kept Aeson prisoner and forced him to renounce his inheritance. Aeson married Alcimede, who bore him a son named Jason. Pelias intended to kill the baby at once, but Alcimede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio I Germanica
Legio I Germanica, ( First Legion "Germanic"), was a legion of the Imperial Roman army, possibly founded in 48 BC by Julius Caesar to fight for him in the civil war against Pompey. The title ''germanic'' is a reference to its service in the Chronology of warfare between the Romans and Germanic tribes, Germanic Wars, rather than the place of origin of its soldiers. After the Revolt of the Batavi (AD 70), the remaining men of the ''Germanica'' were added to Galba's seventh legion, which became Legio VII Gemina, VII ''Gemina''. The emblem of Legio I is unknown, but it was probably Taurus (constellation), Taurus, like all the other legions levied by Caesar (except the Legio V Alaudae, V ''Alaudae''). Origin There are three theories about I ''Germanica'' recruitment. The most favored is that it was raised by Julius Caesar Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia Superior
Pannonia Superior () was a Roman province created from the division of Pannonia in 103 AD, its capital in Carnuntum. It overlapped in territory with modern-day Hungary, Croatia, Austria, Slovakia, and Slovenia. History It was as governor of the province that Septimius Severus made his bid for the Roman Imperial throne in April 193 CE. In 308 Emperor Diocletian chaired a historic meeting with his co-emperors Maximian and Galerius in Carnuntum, to solve the rising tensions within the Tetrarchy. Diocletian and Maximian were both present on 11 November 308, to see Galerius appoint Licinius to be Augustus (title), Augustus in place of Valerius Severus, who had died at the hands of Maxentius. Galerius ordered Maximian, who had attempted to return to power after his own retirement, to step down permanently. At Carnuntum people begged Diocletian to return to the throne, to resolve the conflicts that had arisen through Constantine the Great's rise to power and Maxentius' usurpation. Dioc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river Natiso (modern Natisone), the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small (about 3,500 inhabitants), but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the second century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun. It is currently a (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, Friuli-Venezia Giulia. History Classical Antiquity Roman Republic Aquileia was founded as a colony by the Romans in 180/181 BC along the Natiso River, on land south of the Julian Alps but about north of the lagoons. The colony served as a strategic frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljubljanica
The Ljubljanica (), known in the Middle Ages as the ''Leybach'', is a river in the southern part of the Ljubljana Basin in Slovenia. The capital of Slovenia, Ljubljana, lies on the river. The Ljubljanica rises south of the town of Vrhnika and flows into the Sava River about downstream from Ljubljana. Its largest affluent is the Mali Graben Canal. Including its source affluent the Little Ljubljanica (), the river is in length. The Little Ljubljanica joins the Big Ljubljanica () after and the river continues its course as the Ljubljanica. The Ljubljanica is the continuation of several karst rivers that flow from the Prezid Karst Field () to Vrhnika on the surface and underground in caves, and so the river is poetically said to have seven names (six name changes): Trbuhovica, Obrh, Stržen, Rak, Pivka, Unica, and Ljubljanica. Archaeological significance The Ljubljanica has become a popular site for archaeologists and treasure hunters to dive for lost relics and artif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek geographer who lived in Anatolia, Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is best known for his work ''Geographica'', which presented a descriptive history of people and places from different regions of the world known during his lifetime. Additionally, Strabo authored historical works, but only fragments and quotations of these survive in the writings of other authors. Early life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amasya, Amaseia in Kingdom of Pontus, Pontus in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' (Latin: ) and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ), originally formed a continuous narrative of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the end of Domitian’s reign (96 AD). The surviving portions of the Annals focus on the reigns of Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see ), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''). Tacitus's ''Histories'' offers insights into Roman attitudes towards Jews, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guard Tower
A watchtower or guardtower (also spelt watch tower, guard tower) is a type of military/paramilitary or policiary tower used for guarding an area. Sometimes fortified, and armed with heavy weaponry, especially historically, the structures are built in areas of established control. These include military bases, cities occupied by military forces, prisons and more. A common equipment is searchlights. It differs from a regular tower in that its primary use is military/policiary and from a turret in that it is usually a freestanding structure. Its main purpose is to provide a high, safe place from which a sentinel or guard may observe the surrounding area. In some cases, non-military towers, such as religious towers, may also be used as watchtowers. Similar constructions include: observation towers, which are generally civilian structures, and control towers, used on airports or harbours. History Military watchtowers The Romans built numerous towers as part of a system o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |