|
Natalya Meklin
Natalya Fyodorovna Kravtsova née Meklin (; 8 September 1922 – 5 June 2005) was a flight commander in the 46th Taman Guards Night Bomber Aviation Regiment, one of the three women's aviation regiments founded by Marina Raskova after the German invasion of the Soviet Union. The regiment later came to be known as the "Night Witches" by German targets. She was awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union in February 1945 for completing 840 sorties and gained significant publicity. Early civilian life Meklin was born on 8 September 1922 to a working-class Russian family in Lubny, then part of the Ukrainian SSR. Her childhood and youth were spent in Smila, Kharkov, and Kiev. In 1940 she graduated from her tenth grade of schooling in Kiev. That year, she joined the glider school at the Kiev Young Pioneer Palace and later graduated from the Moscow Aviation Institute in 1941. World War II career In October 1941, several months after the German invasion of the Soviet Union, Meklin appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubny
Lubny (, ) is a city in Poltava Oblast, central Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Lubny Raion. It also hosts the administration of , one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: History Lubny is reputed to be one of the oldest cities in Ukraine, allegedly founded in 988 by knyaz (prince) Vladimir the Great (Volodymyr) of Kyiv. The first written record, however, dates from 1107. Initially, it was a small wooden fortress above the Sula River. The fortress quickly grew, and in the 15th or 16th century, it was owned by the powerful Wisniowiecki family. The town was ruled by Magdeburg rights and had a coat of arms. In 1596, Lubny was the site of the last battle of Severyn Nalyvaiko against the Poles. In the 17th century the city was one of the largest in the area. In 1638 it had 2,646 inhabitants. After Khmelnytsky Uprising, between 1648 and 1781, the town was the headquarters of the Lubny Cossack Regiment. In 1782 Lubny became an uyezd center of Kiev Vicer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard-bearer
A standard-bearer, also known as a colour-bearer or flag-bearer, is a person who bears an emblem known as a standard or military colours, i.e. either a type of flag or an inflexible but mobile image, which is used (and often honoured) as a formal, visual symbol of a state, prince, military unit, etc. This can either be an occasional duty, often seen as an honour (especially on parade), or a permanent charge (also on the battlefield); the second type has even led in certain cases to this task being reflected in official rank titles such as Chorąży, Ensign, Cornet, Fähnrich and Alferes/ Alférez. Role In the context of the Olympic Games, a flagbearer is the athlete who carries the flag of their country during the opening and closing ceremonies. While at present a purely ceremonial function, as far back as Roman warfare and medieval warfare bearing the standard had an important role on the battlefield. The standard-bearer acted as an indicator of where the position of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Soviet Writers
The Union of Soviet Writers, USSR Union of Writers, or Soviet Union of Writers () was a creative union of professional writers in the Soviet Union. It was founded in 1934 on the initiative of the Central Committee of the Communist Party (1932) after disbanding a number of other writers' organizations, including Proletkult and the Russian Association of Proletarian Writers. The aim of the Union was to achieve party and state control in the field of literature. For professional writers, membership of the Union became effectively obligatory, and non-members had much more limited opportunities for publication. The result was that exclusion from the Union meant a virtual ban on publication. However, the history of the Union of Writers also saw cases of voluntary self-exclusion from its cadre. Thus, Vasily Aksyonov, Semyon Lipkin, and Inna Lisnyanskaya left the Union of Writers in a show of solidarity after the exclusion of Viktor Yerofeyev and Yevgeny Popov in punishment for self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State University
Moscow State University (MSU), officially M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,. is a public university, public research university in Moscow, Russia. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches. Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner were affiliated with the university. History Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov and Mikhail Lomonosov promoted the idea of a university in Moscow, and Elizabeth of Russia, Russian Empress Elizabeth decreed its establishment on . The first lectures were given on . Saint Petersburg State University and MSU each claim to be Russia's oldest university. Though Moscow State University was founded in 1755, St. Petersburg which has had a continuous existence as a "university" since 1819 sees itself as the successor of an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komsomolskaya Pravda
''Komsomolskaya Pravda'' (; ) is a daily Russian tabloid newspaper that was founded in 1925. Its name is in reference to the official Soviet newspaper '' Pravda'' (English: 'Truth'). History and profile During the Soviet era, ''Komsomolskaya Pravda'' was an all-union newspaper of the Soviet Union and an official organ of the Central Committee of the Komsomol. Established in accordance with a decision of the 13th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (b), it first appeared on 24 May 1925 in an edition of 31,000 copies. ''Komsomolskaya Pravda'' began as the official organ of the Komsomol, the youth wing of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). As such, it targeted the same 14 to 28 demographics as its parent organization, focusing initially on popular science and adventure articles while teaching the values of the CPSU. During this period, it was twice awarded the Order of Red Banner of Labour (in 1950 and 1957) and was also the recipient of the Order of Len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
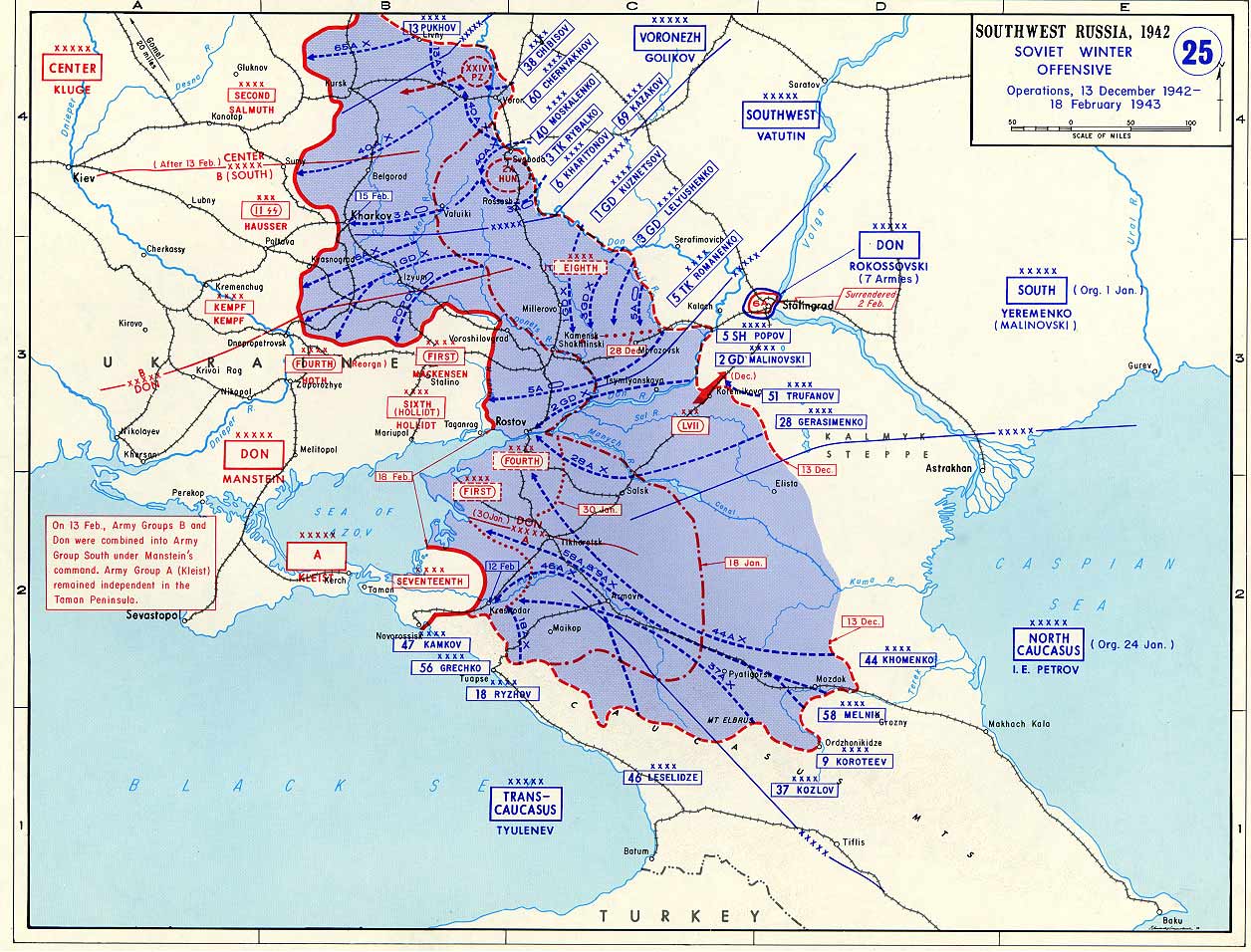
Konstantin Rokossovsky
Konstantin Konstantinovich Rokossovsky ( 1896 – 3 August 1968) was a Soviet and Polish general who served as a top commander in the Red Army during World War II and achieved the ranks of Marshal of the Soviet Union and Marshal of Poland. He also served as Defence Minister of Poland from 1949 to 1956. Rokossovsky was born to a Polish noble family in Warsaw in present-day Poland, then part of the Russian Empire, or according to other sources in Velikiye Luki in present-day Russia. He served in the Imperial Russian Army during World War I, and in 1918, joined the Red Army and fought with distinction during the Russian Civil War. Rokossovsky rose to hold senior Red Army commands by 1937, when he fell victim to Joseph Stalin's Great Purge and was branded a traitor, imprisoned and tortured. After Soviet failures in the Winter War, Rokossovsky was released from prison in 1940 and returned to command of an army corps. Following Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of The Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet Communist Party (SCP), was the founding and ruling political party of the Soviet Union. The CPSU was the One-party state, sole governing party of the Soviet Union until 1990 when the Congress of People's Deputies of the Soviet Union, Congress of People's Deputies modified Article 6 of the Soviet Constitution, Article 6 of the 1977 Soviet Constitution, which had previously granted the CPSU a monopoly over the political system. The party's main ideology was Marxism–Leninism. The party was outlawed under Russian President Boris Yeltsin's decree on 6 November 1991, citing the 1991 Soviet coup attempt as a reason. The party started in 1898 as part of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. In 1903, that party split into a Menshevik ("mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Belorussian Front
The 2nd Belorussian Front (, ''Vtoroi Belorusskiy front'', also romanized "Byelorussian SSR, Byelorussian"), was a Front (military formation), major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a Western army group. It was created in February 1944 as the Soviets were pushing the Germans back towards Byelorussia. General Colonel Pavel Kurochkin was its first commander. On hiatus in April 1944, its headquarters were reformed from the army headquarters of the disbanding 10th Army (Soviet Union), 10th Army. They took part in the Battle of Berlin, capture of Berlin, the capital of Nazi Germany. History The 2nd Belorussian Front was formed on the western axis on 24 February 1944 in accordance with a Stavka of the Supreme High Command, Stavka directive of 17 February, and included the 47th Army, 47th, 61st Army (Soviet Union), 61st, 70th Army (Soviet Union), 70th Armies, supported by the 6th Air Army and the Dnieper Flotilla. ''General-polkovnik'' Pavel Kur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Ukrainian Front
The 4th Ukrainian Front () was the name of two distinct Red Army strategic army groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The front was first formed on 20 October 1943, by renaming the Southern Front and was involved in the Lower Dnieper Strategic Offensive Operation, two battles of Kiev and the Crimean Strategic Offensive Operation. After the liberation of Crimea, the front was disbanded in May 1944. For the second time the 4th Ukrainian Front was created on 4 August 1944, by separating the left wing of the 1st Ukrainian Front. The front took part in the Carpathian Offensive simultaneously with the Battle of the Dukla Pass. Afterwards, the front was involved in the battles in East-, North- and Central Slovakia, as well as in the Moravian-Ostrava Offensive Operation on the Polish-Moravian borders and finally in the Prague Offensive which was the final battle of World War II in Europe. The actions of the 4th Ukrainian Front were important for the liberation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Caucasian Front
The North Caucasus Front, also translated as North Caucasian Front, was a major formation of the Red Army during the Second World War. The North Caucasus Front describes either of two distinct organizations during the war. First Creation The first formation was created on May 20, 1942 and was commanded by Marshal Semyon M. Budenny throughout its existence. The Front incorporated forces from the (disbanded) Crimean Front and received additional forces from the (disbanded) Southern Front on July 28, 1942. The Front was composed of * 44th Soviet Army (Andrei Khryashchev and Ivan Yefimovich Petrov), * 47th Soviet Army ( Grigory Kotov), * 51st Soviet Army ( Nikolai Kirichenko and Trofim Kolomiets). The 1st Rifle Corps reappeared in the Soviet OOB on 1 June 1942, directly subordinated to the North Caucasus Front, and was made up of four rifle brigades. The North Caucasus Front at different times also included the 9th, 12th, 18th, 24th, 37th, 56th Army, 4th and 5th Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Front (Soviet Union)
The Southern Front was a front, a formation about the size of an army group of the Soviet Army during the Second World War. The Southern Front directed military operations during the Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina in 1940 and then was formed twice after the June 1941 invasion by Germany, codenamed Operation Barbarossa. During the Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina in 1940, the Soviets deployed three armies ( 12th, 5th and 9th). Altogether the Soviet Southern Front opposing Bessarabia and Bukovina consisted of 32 (or 31) rifle divisions, 2 (or 3) motorised rifle divisions, 6 cavalry divisions, 11 tank brigades, 3 airborne brigades (one in reserve), 14 corps artillery regiments, 16 artillery regiments of the Reserve of the Supreme High Command and 4 heavy artillery divisions. These force totalled around 460,000 men, ca. 12,000 guns and mortars, ca. 3,000 tanks and 2,160 aircraft. First Formation After the German invasion, the Southern Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polikarpov Po-2
The Polikarpov Po-2 (also U-2 before 1944, for its initial Glossary of Russian and USSR aviation acronyms: Aircraft designations, ''uchebnyy'', 'training', role as a flight instruction aircraft) was an all-weather multirole Soviet Union, Soviet biplane, nicknamed ''Kukuruznik'' (,Gunston 1995, p. 292. NATO reporting name "Mule"). The reliable, uncomplicated design of the Po-2 made it an ideal trainer aircraft, as well as doubling as a low-cost attack aircraft, ground attack, aerial reconnaissance, psychological warfare and liaison aircraft during war, proving to be one of the most versatile light combat types to be built in the Soviet Union.Angelucci and Matricardi 1978, p. 214. As of 1978, it remained in production for a longer period of time than any other Soviet-era aircraft. It holds the distinction of the only biplane to take down a jet aircraft. Production figures for Polikarpov U-2 and Po-2 bombers and trainers combined are between 20,000 and 30,000 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |