|
Narkomzem
The People's Commissariat for Agriculture, abbreviated as ''Narkomzem'' was established in the USSR in 1929. Its headquarters building was located at Orlikov Pereulok, 1, Moscow, designed by Aleksey Shchusev in 1928. ''Narkomzem'' was reformed as the Soviet Ministry of Agriculture and Food (''Minsel'khoz'') in 1946. History The commissariat united all republican commissariats of the Soviet Union. It was formally known as the People's Commissariat for Agriculture (russian: Народный комиссариат земледелия - ''Narkomzem'') was set up in Petrograd in October 1917. Vladimir Milyutin was appointed the first People's Commissar of Agriculture. He was a member of the Council of People's Commissars. The Ministry was abolished in November 1985 with the creation of the State Agro-Industrial Committee (''Gosagroprom'') which took over the functions of the Ministry for Agriculture, the Ministry for Fruit and Vegetable Production, the Ministry for the Meat and Dairy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksey Shchusev
Alexey Victorovich Shchusev (academic spelling), german: Schtschussew, french: Chtchoussev, pl, Szchusiew. (russian: Алексе́й Ви́кторович Щу́сев; – 24 May 1949) was a Russian and Soviet architect who was successful during three consecutive epochs of Russian architecture – Art Nouveau (broadly construed), Constructivism, and Stalinist architecture, being one of the few Russian architects to be celebrated under both the Romanovs and the communists, becoming the most decorated architect in terms of Stalin prizes awarded. In the 1900s, Shchusev established himself as a church architect, and developed his proto-modernist style, which blended Art Nouveau with Russian Revival architecture. Immediately before and during World War I he designed and built railway stations for the von Meck family, notably the Kazansky Rail Terminal in Moscow. After the October Revolution, Shchusev pragmatically supported the Bolsheviks, and was rewarded with the contrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Alexandrovich Chernov
Mikhail Alexandrovich Chernov (russian: Михаи́л Александро́вич Черно́в; 20 November 1891 – 15 March 1938) was a Russian politician and Soviet statesman who was executed during the Great Purge. He was born in Vichuga, now in Ivanovo Oblast, to a family of weavers. In 1909 he became a Menshevik and graduated from the gymnasium in Kostroma in 1911. Between 1913 and 1917 he attended Moscow University, where he studied mathematics and physics. During this period he became friendly with Dmitri Furmanov. In 1914 his daughter was born in Ivanovo. Work in Ivanovo *1909 - a member of the Menshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. *1916 - delivered workplaces courses with Furmanov * 3 Jun, 1918 - organized by «the Committee on the Establishment of Ivanovo-Voznesensky Polytechnic Institute» (based evacuated Riga Polytechnic Institute). Mikhail Frunze appointed Chernov as secretary (managing director) of the committee. * 1919 - Memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakov Yakovlev
Yakov Arkadyevich Yakovlev (real name: Epstein; russian: Я́ков Арка́дьевич Я́ковлев, 9 June 1896, Grodno – 29 July 1938) was a Soviet politician and statesman who played a central role in the forced collectivisation of agriculture in the 1920s. Early career Yakov Yakovlev was born in Grodno, in Belarus. His father was a teacher, of Jewish descent. He joined the Bolsheviks in 1913, as a student at St Petersburg Polytechnic. After the Bolshevik Revolution in 1917, he was secretary of the party organisation in Yekaterinoslav (Dnipro) in Ukraine. He was a leader of the right wing of the Ukrainian Communist Party (b), who were in control through most of the Russian Civil War. Ousted by the left in March 1920, he was appointed a member of the Politburo of the Ukrainian party in April, after Moscow had intervened. In 1921, Yakovlev was transferred to Moscow, to work for the RSFSR People's Commissariat for Education, and the Agitprop department of the Central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasili Yakovenko
Vasili, Vasily, Vasilii or Vasiliy (Russian: Василий) is a Russian masculine given name of Greek origin and corresponds to ''Basil''. It may refer to: * Vasili I of Moscow Grand Prince from 1389–1425 * Vasili II of Moscow Grand Prince from 1425–1462 *Vasili III of Russia Tsar from 1505–1533 *Vasili IV of Russia Tsar from 1606–1610 *Basil Fool for Christ (1469–1557), also known as Saint Basil, or Vasily Blazhenny *Vasily Alekseyev (1942–2011), Soviet weightlifter * Vasily Arkhipov (1926–1998), Soviet Naval officer in the Cuban Missile Crisis * Vasily Boldyrev (1875–1933), Russian general *Vasily Chapayev (1887–1919), Russian Army commander *Vasily Chuikov (1900–1982), Soviet marschal * Vasily Degtyaryov (1880–1949), Russian weapons designer and Major General * Vasily Dzhugashvili (1921–1962), Stalin's son *Vasili Golovachov (born 1948), Russian science fiction author *Vasily Grossman (1905–1964), Soviet writer and journalist * Vasily Ignatenko (196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semyon Sereda
Semyon Pafnutyevich Sereda (russian: Семён Пафнутьевич Середа; 1 February 1871 – 21 May 1933) was a Russian Bolshevik revolutionary and Soviet politician. He was the son of a railway employee. From 1896 to 1917 he worked as a statistician. Sereda joined the Bolshevik wing of the Russian Social Democratic Labor Party in 1903. In 1917, he became a member of the Ryazan ''gubkom'', and from 1 March 1918 until 1 December 1921 served as the Peoples's Commissar for Agriculture. In this capacity he led the grain requisition and punitive operations against peasants in Yeletsky Uyezd of Oryol Governorate in 1918. Sereda was one of the main initiators of the creation of state farms and industrial communities. From January 1920 he was a member of the Presidium of Supreme Soviet of the National Economy and Gosplan The State Planning Committee, commonly known as Gosplan ( rus, Госплан, , ɡosˈpɫan), was the agency responsible for central economic planning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Kolegayev
Andrei Lukic Kolegayev (russian: Андрей Лукич Колегаев) (22 March 1887 – 23 March 1937) was a Left Socialist-Revolutionary and later Soviet statesman who advocated an alliance with the Bolsheviks. He was born in Surgut, Tobolsk Governorate in the family of an exiled Narodnaya Volya revolutionary. Kolegayev joined the Socialist-Revolutionaries in 1906 and the following year he was expelled from Kharkov University. He was arrested four times and spent seven years in exile. He participated in the October Revolution and was a delegate to the Second All-Russian Congress of Soviets. He was People's Commissar for Agriculture from 23 December 1917 to 1 March 1918. The officials of the former Ministry of the Interim Government sabotaged the decisions the new government and declared a strike. He was given the post of Commissar of Agriculture, as he was a Left SR. In November 1918 he broke with the Left SRs and joined the Russian Communist Party (bolsheviks). During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Alibek
Kanatzhan "Kanat" Alibekov ( kk, Қанатжан Байзақұлы Әлібеков, Qanatjan Baizaqūly Älıbekov; russian: Канатжан Алибеков, Kanatzhan Alibekov; born 1950), known as Kenneth "Ken" Alibek since 1992, is a Kazakhstani-American microbiologist, and biological warfare (BW) administrative management expert. He rose rapidly in the ranks of the Soviet Army to become the First Deputy Director of Biopreparat, with a rank of Colonel, during which time he claimed to oversee a vast program of 40 BW facilities with 32,000 employees. During his career as a Soviet bioweaponeer, in the late 1970s and 1980s, Alibekov managed projects that included weaponizing glanders and Marburg hemorrhagic fever, and created Russia's first tularemia bomb. Jacobsen, Annie (2015), ''The Pentagon's Brain: An Uncensored History of DARPA, America's Top Secret Military Research Agency''; New York: Little, Brown and Company, pg 293. His most prominent accomplishment was the cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
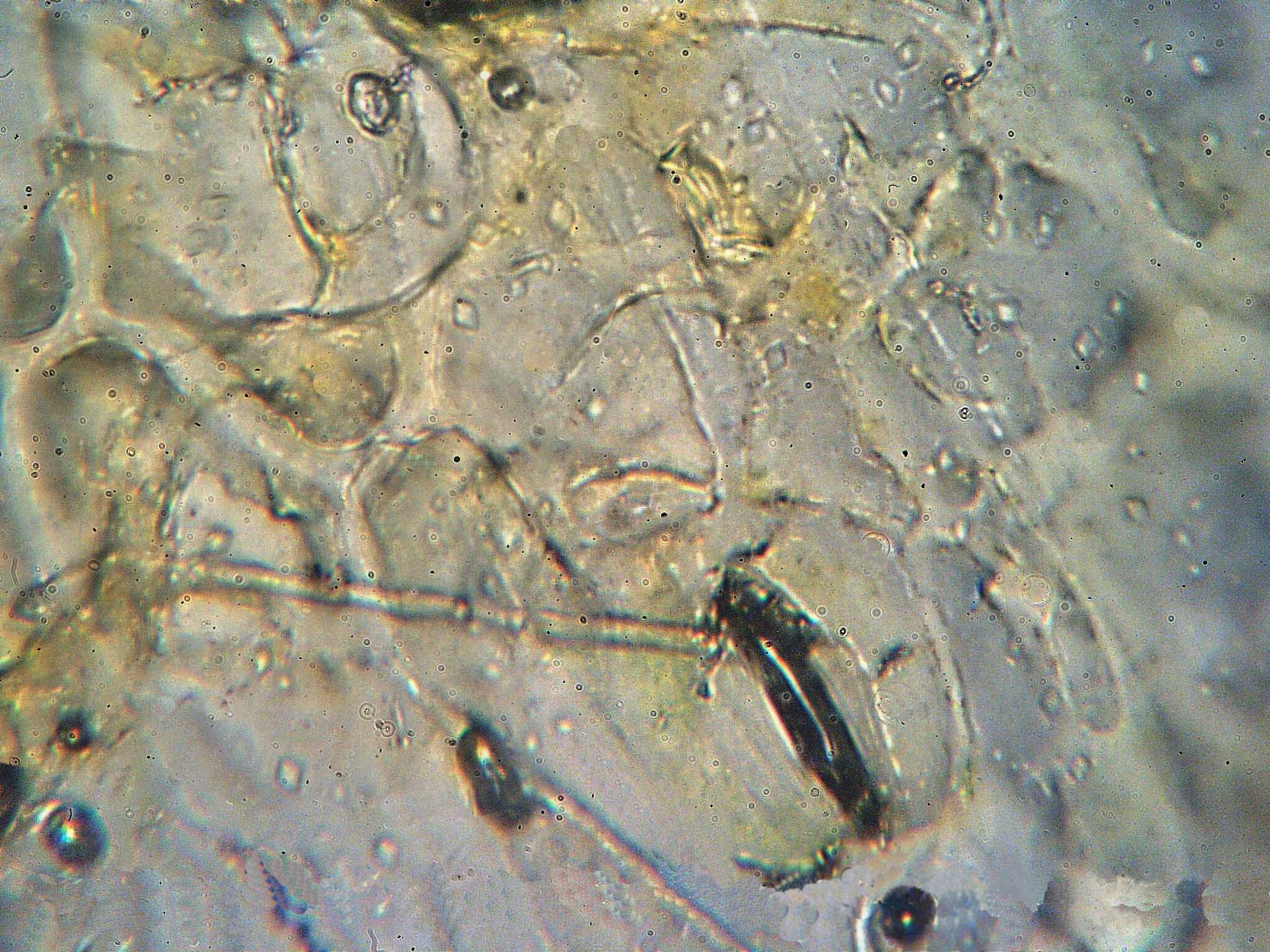
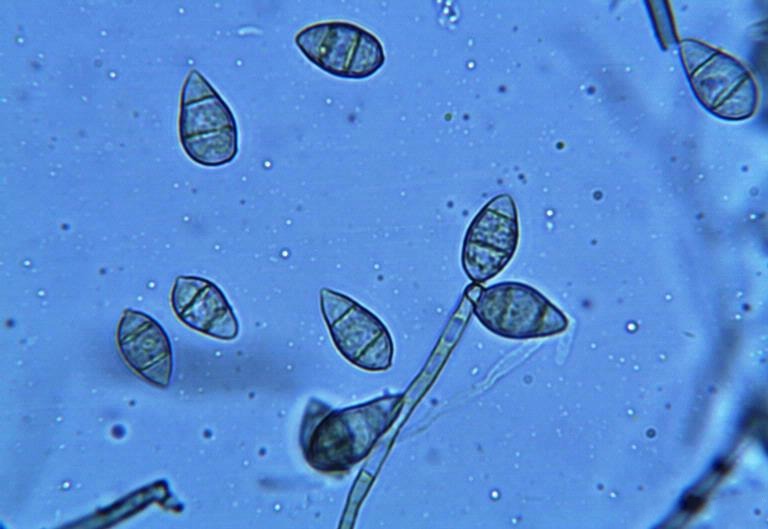
Rust (fungus)
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogen In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...ic fungus, fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five Morpholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
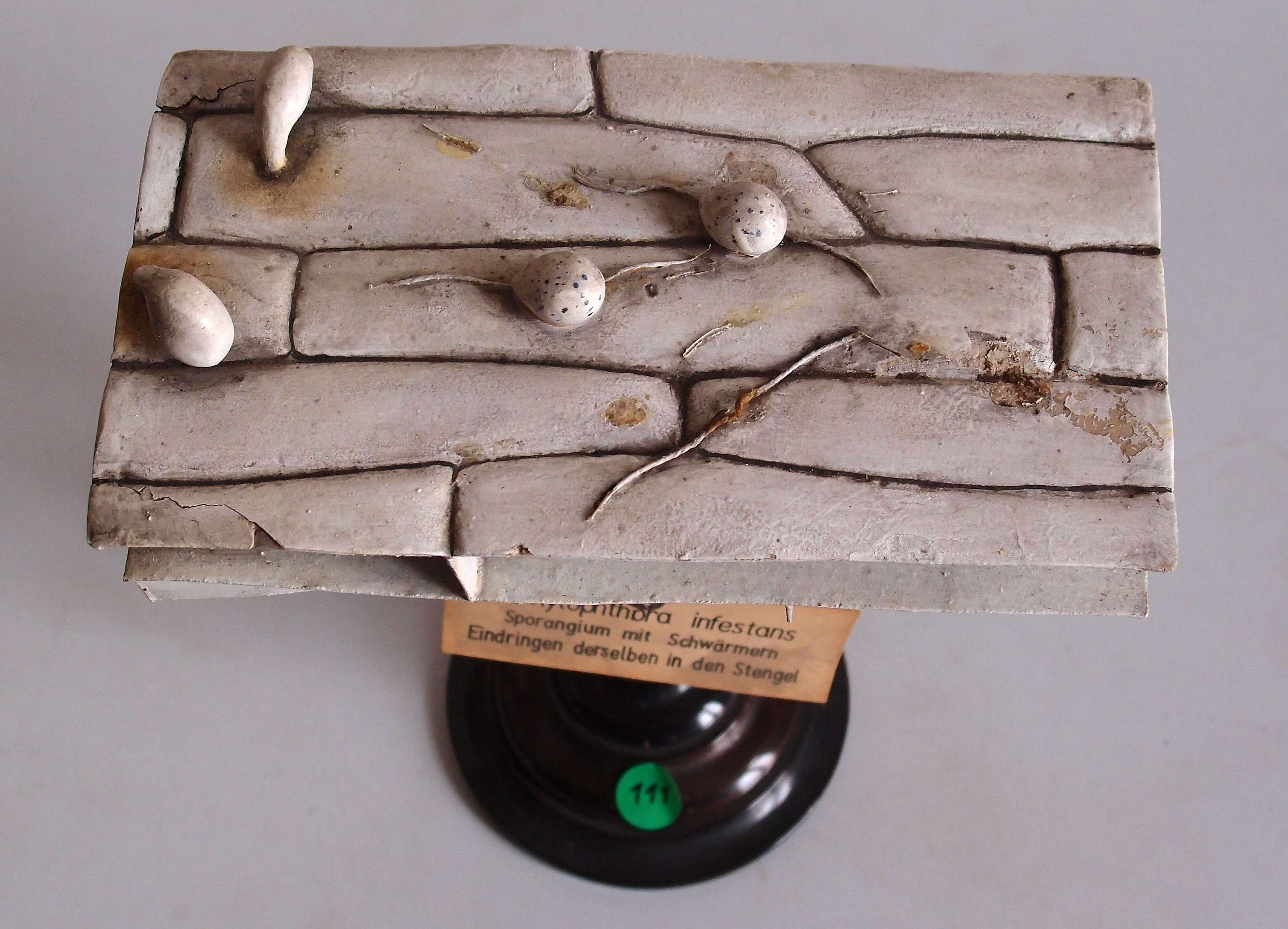
Phytophthora Infestans
''Phytophthora infestans'' is an oomycete or water mold, a fungus-like microorganism that causes the serious potato and tomato disease known as late blight or potato blight. Early blight, caused by '' Alternaria solani'', is also often called "potato blight". Late blight was a major culprit in the 1840s European, the 1845–1852 Irish, and the 1846 Highland potato famines. The organism can also infect some other members of the Solanaceae. The pathogen is favored by moist, cool environments: sporulation is optimal at in water-saturated or nearly saturated environments, and zoospore production is favored at temperatures below . Lesion growth rates are typically optimal at a slightly warmer temperature range of . Etymology The genus name ''Phytophthora'' comes from the Greek –(), meaning : "plant" – plus the Greek (), meaning : "decay, ruin, perish". The species name ''infestans'' is the present participle of the Latin verb , meaning : "attacking, destroying", from whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv
''Xanthomonas'' (from greek: ''xanthos'' – “yellow”; ''monas'' – “entity”) is a genus of bacteria, many of which cause plant diseases. There are at least 27 plant associated ''Xanthomonas spp.'', that all together infect at least 400 plant species. Different species typically have specific host and/or tissue range and colonization strategies. Taxonomy The genus ''Xanthomonas'' has been subject of numerous taxonomic and phylogenetic studies and was first described as ''Bacterium vesicatorium'' as a pathogen of pepper and tomato in 1921. Dowson later reclassified the bacterium as ''Xanthomonas campestris'' and proposed the genus ''Xanthomonas''.''Xanthomonas'' was first described as a monotypic genus and further research resulted in the division into two groups, A and B. Later work using DNA:DNA hybridization has served as a framework for the general ''Xanthomonas'' species classification. Other tools, including multilocus sequence analysis and amplified fragment-length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnaporthe Grisea
''Magnaporthe grisea'', also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast, and Imochi ( Japanese:稲熱) is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that ''M. grisea'' consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from '' Digitaria'' have been more narrowly defined as ''M. grisea''. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed ''Magnaporthe oryzae'', within the same ''M. grisea'' complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors. Members of the ''Magnaporthe grisea'' complex can also infect other agriculturally important cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)