|
Nardus
''Nardus'' is a genus of plants belonging to the grass family, containing the single species ''Nardus stricta'', known as matgrass. It is placed in its own tribe Nardeae within the subfamily Pooideae. The name derives from ancient Greek ' () from the earlier Akkadian ''lardu''. It is not to be confused with spikenard, '' Nardostachys jatamansi''. Distribution and ecology ''Nardus stricta'' is native to Eurasia (from Iceland and the Azores to Mongolia), North Africa (Algeria, Morocco), and northeastern North America (Greenland, eastern Canada, and the northeastern United States). ''Nardus stricta'' occurs on heath, moorland, hills, and mountains on nutrient poor acidic sandy to peaty soils and is strongly calcifuge, avoiding calcareous soils. It can occur from low elevations to over , becoming a community-dominant in late snow patches on mountains. ''Nardus stricta'' may also become a dominant species in habitats grazed by cattle or sheep because it is tough and unpalatable. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spikenard
Spikenard, also called nard, nardin, and muskroot, is a class of aromatic amber-colored essential oil derived from '' Nardostachys jatamansi'', a flowering plant in the honeysuckle family which grows in the Himalayas of Nepal, China, and India. The oil has been used over centuries as a perfume, a traditional medicine, or in religious ceremonies across a wide territory from India to Europe. Historically, the name ''nard'' has also referred to essential oils derived from other species including the closely related valerian genus, as well as Spanish lavender; these cheaper, more common plants have been used in perfume-making, and sometimes to adulterate true spikenard. Etymology The name ''nard'' is derived from Latin , from Ancient Greek (), from (''nērd''). This word may ultimately derive either from Sanskrit ( 'Indian spikenard'), or from ''Naarda'', an ancient Assyrian city (possibly the modern town of Dohuk, Iraq). The " spike" in the English name refers to the inflo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apomixis
In botany, apomixis is asexual development of seed or embryo without fertilization. However, other definitions include replacement of the seed by a plantlet or replacement of the flower by bulbils. Apomictically produced offspring are genetically identical to the parent plant, except in nonrecurrent apomixis. Its etymology is Greek for "away from" + "mixing". Normal asexual reproduction of plants, such as propagation from cuttings or leaves, has never been considered to be apomixis. In contrast to parthenocarpy, which involves seedless fruit formation without fertilization, apomictic fruits have viable seeds containing a proper embryo, with asexual origin. In flowering plants, the term "apomixis" is used in a restricted sense to mean agamospermy, i.e. clonal reproduction through seeds. Although agamospermy could theoretically occur in gymnosperms, it appears to be absent in that group. Apogamy is a related term that has had various meanings over time. In plants with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Daniel Joseph Koch
Wilhelm Daniel Joseph Koch (5 March 1771 – 14 November 1849) was a German physician and botanist from Kusel, which at various points in his life was under the Holy Roman Empire, part of France and then part of the Kingdom of Bavaria. Education Koch studied medicine at the Universities of University of Jena, Jena and University of Marburg, Marburg, and afterwards was a ''City physician, Stadtphysicus'' (state physician) in Trarbach. He then took the same position at Kaiserslautern in 1798, which would come under French control and then move to Bavarian control as did his home city. In 1824 he became a professor of medicine and botany at the University of Erlangen, where he stayed for the remainder of his life. At Erlangen, he was also director of the botanical gardens. In 1833, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Death Koch died in Erlangen. Notable works Among his better written efforts was a synopsis on German and Swiss flora titled ''Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awn (botany)
An awn is a hairy or bristle-like growth on a plant. On the seeds of grasses such as barley or rye, they form foxtails which assist seed dispersal by being barbed and so sticking to passing animals. Also, the awns may twist or curl as they are wetted and dry out and this action can make fallen seeds walk until they fall into a crevice into which they then burrow. Besides grasses, other families of plants which have awns include Asteraceae such as sunflowers and Geraniaceae such as geraniums. In the latter, the awns help disperse the seeds by developing a tension which then catapults the seeds when the seed head ripens and dries out. Description In grasses, awns typically extend from the lemmas of the florets. This often makes the hairy appearance of the grass synflorescence. Awns may be long (several centimeters) or short, straight or curved, single or multiple per floret. Some biological genera are named after their awns, such as the three-awns (''Aristida''). In s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
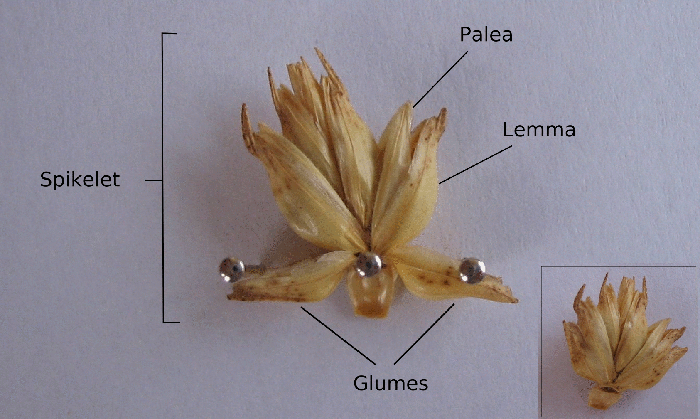
Lemma (botany)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spikelet
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Society Of The British Isles
The Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland (BSBI) is a scientific society for the study of flora, plant distribution and taxonomy relating to Great Britain, Ireland, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. The society was founded as the Botanical Society of London in 1836, and became the Botanical Society of the British Isles, eventually changing to its current name in 2013. It includes both professional and amateur members and is the largest organisation devoted to botany in the British Isles. Its history is recounted in David Allen's book ''The Botanists''. The society publishes handbooks and journals, conducts national surveys and training events, and hosts conferences. It also awards grants and bursaries, sets professional standards (with Field Identification Skills Certificates (FISCs)), and works in an advisory capacity for governments and NGOs. The society is managed by a council of elected members, and is a Registered Charity in England & Wales (212560) and Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligule
A ligule (from "strap", variant of ''lingula'', from ''lingua'' "tongue") is a thin outgrowth at the junction of leaf A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the plant stem, stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leav ... and leafstalk of many grasses (family Poaceae) and sedges (family Cyperaceae). A ligule is also a strap-shaped extension of the corolla, such as that of a ray floret in plants in the daisy family Asteraceae. Poaceae and Cyperaceae The ligule is part of the leaf that is found at the junction of the blade and sheath of the leaf. It may take several forms, but it is commonly some form of translucent membrane or a fringe of hairs. The membranous ligule can be very short 1–2 mm ( Kentucky bluegrass, ''Poa pratensis'') to very long 10–20 mm ( Johnson grass, ''Sorghum halepense''), it can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involute
In mathematics, an involute (also known as an evolvent) is a particular type of curve that is dependent on another shape or curve. An involute of a curve is the Locus (mathematics), locus of a point on a piece of taut string as the string is either unwrapped from or wrapped around the curve. The evolute of an involute is the original curve. It is generalized by the Roulette (curve), roulette family of curves. That is, the involutes of a curve are the roulettes of the curve generated by a straight line. The notions of the involute and evolute of a curve were introduced by Christiaan Huygens in his work titled ''Horologium Oscillatorium, Horologium oscillatorium sive de motu pendulorum ad horologia aptato demonstrationes geometricae'' (1673), where he showed that the involute of a cycloid is still a cycloid, thus providing a method for constructing the cycloidal pendulum, which has the useful property that its period is independent of the amplitude of oscillation. Involute of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Shape
The following terms are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (that is, the leaf blade or 'lamina' is undivided) or compound (that is, the leaf blade is divided into two or more leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, and may be smooth or have hair, bristles, or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article. The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from the same plant. For example, whether to call leaves on the same tree "ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culm (botany)
A culm is the aerial (above-ground) Plant stem, stem of a Poaceae, grass or Cyperaceae, sedge. It is derived from Latin , meaning "stalk." It originally referred to the stem of any type of plant. In horticulture or agriculture, it is especially used to describe the stalk or woody stems of bamboo, cane (grass), cane or cereal, grain grasses. Malting In the production of malted grains, the culms refer to the rootlets of the germinated grains. The culms are normally removed in a process known as "deculming" after kilning when producing barley malt, but form an important part of the product when making sorghum or millet malt. These culms are very nutritious and are sold off as animal feed. References Plant morphology {{Plant-morphology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |