|
Nanticoke Creek
Nanticoke Creek is a tributary of the Susquehanna River in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately long and flows through Hanover Township and Nanticoke. The watershed of the creek has an area of . The creek has one named tributary, which is known as Espy Run. Nanticoke Creek impaired by pH and metals due to abandoned mine drainage. Abandoned mine drainage discharges in the creek's watershed include the Truesdale Mine Discharge and the Askam Borehole. The creek is located in the Northern Middle Anthracite Field and is in the Anthracite Valley Section of the ridge and valley physiographic province. The main rock formations in the watershed include the Mauch Chunk Formation, the Pottsville Group, and the Llewellyn Formation. The surficial geology consists of coal dumps, surface mining land, alluvium, Wisconsinan Outwash, Wisconsinan Till, urban land, and bedrock. The watershed of Nanticoke Creek is mainly forested, but urban land and mining la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake Bay
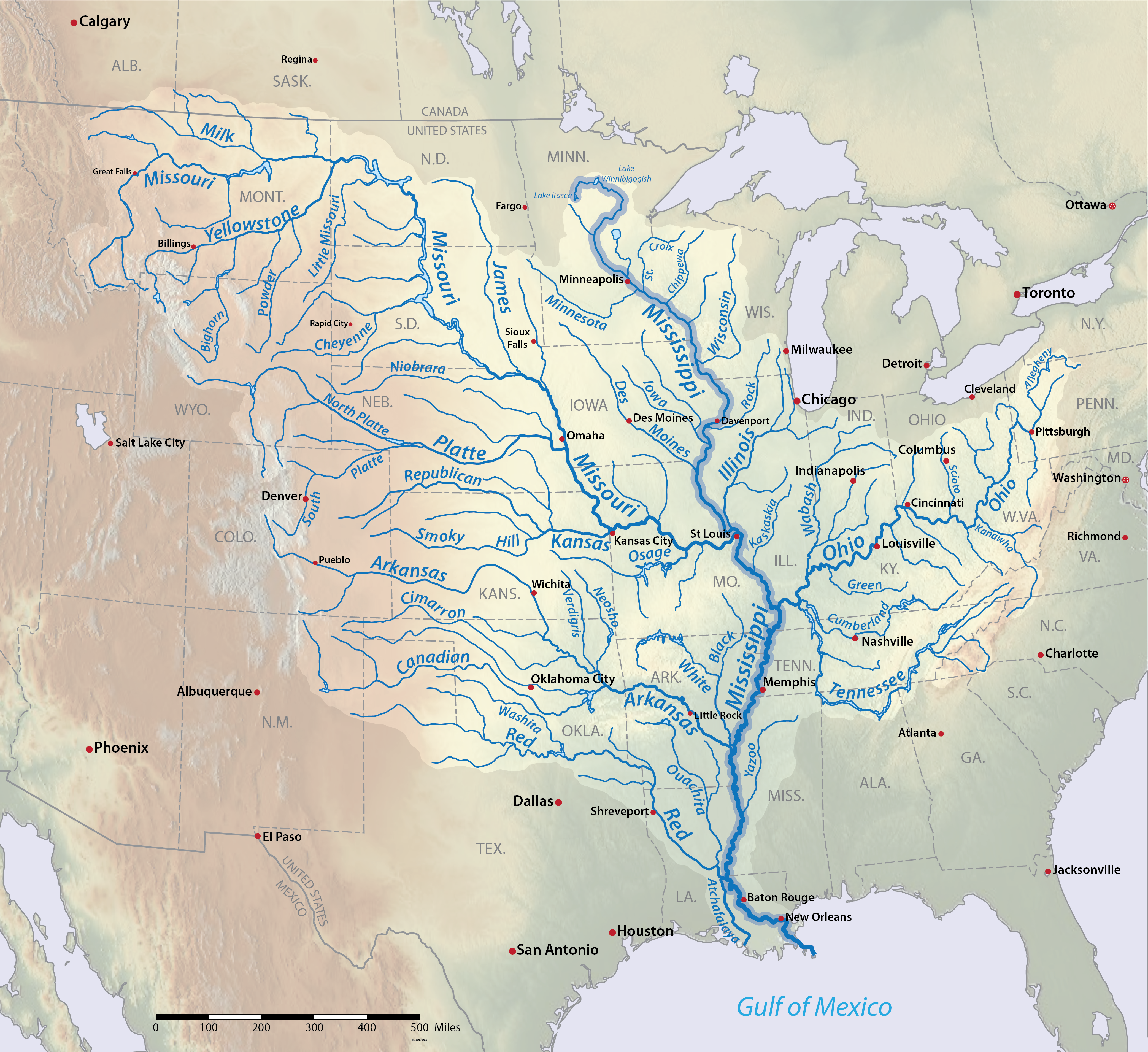
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles (headland), Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the bay's drainage basin, which covers parts of six states (New York (state), New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia) and all of Washington, D.C. The bay is approximately long from its northern headwaters in the Susquehanna River to its outlet i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Department Of Environmental Protection
The Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) is the agency in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania responsible for protecting and preserving the land, air, water, and public health through enforcement of the state's environmental laws. It was created by Act 18 of 1995, which split the Department of Environmental Resources into the Department of Environmental Protection and the Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. Its current secretary is Jess Shirley. The Department of Environmental Resources was created by Act 275 of 1970, which abolished the Department of Forest and Waters. The Department of Forest and Waters was created by the General Assembly in 1901. The Department of Environmental Protection is charged with the responsibility for development of a balanced ecological system incorporating social, cultural, and economic needs of the commonwealth through development and protection. The department is responsible for the state's land, air, and water man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pronunciation of the word "chloride" is . Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Other examples of ionic chlorides include potassium chloride (), calcium chloride (), and ammonium chloride (). Examples of covalent chlorides include methyl chloride (), carbon tetrachloride (), sulfuryl chloride (), and monochloramine (). Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much larger than a chlorine atom (diameter 99 pm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolved Oxygen
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%). Oxygen saturation can be measured regionally and noninvasively. Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is commonly measured using pulse oximetry. Tissue saturation at peripheral scale can be measured using NIRS. This technique can be applied on both muscle and brain. In medicine In medicine, oxygen saturation refers to ''oxygenation'', or when oxygen molecules () enter the tissues of the body. In this case blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air into the blood. Oxygen saturation (() sats) measures the percentage of hemoglobin bindin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens (unit)
The siemens (symbol: S) is the unit of electric conductance, electric susceptance, and electric admittance in the International System of Units (SI). Conductance, susceptance, and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance, reactance, and impedance respectively; hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm () and is also referred to as the '' mho''. The siemens was adopted by the IEC in 1935, and the 14th General Conference on Weights and Measures approved the addition of the siemens as a derived unit in 1971. The unit is named after Ernst Werner von Siemens. In English, the same word ''siemens'' is used both for the singular and plural. Like other SI units named after people, the name of the unit (siemens) is not capitalized. Its symbol (S), however, ''is'' capitalized to distinguish it from the '' second'', whose symbol (s) is lower case. The related property, electrical conductivity, is measured in units of siemens per metre (S/m). Definition For an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Conductance
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter (rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-metre (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity (or specific conductance) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter (sigma), but (kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and (gamma) are sometimes used. The SI unit of electrical conductivity is siemens per metre (S/m). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Stem
In hydrology, a main stem or mainstem (also known as a trunk) is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". The mainstem extends all the way from one specific headwater to the outlet of the river, although there are multiple ways to determine which headwater (or first-order tributary) is the source of the main stem. Water enters the main stem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow.. A drainage basin may also be referred to as a ''watershed'' or ''catchment''. Hydrological classification systems assign numbers to tributaries and mainstems within a drainage basin. In the Strahler number, a modification of a system devised by Robert E. Horton in 1945, channels with no tributaries are called "first-order" streams. When two first-order streams meet, they are said to form a second-order stream; when two second-order streams meet, they form a third-order stream, and so on. In the Horton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidity
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Arrhenius acids. Brønsted and Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. The word ''acid'' is derived from the Latin , meaning 'sour'. An aqueous solution of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkalinity
Alkalinity (from ) is the capacity of water to resist Freshwater acidification, acidification. It should not be confused with base (chemistry), basicity, which is an absolute measurement on the pH scale. Alkalinity is the strength of a buffer solution composed of weak acids and their conjugate acid, conjugate bases. It is measured by Titration, titrating the Solution (chemistry), solution with an acid such as HCl until its pH changes abruptly, or it reaches a known endpoint where that happens. Alkalinity is expressed in units of concentration, such as meq/L (milliequivalents per liter), μeq/kg (microequivalents per kilogram), or mg/L CaCO3 (milligrams per liter of calcium carbonate). Each of these measurements corresponds to an amount of acid added as a titrant. In Fresh water, freshwater, particularly those on non-limestone terrains, alkalinities are low and involve a lot of ions. In the ocean, on the other hand, alkalinity is completely dominated by carbonate and bicarbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newport Creek
Newport Creek is a tributary of the Susquehanna River in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is in length. Named tributaries of the creek include South Branch Newport Creek. The entire watershed of Newport Creek is considered by the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection to be impaired. Course Newport Creek begins in the community of Glen Lyon, Pennsylvania, Glen Lyon. It flows in an east-northeast direction into Newport Township, Pennsylvania, Luzerne County, not far from some strip mines. The creek parallels the Delaware and Hudson Railroad for some distance before turning north and then northeast to follow the railroad. The creek gets much closer to the strip mines at this point. It continues east, out of Newport Township and into the community of Nanticoke, Pennsylvania, Nanticoke, where the tributary South Branch Newport Creek flows into Newport Creek. Newport Creek then flows through Nanticoke, passing a mountain known as Honey Pot (Pennsylva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discharge (hydrology)
In hydrology, discharge is the volumetric flow rate (volume per time, in units of m3/h or ft3/h) of a stream. It equals the product of average flow velocity (with dimension of length per time, in m/h or ft/h) and the cross-sectional area (in m2 or ft2). It includes any suspended solids (e.g. sediment), dissolved chemicals like (aq), or biologic material (e.g. diatoms) in addition to the water itself. Terms may vary between disciplines. For example, a fluvial hydrologist studying natural river systems may define discharge as streamflow, whereas an engineer operating a reservoir system may equate it with outflow, contrasted with inflow. Formulation A discharge is a measure of the quantity of any fluid flow over unit time. The quantity may be either volume or mass. Thus the water discharge of a tap (faucet) can be measured with a measuring jug and a stopwatch. Here the discharge might be 1 litre per 15 seconds, equivalent to 67 ml/second or 4 litres/minute. This is an average meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |