|
Nanosystems Initiative Munich
The Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM) is a German research cluster in the field of nano sciences. It is one of the excellence clusters being funded within the German Excellence Initiative of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The cluster joins the scientific work of about 60 research groups in the Munich region and combines several disciplines: physics, biophysics, physical chemistry, biochemistry, pharmacology, biology, electrical engineering and medical science. Using the expertise in all these fields the cluster aims to create new nanosystems for information technology as well as for life sciences. The participating institutions of the Nanosystems Initiative Munich are the Ludwig Maximilians University, the Technical University of Munich, the University of Augsburg, the Max Planck Institutes of Quantum Optics and Biochemistry, the Munich University of Applied Sciences, the Walther Meissner Institute and the "Center for New Technologies" at Deutsches Museum The Deuts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
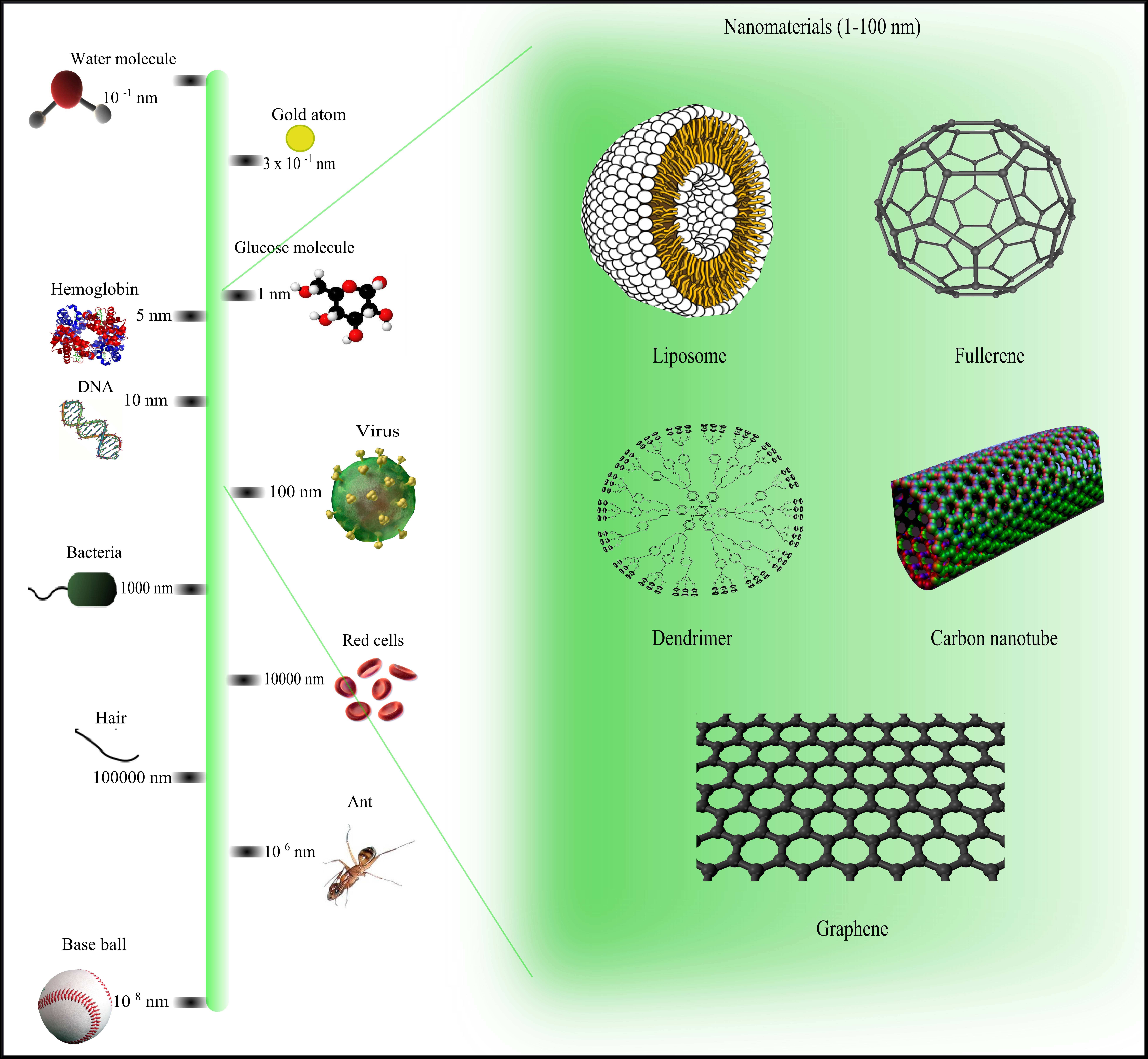
Nano Sciences
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Maximilians University
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich, LMU or LMU Munich; ) is a public university, public research university in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Originally established as the University of Ingolstadt in 1472 by Duke Ludwig IX of Bavaria-Landshut, it is Germany's List of universities in Germany, sixth-oldest university in continuous operation. In 1800, the university was moved from Ingolstadt to Landshut by King Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria when the city was threatened by the French, before being transferred to its present-day location in Munich in 1826 by King Ludwig I of Bavaria. In 1802, the university was officially named Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität by King Maximilian I of Bavaria in honor of himself and Ludwig IX. LMU is currently the second-largest university in Germany in terms of student population; in the 2023/24 winter semester, the university had a total of 52,972 matriculated students. Of these, 10,138 were freshmen, while internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology Institutions
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Maximilian University Of Munich
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich, LMU or LMU Munich; ) is a public university, public research university in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Originally established as the University of Ingolstadt in 1472 by Duke Ludwig IX of Bavaria-Landshut, it is Germany's List of universities in Germany, sixth-oldest university in continuous operation. In 1800, the university was moved from Ingolstadt to Landshut by King Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria when the city was threatened by the French, before being transferred to its present-day location in Munich in 1826 by King Ludwig I of Bavaria. In 1802, the university was officially named Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität by King Maximilian I of Bavaria in honor of himself and Ludwig IX. LMU is currently the second-largest university in Germany in terms of student population; in the 2023/24 winter semester, the university had a total of 52,972 matriculated students. Of these, 10,138 were freshmen, while internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsches Museum
The Deutsches Museum (''German Museum'', officially (English: ''German Museum of Masterpieces of Science and Technology'')) in Munich, Germany, is the world's largest museum of science museum, science and technology museum, technology, with about 125,000 exhibited objects from 50 fields of science and technology. It receives about 1.5 million visitors per year. The museum was founded on 28 June 1903, at a meeting of the Verein Deutscher Ingenieure, Association of German Engineers (VDI) as an initiative of Oskar von Miller. It is the largest museum in Munich. For a period of time the museum was also used to host pop and rock concerts including The Who, Jimi Hendrix and Elton John. Museumsinsel The main site of the Deutsches Museum is a small island in the Isar river, which had been used for rafting wood since the Middle Ages. The island did not have any buildings before 1772 because it was regularly flooded prior to the building of the Sylvensteinspeicher. In 1772 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich University Of Applied Sciences
The Munich University of Applied Sciences (HM) () is the largest university of applied sciences in Bavaria with about 17,800 students. The Munich University of Applied Sciences was founded in 1971 by the amalgamation of seven colleges of technology and higher education, some of which date back to the early 19th century. Today it is the largest university of its kind in Bavaria and one of the largest in Germany. HM collaborates with more than 200 partner universities in Europe, North and South America and Asia. International students make up 13% of the student body. Overview In the winter semester 2022/23, 18,386 students were enrolled at Munich University of Applied Sciences (39.3% female, 60.7% male). There are 510 professorships, about 700 part-time lecturers, and 511 non-academic staff in its 14 faculties. The university has 98 degree programmes in the fields of natural sciences/engineering, economics, business, social sciences and design. It is spread over several locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute Of Biochemistry
The Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry (; abbreviated MPIB) is a research institute of the Max Planck Society located in Martinsried, a suburb of Munich. The institute was founded in 1973 by the merger of three formerly independent institutes: the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, the Max Planck Institute of Protein and Leather Research (founded 1954 in Regensburg), and the Max Planck Institute of Cell Chemistry (founded 1956 in Munich). With about 750 employees in currently nine research departments and more than 20 research groups, the MPIB is one of the largest institutes of the Max Planck Society. Departments There are nine departments currently in the institute: * Cell and Virus Structure (John A. G. Briggs) * Cellular Biochemistry ( Franz-Ulrich Hartl) * Cellular and Molecular Biophysics ( Petra Schwille) * Machine Learning and Systems Biology ( Karsten Borgwardt) * Molecular Machines and Signaling ( Brenda Schulman) * Molecular Medicine (Reinhard Fässler) * Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute Of Quantum Optics
The Max-Planck-Institute of Quantum Optics (abbreviation: MPQ; ) is a part of the Max Planck Society which operates 87 research facilities in Germany. The institute is located in Garching, Germany, which in turn is located 10 km north-east of Munich. Five research groups work in the fields of attosecond physics, laser physics, quantum information theory, laser spectroscopy, quantum dynamics and quantum many body systems. Structure Divisions * Attosecond physics (Ferenc Krausz) * Laser spectroscopy (Theodor W. Hänsch) * Quantum dynamics ( Gerhard Rempe) * Quantum many body systems (Immanuel Bloch) * Theory (Juan Ignacio Cirac Sasturain) Research groups * RyD-QMB, Rydberg Dressed Quantum Many-Body Systems (Christian Groß) * Antimatter spectroscopy (Masaki Hori) * Otto Hahn Group Quantum Networks (Andreas Reiserer) * Theory of Quantum Matter (Richard Schmidt) * Entanglement of Complex Quantum Systems (Norbert Schuch) Research The institute investigates the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Augsburg
The University of Augsburg () is a university located in the Universitätsviertel section of Augsburg, Germany. It was founded in 1970 and is organized in 8 Faculties. The University of Augsburg is a relatively young campus university with approx. 18,000 students in October 2012. About 14% of its students come from foreign countries, a larger percentage than at comparable German universities. In October 2011 Sabine Doering Manteuffel succeeded Alois Loidl as rector of the university. She is the first female rector of a Bavarian university. Organisation The university is divided into 8 faculties: * Faculty of Economics and Business (founded 1970) * Faculty of Law (founded 1971) * Faculty of Catholic Theology (founded 1971) * Faculty of Philosophy and Social Sciences (founded 1972) * Faculty of History and Philology (founded 1972) * Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences (founded 1981) * Faculty oApplied Computer Science(founded 2003) * Faculty of Medicine (founded 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Munich
The Technical University of Munich (TUM or TU Munich; ) is a public research university in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied and natural sciences. Established in 1868 by King Ludwig II of Bavaria, the university now has additional campuses in Garching, Freising, Heilbronn, Straubing, and Singapore, with the Garching campus being its largest. The university is organized into seven schools, and is supported by numerous research centers. It is one of the largest universities in Germany, with 52,931 students and an annual budget of €1,892.9 million including the university hospital. A ''University of Excellence'' under the German Universities Excellence Initiative, TUM is among the leading universities in the European Union. Its researchers and alumni include 18 Nobel laureates and 24 Leibniz Prize winners. History 19th century In 1868, King Ludwig II of Bavaria founded the ''Polytechnische Schule München'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Science
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
The German Research Foundation ( ; DFG ) is a German research funding organization, which functions as a self-governing institution for the promotion of science and research in the Federal Republic of Germany. In 2019, the DFG had a funding budget of €3.3 billion. Function The DFG supports research in science, engineering, and the humanities through a variety of grant programmes, research prizes, and by funding infrastructure. The self-governed organization is based in Bonn and financed by the German states and the federal government of Germany. the organization consists of approximately 100 research universities and other research institutions. The DFG endows various research prizes, including the Leibniz Prize. The Polish-German science award Copernicus is offered jointly with the Foundation for Polish Science. According to a 2017 article in ''The Guardian'', the DFG has announced it will publish its research in online open-access journals. Background In 1937, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |