|
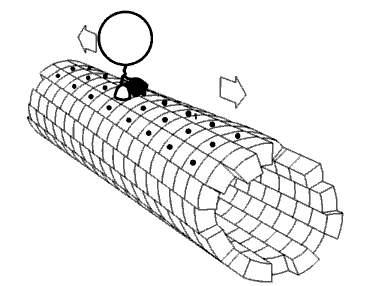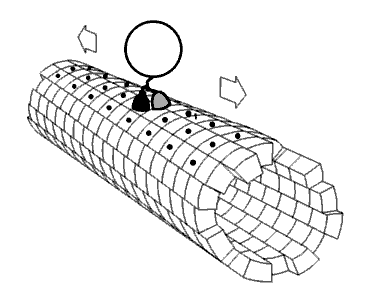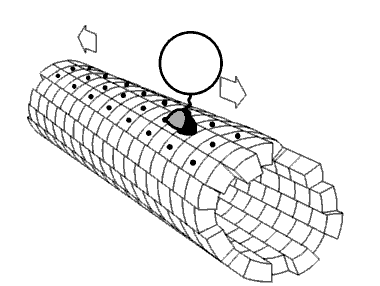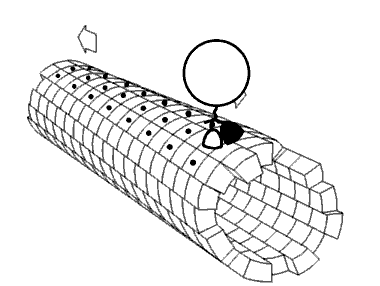
Nanomotor Inside Cell
A nanomotor is a molecular or nanoscale device capable of converting energy into movement. It can typically generate forces on the order of piconewtons. While nanoparticles have been utilized by artists for centuries, such as in the famous Lycurgus cup, scientific research into nanotechnology did not come about until recently. In 1959, Richard Feynman gave a famous talk entitled "There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom" at the American Physical Society's conference hosted at Caltech. He went on to wage a scientific bet that no one person could design a motor smaller than 400 µm on any side. The purpose of the bet (as with most scientific bets) was to inspire scientists to develop new technologies, and anyone who could develop a nanomotor could claim the $1,000 USD prize. However, his purpose was thwarted by William McLellan, who fabricated a nanomotor without developing new methods. Nonetheless, Richard Feynman's speech inspired a new generation of scientists to pursue researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoscopic Scale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a lower bound to the mesoscopic scale for most solids. For technical purposes, the nanoscopic scale is the size at which fluctuations in the averaged properties (due to the motion and behavior of individual particles) begin to have a significant effect (often a few percent) on the behavior of a system, and must be taken into account in its analysis. The nanoscopic scale is sometimes marked as the point where the properties of a material change; above this point, the properties of a material are caused by 'bulk' or 'volume' effects, namely which atoms are present, how they are bonded, and in what ratios. Below this point, the properties of a material change, and while the type of atoms present and their relative orientations are still importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liangfang Zhang
Liangfang Zhang is a Chinese-American nanoengineer. He is the Chancellor Professor of Nanoengineering and Bioengineering and Director of Chemical Engineering at the University of California, San Diego. Zhang is a Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering, American Association for the Advancement of Science, and the National Academy of Inventors. Early life and education Zhang was born in Wuwei County, China and began attending university at the age of 15. He completed his Bachelor of Science and Master’s degree in chemical engineering from Tsinghua University before moving to the United States and enrolling at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign for his PhD. While attending Tsinghua, Zhang helped create a tough rubber polymer that could be used in construction engineering. As a PhD candidate, Zhang worked with Steve Granick to turn nanoparticles into biocompatible capsules. This way of stabilizing lipids enabled them to be used in drug delive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabatic Quantum Motor
An adiabatic quantum motor is a mechanical device, typically nanometric, driven by a flux of quantum particles and able to perform cyclic motions. The adjective “adiabatic” in this context refers to the limit when the dynamics of the mechanical degrees of freedom is slow compared with the dwell time of the particles passing through the device. In this regime, it is commonly assumed that the mechanical degrees of freedom behave classically. This class of devices works essentially as quantum pumps operated in reverse. While in a quantum pump, the periodic movement of some parameters pumps quantum particles from one reservoir to another, in a quantum motor a DC current of particles induces the cyclic motion of the device. One key feature of these motors is that quantum interferences can be used to increase their efficiency by enhancing the reflection coefficient In physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of a wave is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Motors
Molecular motors are natural (biological) or artificial molecular machines that are the essential agents of movement in living organisms. In general terms, a motor is a device that consumes energy in one form and converts it into motion or mechanical work; for example, many protein-based molecular motors harness the chemical free energy released by the hydrolysis of ATP in order to perform mechanical work. In terms of energetic efficiency, this type of motor can be superior to currently available man-made motors. One important difference between molecular motors and macroscopic motors is that molecular motors operate in the thermal bath, an environment in which the fluctuations due to thermal noise are significant. Examples Some examples of biologically important molecular motors: * Cytoskeletal motors ** Myosins are responsible for muscle contraction, intracellular cargo transport, and producing cellular tension. ** Kinesin moves cargo inside cells away from the nucleus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brownian Motor
Brownian motors are nanoscale or molecular machines that use chemical reactions to generate directed motion in space. The theory behind Brownian motors relies on the phenomenon of Brownian motion, random motion of particles suspended in a fluid (a liquid or a gas) resulting from their collision with the fast-moving molecules in the fluid. On the nanoscale (1-100 nm), viscosity dominates inertia, and the extremely high degree of thermal noise in the environment makes conventional directed motion all but impossible, because the forces impelling these motors in the desired direction are minuscule when compared to the random forces exerted by the environment. Brownian motors operate specifically to utilise this high level of random noise to achieve directed motion, and as such are only viable on the nanoscale. The concept of Brownian motors is a recent one, having only been coined in 1995 by Peter Hänggi, but the existence of such motors in nature may have existed for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-newtonian Fluids
A non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid that does not follow Newton's law of viscosity, i.e., constant viscosity independent of stress. In non-Newtonian fluids, viscosity can change when under force to either more liquid or more solid. Ketchup, for example, becomes runnier when shaken and is thus a non-Newtonian fluid. Many salt solutions and molten polymers are non-Newtonian fluids, as are many commonly found substances such as custard, toothpaste, starch suspensions, corn starch, paint, blood, melted butter, and shampoo. Most commonly, the viscosity (the gradual deformation by shear or tensile stresses) of non-Newtonian fluids is dependent on shear rate or shear rate history. Some non-Newtonian fluids with shear-independent viscosity, however, still exhibit normal stress-differences or other non-Newtonian behavior. In a Newtonian fluid, the relation between the shear stress and the shear rate is linear, passing through the origin, the constant of proportionality being the coefficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz Coil
A Helmholtz coil is a device for producing a region of nearly uniform magnetic field, named after the German physicist Hermann von Helmholtz. It consists of two electromagnets on the same axis, carrying an equal electric current in the same direction. Besides creating magnetic fields, Helmholtz coils are also used in scientific apparatus to cancel external magnetic fields, such as the Earth's magnetic field. When the pair of two electromagnetics of a Helmholtz coil carry an equal electric current in the opposite direction, it is known as anti-Helmholtz coil, which creates a region of nearly uniform magnetic field gradient, and is used for creating magnetic traps for atomic physics experiments. Description A Helmholtz pair consists of two identical circular magnetic coils that are placed symmetrically along a common axis, one on each side of the experimental area, and separated by a distance h equal to the radius R of the coil. Each coil carries an equal electric current in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helical Nanomotor
Helical may refer to: * Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape * Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive * Helical spring, a coilspring * Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock * Helicoil A threaded insert, also known as a threaded bushing, is a fastener element that is inserted into an object to add a threaded hole. They may be used to repair a stripped threaded hole, provide a durable threaded hole in a soft material, place a thr ..., a mechanical thread repairing insert * H-el-ical//, stage name for Hikaru, Japanese singer {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesin
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (thus kinesins are ATPases, a type of enzyme). The active movement of kinesins supports several cellular functions including mitosis, meiosis and transport of cellular cargo, such as in axonal transport, and intraflagellar transport. Most kinesins walk towards the plus end of a microtubule, which, in most cells, entails transporting cargo such as protein and membrane components from the center of the cell towards the periphery. This form of transport is known as anterograde transport. In contrast, dyneins are motor proteins that move toward the minus end of a microtubule in retrograde transport. Discovery Kinesins were discovered in 1985, based on their motility in cytoplasm extruded from the giant axon of the squid. They turned out as MT-based anterograde intracellular tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Dynamics
Proteins are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. The study of protein dynamics is most directly concerned with the transitions between these states, but can also involve the nature and equilibrium populations of the states themselves. These two perspectives—kinetics and thermodynamics, respectively—can be conceptually synthesized in an "energy landscape" paradigm: highly populated states and the kinetics of transitions between them can be described by the depths of energy wells and the heights of energy barriers, respectively. Local flexibility: atoms and residues Portions of protein s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |